- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents
A research summary is a concise overview of a study’s purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions. Writing an effective research summary allows you to distill key insights for an audience, enabling them to quickly understand the core message and significance of the study. This guide provides an in-depth look at the structure of a research summary, examples, and tips for writing one that is clear, informative, and engaging.

Research Summary
A research summary condenses the essential parts of a research paper or study into a brief format, usually ranging from a single paragraph to a page. The goal is to give readers a clear understanding of the study’s objectives, methodology, major findings, and implications. Research summaries are often used in academic papers, grant proposals, and professional reports.
Key Characteristics of a Research Summary :
- Conciseness : Communicates the main points without unnecessary detail.
- Clarity : Presents information in a straightforward and easily understandable manner.
- Structure : Follows a logical flow, typically mirroring the structure of the full research report.
Structure of a Research Summary
A well-structured research summary generally includes the following sections:
The title should reflect the main topic or research question, helping readers quickly understand what the study is about. If applicable, the title should also hint at the methodology or scope of the study.
2. Introduction
The introduction provides context for the research question and explains why the study is important. Briefly summarize the problem or gap in knowledge that the study addresses and state the research objectives or hypotheses.
Example : “This study investigates the impact of social media on adolescent mental health, specifically focusing on self-esteem and anxiety. The research aims to understand how social media usage patterns relate to these psychological outcomes.”
3. Methodology
This section briefly outlines the research design, sample size, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. The goal is to give readers an idea of how the study was conducted.
Example : “The study employed a mixed-methods approach, using an online survey of 500 adolescents and in-depth interviews with 20 participants to gather quantitative and qualitative data on social media habits and mental health.”
The results section summarizes the major findings of the study without going into detailed statistics or data. Focus on the key insights that answer the research question or support the hypotheses.
Example : “The analysis revealed a positive correlation between increased social media use and higher levels of anxiety. Participants who spent more than three hours per day on social media reported lower self-esteem scores compared to those with limited usage.”
5. Conclusion
The conclusion provides a brief interpretation of the results, discussing their implications and potential applications. This section may also suggest areas for further research.
Example : “The findings suggest that prolonged social media exposure may negatively impact adolescent mental health. Future research could explore intervention strategies to promote healthier social media habits.”
6. Keywords (Optional)
Some research summaries include keywords to help readers find relevant studies quickly. Keywords should relate to the study’s main concepts or topics, such as “social media,” “mental health,” “adolescents,” and “self-esteem.”
Example of a Research Summary
Title : Effects of Physical Activity on Cognitive Function in Older Adults
Introduction : This study examines the impact of regular physical activity on cognitive function in adults aged 65 and older. With age-related cognitive decline being a major public health concern, understanding the benefits of exercise on brain health could inform preventive strategies.
Methodology : A randomized controlled trial was conducted with 200 participants divided into an exercise group and a control group. The exercise group participated in supervised workouts three times per week, while the control group maintained their usual activities. Cognitive assessments were administered at baseline and after six months.
Results : Participants in the exercise group showed significant improvements in memory and executive function compared to the control group, who exhibited no cognitive gains.
Conclusion : Regular physical activity appears to benefit cognitive function in older adults, potentially delaying age-related cognitive decline. Further research is needed to explore optimal exercise regimens for brain health.
Writing Guide for a Research Summary
Step 1: read the full research report.
To write an accurate summary, read the complete research report or study. Take notes on the main points, including the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
Step 2: Identify the Core Message
Distill the study’s core message by identifying the research objectives, key findings, and implications. This will form the foundation of your summary, ensuring that it remains focused and relevant.
Step 3: Use Clear and Concise Language
A research summary should be concise and free from unnecessary jargon. Use simple language to make the study accessible to a broad audience, especially if the summary is intended for readers outside the research field.
Step 4: Follow the Structure
Adopt a clear structure to organize information logically. Begin with an introduction to the research question, briefly describe the methodology, highlight the main findings, and conclude with the study’s implications.
Step 5: Revise for Brevity and Clarity
Revise your draft to remove redundant information and ensure that each sentence adds value. Aim to keep the summary short, ideally within one or two paragraphs for a single-page summary or slightly longer for comprehensive reviews.
Step 6: Include Keywords if Needed
If the summary will be published in an academic or searchable format, add relevant keywords to help readers find the study easily. Select terms that represent the study’s main themes or topics.
Tips for Writing an Effective Research Summary
- Focus on Key Points : Avoid including minor details and focus on summarizing the main findings.
- Avoid Technical Jargon : Use plain language, especially if the summary is for a general audience.
- Use Active Voice : Active voice makes sentences clearer and more direct.
- Keep it Objective : Avoid adding personal opinions or interpretations beyond what is presented in the study.
- Proofread : Check for clarity, grammar, and adherence to the structure.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Including Too Much Detail : A research summary should only cover the essential points without overwhelming readers.
- Overuse of Technical Terms : Unless intended for a specialist audience, limit technical language to ensure accessibility.
- Neglecting the Structure : Follow the structure to maintain a logical flow of information.
- Personal Interpretations : Stick to summarizing the study’s findings and implications without inserting your own analysis.
- Ignoring the Objective : Keep in mind the purpose of the summary, whether for an academic journal, project proposal, or professional report.
A research summary provides a snapshot of a study’s essential points, helping readers quickly understand the objectives, methods, findings, and implications of the research. By following a structured approach, using clear language, and focusing on the core message, you can write an effective research summary that communicates the study’s contributions. Whether for academic or professional purposes, a well-crafted summary makes research accessible, engaging, and valuable for a wide audience.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., & Williams, J. M. (2016). The Craft of Research . University of Chicago Press.
- Swales, J. M., & Feak, C. B. (2012). Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Tasks and Skills . University of Michigan Press.
- Babbie, E. (2020). The Practice of Social Research . Cengage Learning.
- Neuman, W. L. (2014). Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches . Pearson.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

Appendix in Research Paper – Examples and...
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies
AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 7 Research Summary Templates with Samples and Examples

Kavesh Malhotra
Turning complex research into a compelling summary is like having a superpower in the vast world of information. A well-crafted research summary isn't just a data crunch; it's a strategic tool. Research shows that concise summaries enhance understanding. Studies reveal that audiences retained 50% more information when presented with well-structured summaries.
Imagine condensing your extensive research into a single page that instantly captivates the reader's attention and highlights the core of your findings. Whether presenting a market research proposal, diving into clinical medicine research, or outlining a project research proposal, a smartly crafted research statement can make your work convenient, accessible, and impactful.
In this blog, we'll guide you through a curated selection of seven Research Summary Templates, each a gem in its own right.
Why Choose Research Summary Templates?
"Efficiency is the soul of every impactful presentation."
- Time-Saving Marvels: These presets are your express pass to creating professional, impactful presentations that save you so much time and energy that would otherwise be spent making a summary from scratch!
- Customizable Frameworks: Tailor each layout to suit your unique research, maintaining flexibility while leveraging a solid starting point.
- Visual Appeal: The slides are not just functional; they are visually engaging, ensuring that your research paper doesn't just get read but leaves a lasting impression.
Let’s begin exploring these templates!
Template 1: Market Research Proposal One-Page Summary Presentation Report Infographic PPT PDF Document
This preset is a game-changer for presenting market research proposals concisely. It encapsulates your research's key aspects in a one-page summary, making a compelling case for readers. It includes details about the project name, researcher's information, and project research proposal details like background, objectives, methodology, and outcomes. Visual elements and a well-organized structure enhance readability, effectively communicating your market insights. Download this preset that transforms your market research proposal into a concise yet comprehensive summary, guiding your stakeholders through the essentials.

DOWNLOAD NOW
Template 2: Executive Summary Clinical Medicine Research Company Profile
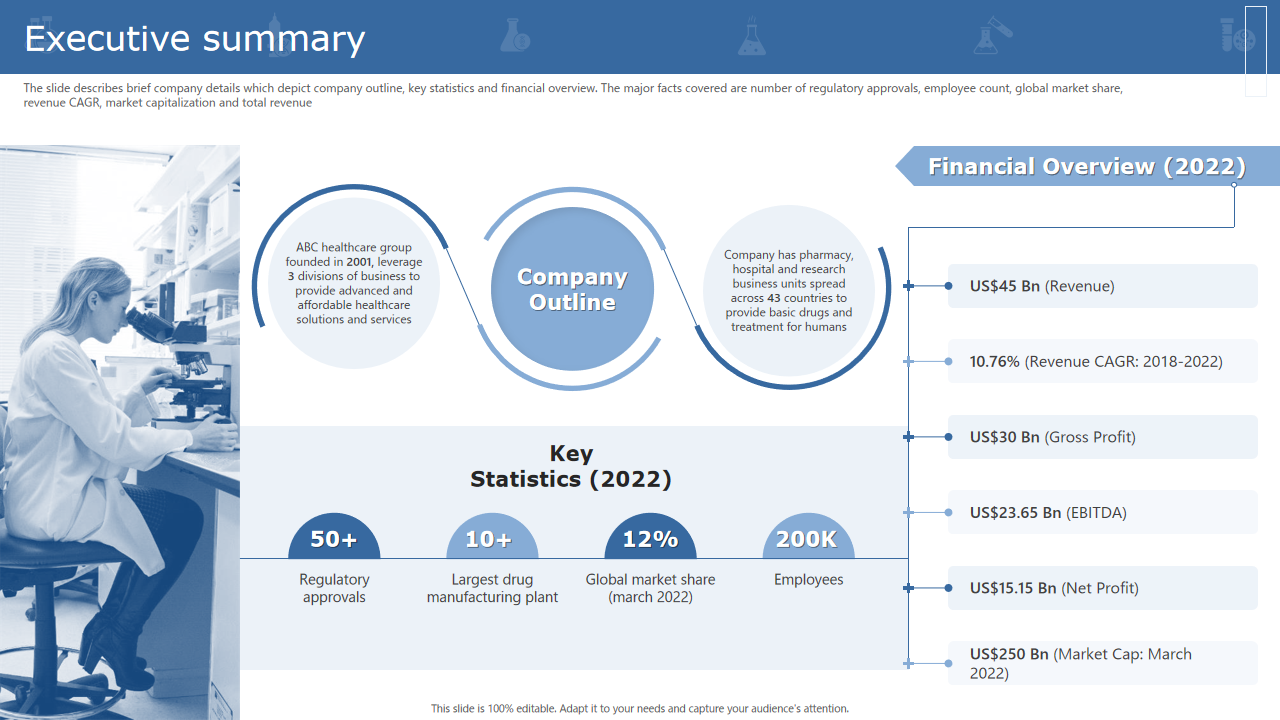
For clinical medicine researchers, this layout provides a succinct yet comprehensive overview. The executive summary format communicates vital information, making it ideal for quickly understanding the research's significance. The slide depicts the company outline, critical statistics, and financial overview. The significant facts covered are the employee count, number of regulatory approvals, global market share, revenue CAGR, total revenue, and market capitalization. Elevate your clinical medicine research with an executive summary that encapsulates the essence of your findings and the potential impact on the medical landscape.
Template 3: Sample Research Paper Outline in One-Page Summary Report
This structure streamlines your detailed research paper into a digestible one-page summary. It breaks down the research paper's structure, ensuring the audience grasps vital points efficiently. It encapsulates five main sections: introduction, issue, literature review, recommendations, and conclusion. The easy-to-follow format makes it a valuable tool for presenting a complex research statement. Download this layout that transforms your detailed research paper into a one-page summary wonder, clearly presenting the structure and key points.

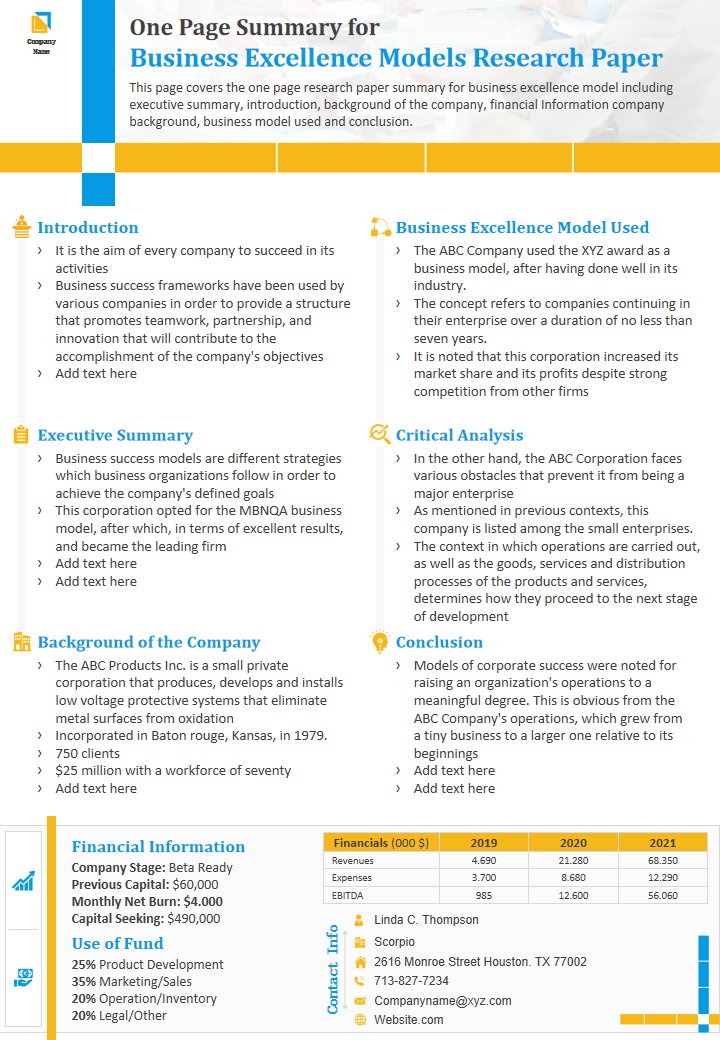
Template 4: One-Page Summary for Business Excellence Models Research Paper
Condense your exploration of business excellence models into a single, impactful page. This slide highlights the introduction, executive summary , company background, financial information, business excellence model used, key findings and insights, and conclusion, presenting them aesthetically pleasing. It's perfect for delivering the essence of your business excellence research with clarity and brevity. Condense your exploration of business excellence models into a single page, making your insights accessible and actionable.
Template 5: One-Page Project Research Proposal Summary Presentation
Efficiently communicate the crux of your project research proposal with this preset. It highlights crucial components of your project research like objectives, study design, budget, project milestones and durations, etc. The one-page summary format ensures that your proposal's key elements are prominently featured. Visual elements enhance engagement, ensuring that key stakeholders swiftly grasp your project's significance. Download this layout and make it an excellent choice for a compelling project research presentation.

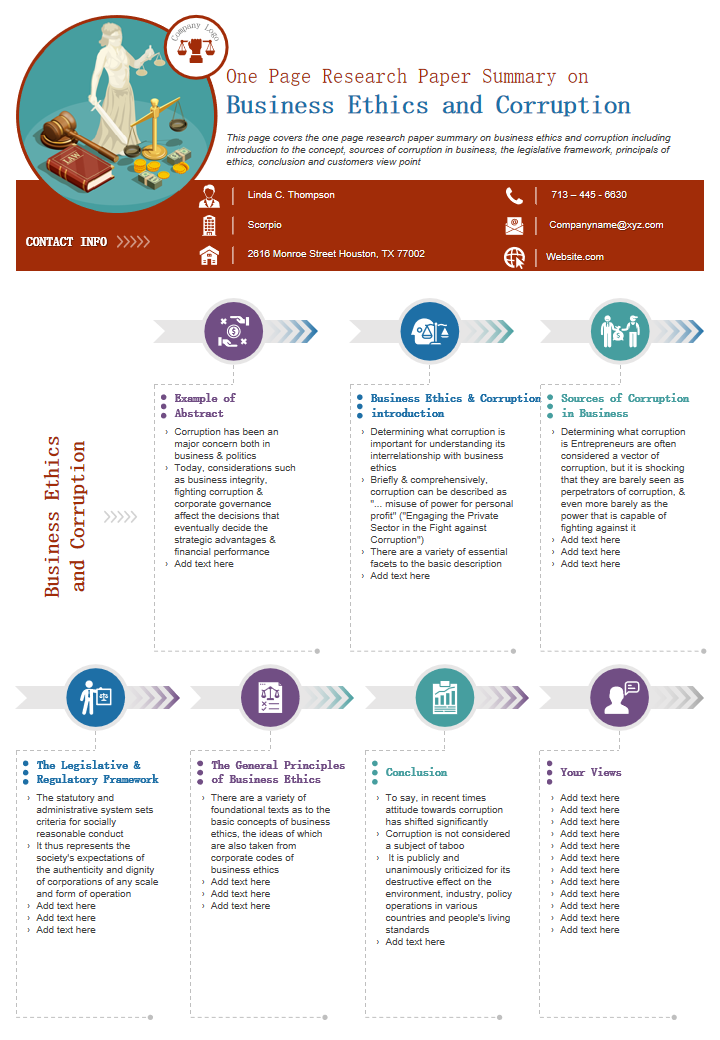
Template 6: One-Page Research Paper Summary on Business Ethics and Corruption
Navigate the complex landscape of business ethics and corruption research with this template. It condenses your research paper into a one-page summary , focusing on crucial ethical considerations:
- Introduction of the concept
- sources of corruption in businesses
- The legislative framework
- Principals of ethics
- Conclusion and
- Customer viewpoint
Clear visuals and a cohesive layout ensure that your insights on ethics and corruption are communicated effectively, giving your research statement the attention it deserves. Download this one-page summary , ensuring readers grasp your project's significance swiftly.
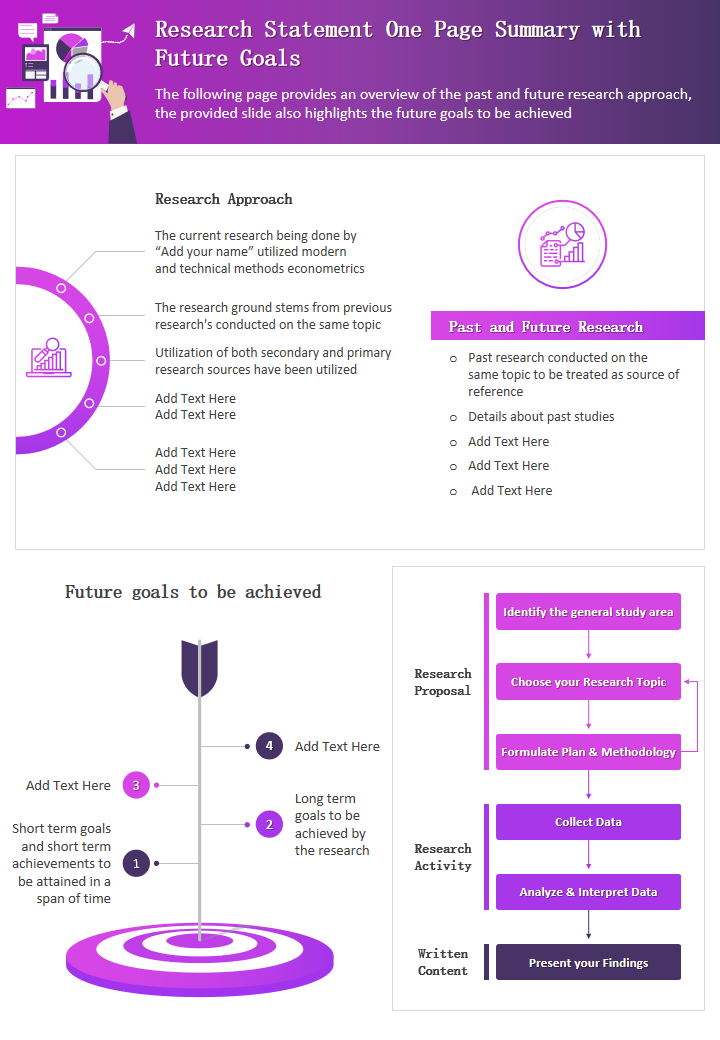
Template 7: Research Statement One Page Summary with Future Goals
Craft a compelling narrative of your research journey, culminating in a one-page summary with future goals. This presentation seamlessly integrates your research statement with a forward-looking perspective. It offers an overview of past and future research approaches and future goals to be achieved, along with a visual flowchart presenting your project research proposal , research activity, and other written content. Download this powerful tool for presenting your research's impact and future directions.
Conclusion: Your Research, Your Way
In the world of academia, business, or healthcare, your research is a cornerstone of progress. Ensure it's not just buried in volumes of data but presented in a way that captivates and communicates. Explore the above research summary templates and transform your research journey into a resonant narrative. Furthermore, dive into the past with our top history research proposal examples , complete with templates and samples for your historical research endeavors.
Remember, brevity is not just appreciated in a world saturated with information; it's often indispensable. So, here , you can streamline your project research proposals with our top 7 one-page templates for compelling and concise presentations.
Craft your research summary with care, and let your findings shine!
Related posts:
- Top 10 PowerPoint Templates to Present Succinct Research Statements
- How Financial Management Templates Can Make a Money Master Out of You
- [Updated 2023] Top 20 PowerPoint Templates to Devise a Systematic Research Methodology
- Top 10 Data Visualizations Playbook Templates with Samples and Examples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Concrete Proposal Templates with Examples and Samples

Top 7 Risk Management Chart Templates with Examples and Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

Your content here...

Writing a Summary – Explanation & Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at October 17th, 2023 , Revised On October 17, 2023
In a world bombarded with vast amounts of information, condensing and presenting data in a digestible format becomes invaluable. Enter summaries.
A summary is a brief and concise account of the main points of a larger body of work. It distils complex ideas, narratives, or data into a version that is quicker to read and easier to understand yet still retains the essence of the original content.
Importance of Summaries
The importance of summarising extends far beyond just making reading more manageable. In academic settings, summaries aid students in understanding and retaining complex materials, from textbook chapters to research articles. They also serve as tools to showcase one’s grasp of the subject in essays and reports.
In professional arenas, summaries are pivotal in business reports, executive briefings, and even emails where key points need to be conveyed quickly to decision-makers. Meanwhile, summarising skills come into play in our personal lives when we relay news stories to friends, recap a movie plot, or even scroll through condensed news or app notifications on our smartphones.
Why Do We Write Summaries?
In our modern information age, the sheer volume of content available can be overwhelming. From detailed research papers to comprehensive news articles, the quest for knowledge is often met with lengthy and complex resources. This is where the power of a well-crafted summary comes into play. But what drives us to create or seek out summaries? Let’s discuss.
Makes Important Things Easy to Remember
At the heart of summarisation is the goal to understand. A well-written summary aids in digesting complex material. By distilling larger works into their core points, we reinforce the primary messages, making them easier to remember. This is especially crucial for students who need to retain knowledge for exams or professionals prepping for a meeting based on a lengthy report.
Simplification of Complex Topics
Not everyone is an expert in every field. Often, topics come laden with jargon, intricate details, and nuanced arguments. Summaries act as a bridge, translating this complexity into accessible and straightforward content. This is especially beneficial for individuals new to a topic or those who need just the highlights without the intricacies.
Aid in Researching and Understanding Diverse Sources
Researchers, writers, and academics often wade through many sources when working on a project. This involves finding sources of different types, such as primary or secondary sources , and then understanding their content. Sifting through each source in its entirety can be time-consuming. Summaries offer a streamlined way to understand each source’s main arguments or findings, making synthesising information from diverse materials more efficient.
Condensing Information for Presentation or Sharing
In professional settings, there is often a need to present findings, updates, or recommendations to stakeholders. An executive might not have the time to go through a 50-page report, but they would certainly appreciate a concise summary highlighting the key points. Similarly, in our personal lives, we often summarise movie plots, book stories, or news events when sharing with friends or family.
Characteristics of a Good Summary
Crafting an effective summary is an art. It’s more than just shortening a piece of content; it is about capturing the essence of the original work in a manner that is both accessible and true to its intent. Let’s explore the primary characteristics that distinguish a good summary from a mediocre one:
Conciseness
At the core of a summary is the concept of brevity. But being concise doesn’t mean leaving out vital information. A good summary will:
- Eliminate superfluous details or repetitive points.
- Focus on the primary arguments, events, or findings.
- Use succinct language without compromising the message.
Objectivity
Summarising is not about infusing personal opinions or interpretations. A quality summary will:
- Stick to the facts as presented in the original content.
- Avoid introducing personal biases or perspectives.
- Represent the original author’s intent faithfully.
A summary is meant to simplify and make content accessible. This is only possible if the summary itself is easy to understand. Ensuring clarity involves:
- Avoiding jargon or technical terms unless they are essential to the content. If they are used, they should be clearly defined.
- Structuring sentences in a straightforward manner.
- Making sure ideas are presented in a way that even someone unfamiliar with the topic can grasp the primary points.
A jumble of ideas, no matter how concise, will not make for a good summary. Coherence ensures that there’s a logical flow to the summarised content. A coherent summary will:
- Maintain a logical sequence, often following the structure of the original content.
- Use transition words or phrases to connect ideas and ensure smooth progression.
- Group related ideas together to provide structure and avoid confusion.
Steps of Writing a Summary
The process of creating a compelling summary is not merely about cutting down content. It involves understanding, discerning, and crafting. Here is a step-by-step guide to writing a summary that encapsulates the essence of the original work:
Reading Actively
Engage deeply with the content to ensure a thorough understanding.
- Read the entire document or work first to grasp its overall intent and structure.
- On the second read, underline or highlight the standout points or pivotal moments.
- Make brief notes in the margins or on a separate sheet, capturing the core ideas in your own words.
Identifying the Main Idea
Determine the backbone of the content, around which all other details revolve.
- Ask yourself: “What is the primary message or theme the author wants to convey?”
- This can often be found in the title, introduction, or conclusion of a piece.
- Frame the main idea in a clear and concise statement to guide your summary.
List Key Supporting Points
Understand the pillars that uphold the main idea, providing evidence or depth to the primary message.
- Refer back to the points you underlined or highlighted during your active reading.
- Note major arguments, evidence, or examples that the author uses to back up the main idea.
- Prioritise these points based on their significance to the main idea.
Draft the Summary
Convert your understanding into a condensed, coherent version of the original.
- Start with a statement of the main idea.
- Follow with the key supporting points, maintaining logical order.
- Avoid including trivial details or examples unless they’re crucial to the primary message.
- Use your own words, ensuring you are not plagiarising the original content.
Fine-tune your draft to ensure clarity, accuracy, and brevity.
- Read your draft aloud to check for flow and coherence.
- Ensure that your summary remains objective, avoiding any personal interpretations or biases.
- Check the length. See if any non-essential details can be removed without sacrificing understanding if it is too lengthy.
- Ensure clarity by ensuring the language is straightforward, and the main ideas are easily grasped.
The research done by our experts have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- Authentic Sources


Dos and Don’ts of Summarising Key Points
Summarising, while seemingly straightforward, comes with its nuances. Properly condensing content demands a balance between brevity and fidelity to the original work. To aid in crafting exemplary summaries, here is a guide on the essential dos and don’ts:
Use your Own Words
This ensures that you have truly understood the content and are not merely parroting it. It also prevents issues of plagiarism.
Tip: After reading the original content, take a moment to reflect on it. Then, without looking at the source, write down the main points in your own words.
Attribute Sources Properly
Giving credit is both ethical and provides context to readers, helping them trace back to the original work if needed. How to cite sources correctly is a skill every writer should master.
Tip: Use signal phrases like “According to [Author/Source]…” or “As [Author/Source] points out…” to seamlessly incorporate attributions.
Ensure Accuracy of the Summarised Content
A summary should be a reliable reflection of the original content. Distorting or misrepresenting the original ideas compromises the integrity of the summary.
Tip: After drafting your summary, cross-check with the original content to ensure all key points are represented accurately and ensure you are referencing credible sources .
Avoid Copy-Pasting Chunks of Original Content
This not only raises plagiarism concerns but also shows a lack of genuine engagement with the material.
Tip: If a particular phrase or sentence from the original is pivotal and cannot be reworded without losing its essence, use block quotes , quotation marks, and attribute the source.
Do not Inject your Personal Opinion
A summary should be an objective reflection of the source material. Introducing personal biases or interpretations can mislead readers.
Tip: Stick to the facts and arguments presented in the original content. If you find yourself writing “I think” or “In my opinion,” reevaluate the sentence.
Do not Omit Crucial Information
While a summary is meant to be concise, it shouldn’t be at the expense of vital details that are essential to understanding the original content’s core message.
Tip: Prioritise information. Always include the main idea and its primary supports. If you are unsure whether a detail is crucial, consider its impact on the overall message.
Examples of Summaries
Here are a few examples that will help you get a clearer view of how to write a summary.
Example 1: Summary of a News Article
Original Article: The article reports on the recent discovery of a rare species of frog in the Amazon rainforest. The frog, named the “Emerald Whisperer” due to its unique green hue and the soft chirping sounds it makes, was found by a team of researchers from the University of Texas. The discovery is significant as it offers insights into the biodiversity of the region, and the Emerald Whisperer might also play a pivotal role in understanding the ecosystem balance.
Summary: Researchers from the University of Texas have discovered a unique frog, termed the “Emerald Whisperer,” in the Amazon rainforest. This finding sheds light on the region’s biodiversity and underscores the importance of the frog in ecological studies.
Example 2: Summary of a Research Paper
Original Paper: In a study titled “The Impact of Urbanisation on Bee Populations,” researchers conducted a year-long observation on bee colonies in three urban areas and three rural areas. Using specific metrics like colony health, bee productivity, and population size, the study found that urban environments saw a 30% decline in bee populations compared to rural settings. The research attributes this decline to factors like pollution, reduced green spaces, and increased temperatures in urban areas.
Summary: A study analysing the effects of urbanisation on bee colonies found a significant 30% decrease in bee populations in urban settings compared to rural areas. The decline is linked to urban factors such as pollution, diminished greenery, and elevated temperatures.
Example 3: Summary of a Novel
Original Story: In the novel “Winds of Fate,” protagonist Clara is trapped in a timeless city where memories dictate reality. Throughout her journey, she encounters characters from her past, present, and imagined future. Battling her own perceptions and a menacing shadow figure, Clara seeks an elusive gateway to return to her real world. In the climax, she confronts the shadow, which turns out to be her own fear, and upon overcoming it, she finds her way back, realising that reality is subjective.
Summary: “Winds of Fate” follows Clara’s adventures in a surreal city shaped by memories. Confronting figures from various phases of her life and battling a symbolic shadow of her own fear, Clara eventually discovers that reality’s perception is malleable and subjective.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long is a summary.
A summary condenses a larger piece of content, capturing its main points and essence. It is usually one-fourth of the original content.
What is a summary?
A summary is a concise representation of a larger text or content, highlighting its main ideas and points. It distils complex information into a shorter form, allowing readers to quickly grasp the essence of the original material without delving into extensive details. Summaries prioritise clarity, brevity, and accuracy.
When should I write a summary?
Write a summary when you need to condense lengthy content for easier comprehension and recall. It’s useful in academic settings, professional reports, presentations, and research to highlight key points. Summaries aid in comparing multiple sources, preparing for discussions, and sharing essential details of extensive materials efficiently with others.
How can I summarise a source without plagiarising?
To summarise without plagiarising: Read the source thoroughly, understand its main ideas, and then write the summary in your own words. Avoid copying phrases verbatim. Attribute the source properly. Use paraphrasing techniques and cross-check your summary against the original to ensure distinctiveness while retaining accuracy. Always prioritise understanding over direct replication.
What is the difference between a summary and an abstract?
A summary condenses a text, capturing its main points from various content types like books, articles, or movies. An abstract, typically found in research papers and scientific articles, provides a brief overview of the study’s purpose, methodology, results, and conclusions. Both offer concise versions, but abstracts are more structured and specific.
You May Also Like
In any form of written communication, be it academic writing, journalism, or even casual blogging, there comes a time when we need to reference another’s words to support, explain, or emphasise our points.
A tertiary source is an information source that compiles, analyses, and synthesises both primary and secondary sources.
In today’s information age, where vast amounts of knowledge are easily accessible, it is crucial to know how to use and represent that knowledge correctly and how to cite sources properly.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works

How to Write a Summary for a Research Paper: Step-by-Step Guide

- Published: November 4, 2024
- Updated: November 18, 2024
- Category: Analysis

Share Post:
Creating a clear, concise summary of a research paper can be a challenging but rewarding task.
Whether you’re summarizing for your own study notes, to share with peers, or as part of a formal academic assignment, a well-constructed summary can convey the core message and findings of the original paper effectively.
Summarizing a research paper not only saves time for readers but also ensures they capture the most essential points without going through pages of data and analysis.
A well-written summary helps others quickly grasp the significance of the research and decide if they want to read the full paper.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Summarize key points to provide a clear, concise overview for readers.
- Read the paper thoroughly to grasp the main ideas and structure.
- Focus on the introduction, objectives, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Rephrase the main points; avoid direct quotes to maintain flow.
- Aim for 10-20% of the paper’s length, focusing only on essential points.
- Simplify language, remove redundancies, and ensure clarity.
- Credit the original work based on your style guide (APA, MLA, etc.).
- Read aloud for flow, check coherence, and proofread meticulously for polish.
Step 1 – Purpose of a Research Summary

A summary condenses the research paper’s content, highlighting the key points: objectives, methodology, results, and conclusions.
It’s particularly useful for those who want a quick overview to assess the relevance of the research for their own work or study.
Your goal with a summary is to capture the essence of the paper, focusing on clarity and conciseness.
Imagine that your readers are researchers, students, or professionals who need the main points without unnecessary details.
Step 2 – Read the Research Paper Carefully and Thoroughly
To write an effective summary, you need a solid understanding of the research paper.
Start by reading the paper from start to finish to get a sense of its structure, main arguments , and findings. You’ll want to go through it at least twice:
- First Read : Get a general understanding of the topic, main thesis, and general direction.
- Second Read : Look closer, noting specific details in the introduction, methods, results, and conclusions. Pay close attention to the research question, hypotheses, methodology, and findings.
Step 3 – Identify Key Sections to Include in Your Summary
- Introduction : Briefly introduce the topic and research question. What problem is the research addressing?
- Objectives and Hypothesis : What were the primary objectives of the research? Was there a specific hypothesis or question that guided the study?
- Methodology : Summarize the methods used. What kind of data was collected, and how was it analyzed ?
- Results : Provide an overview of the main findings. Focus on the data points that were significant and any patterns or correlations observed.
- Conclusion : Highlight the main conclusions or recommendations. What did the research achieve, and what is its significance?
Each of these sections will be summarized into a few sentences or a short paragraph in your final summary.
Step 4 – Write the Summary in Your Own Words
Avoid directly quoting the research paper unless absolutely necessary, as this can make the summary feel less streamlined and may detract from its flow.
Use clear, straightforward language and avoid complex jargon whenever possible.
Remember, the purpose of the summary is to communicate the research’s essence without all the extra details, so focus on the “big picture” points.
Instead of writing: “The research explores the multifaceted relationships between demographic variables and the reported instances of subjective well-being.”
Try: “The study examines how factors like age, income, and education impact individual happiness levels.”
Step 5 – Keep It Concise and Focused
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Highbrow Research (@_highbrowresearch)
A good research summary should be around 10-20% of the original paper’s length, depending on the depth required by your assignment or audience.
Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for brevity without sacrificing the clarity of essential points.
It can help to write a rough draft first and then refine it. Look for places where you may have included redundant information or extraneous details, and trim those down.
Step 6 – Review and Edit for Clarity
After you’ve drafted your summary, take a break and then return to it with fresh eyes.
This will help you spot any sentences that may be unclear or overly wordy.
Review your summary to ensure it’s coherent and that the main points of the research paper are accurately reflected.
Ask yourself:
- Have I clearly captured the research question and objectives?
- Are the main findings easy to understand?
- Is the conclusion well-aligned with the research’s significance?
Step 7 – Cite the Original Research Paper
Depending on your style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.), make sure to cite the research paper appropriately.
This can be done at the beginning or end of your summary.
Example of an In-Text Citation
“In their study, Smith and Lee (2021) explored the relationship between income levels and life satisfaction, concluding that higher income positively impacts happiness.”
Step 8 – Add a Final Review and Proofread
Once you’ve written and organized your summary, take the time for a final review to make sure it’s polished and impactful.
This step can make a big difference in ensuring your summary reads smoothly, clearly, and accurately represents the key points of the research paper.
Start by reading it through from beginning to end, ideally out loud, as this can help you catch any awkward phrasing or spots where the flow could be improved.
During this review, look for opportunities to fine-tune your language.
Are there areas where you could simplify your wording without losing meaning? Are all points clearly expressed without extra filler?
This is also a good moment to double-check that you’ve included all major elements: the research question, objectives, methodology, key findings, and conclusions.
Each of these should be represented concisely, with a logical flow from one section to the next.

Next, check for coherence. Does each section transition naturally into the next?
If something seems unclear or overly complex, consider rephrasing it for simplicity and readability.
As you review, remember that a summary should be engaging, so avoid overly technical language unless necessary and aim for straightforward explanations.
Finally, be meticulous with proofreading for grammar, punctuation, and style. Even minor errors can distract readers and reduce the professionalism of your summary.
- Guide , paper , Research , Research Summary , Summary , Tips , Writing

Thomas Caldwell
Latest post.

How To Foster Inclusion in Modern Teaching Techniques?

10 Good Study Habits of Straight-A Students – Study Smarter, Not Harder

How to Keep Your Classroom Modern and Relevant in the Digital Age

What Is Work Study?

How Much Do College Professors Make Per Year?

How Long Is Law School? Complete Overview for 2025

Get in Touch
Email: [email protected]

Research Paper Summary
Ai generator.

Whether you are a student, an academic scholar, or even working in business, there is no denying that a research paper summary is the one tool that you are going to expect when it comes to writing your research paper or research studies. There is also no denying how useful the summary is going to be when you have to report it to your superiors or your professors without having to go through the entire research paper. Students know for themselves that writing a summary of their research paper is useful. With that, here are examples of research paper summaries to download.
10+ Research Paper Summary Examples
1. economics research paper summary.

2. Goals Research Paper Summary

Size: 243 KB
3. Past Research Paper Summary

Size: 371 KB
4. Project Management Research Paper Summary

Size: 681 KB
5. Qualitative Research Paper Summary

Size: 109 KB
6. Reading Research Paper Summary

7. Research Paper Proposal Summary

Size: 187 KB
8. Research Paper Summary Format

Size: 120 KB
9. Research Paper Summary Generator

10. Sample Research Paper Summary

Size: 111 KB
11. Style Research Paper Summary

Size: 199 KB
What Is a Research Paper Summary?
Research paper summaries are short but descriptive writings that are expected in a research paper . What goes in a research paper summary is the main topic or the main plot of your research paper. However, what is and should never be included are any new discoveries, arguments and new leads that help your research. The purpose of the summary is to simply give out the general point of view or the outline of your research paper and nothing else. This is often the mistake made by students when they think of a research paper summary. The need to add all new leads to help their research in the summary. The only main thing to focus on your summary is the overview and the general outline .
How to Write a Research Paper Summary
Being able to write a research paper summary is important and quite a useful skill. As this does not only work for students on their research paper, but it also works for employees who are given the task to write a project summary. It basically works just the same. To get a glimpse of what you can do to make your research paper summary, here are simple steps you can follow.
Step 1: Take the Main Part of Your Research
When you make your summary, the first paragraph will mainly be about your research paper. The first part is to take the main part of your research. The main part or the main topic should be what it is about. Make sure what you are writing is what your research paper is about, as there are times when your topic may not be the main goal of your paper.
Step 2: Break It Down to Smaller Topics
Since the first paragraph is focused on the introduction and the main topic, the second paragraph will focus mainly on breaking down your main or general topic into smaller subtopics. By doing this, it is easier for you to divide and explain every single important detail of your research paper. Students are often tasked to do this in order for them to get a better outlook of their research paper and how they are able to piece together the smaller topics to the main topic.
Step 3: Get the Gist
The third and final paragraph will be the gist of your research paper. This includes the heart or the main part, the findings and the conclusion. The gist has to be a general summary of your research paper. It should have the facts that support it, the findings of your research and the hypothesis. Add in your conclusion at the end.
Step 4: Proofread Your Work
Lastly, make sure to proofread your entire research paper summary. This is just to make sure you did not misspell any words, your punctuations are in the correct place and the tone of your writing fits the paper you are making.
What is a research paper summary?
Research paper summaries are short but descriptive writings that are expected in a research paper. What goes in a research paper summary is the main topic or the main plot of your research paper.
What are the characteristics of a research paper summary?
The characteristics of a research paper summary are the following:
- The introduction and the main topic
- The breaking of the main topic to sub topics
- The gist of the research paper summary
- The conclusion
How lengthy can a research paper summary be?
The normal length of a research paper summary should not exceed more than a page. However, when it comes to the number of words for a summary, your wording should not exceed the maximum number of four hundred words.
When it comes to writing a research paper, there is no denying that you must also write a summary for it. Since a research paper can sometimes be overwhelming to those who will be listening to you talk about it, you can relieve it by making a summary of your paper. This will also help them follow what you are discussing and what it is about.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
COMMENTS
EXAMPLE RESEARCH SUMMARY . Danielle Wilson . Psych 100 Section 005 . Tuesday Thursday 1:00PM . Ms. Trich Kremer . 913553226 . Student ID Number You will be writing a summary of a PEER REVIEWED research article. Instructor’s name Time/Day the class meets Class and Section Your Name Please read all of these boxes to make sure you are following ...
Mar 26, 2024 · Structure of a Research Summary. A well-structured research summary generally includes the following sections: 1. Title. The title should reflect the main topic or research question, helping readers quickly understand what the study is about. If applicable, the title should also hint at the methodology or scope of the study. 2. Introduction
Jul 23, 2024 · To organize your research summary, each topic must be discussed in separate paragraphs. How you came up with a factual research must be briefly explained in a separate paragraph. If you have a lengthy research paper, try not to write not more than 10% of the entire paper.
Nov 29, 2023 · Elevate your clinical medicine research with an executive summary that encapsulates the essence of your findings and the potential impact on the medical landscape. DOWNLOAD NOW . Template 3: Sample Research Paper Outline in One-Page Summary Report. This structure streamlines your detailed research paper into a digestible one-page summary. It ...
Oct 17, 2023 · Examples of Summaries. Here are a few examples that will help you get a clearer view of how to write a summary. Example 1: Summary of a News Article. Original Article: The article reports on the recent discovery of a rare species of frog in the Amazon rainforest. The frog, named the “Emerald Whisperer” due to its unique green hue and the ...
Aug 28, 2024 · What is a Research Summary and Why Is It Important? A research summary is a type of paper designed to provide a brief overview of a given study - typically, an article from a peer-reviewed academic journal. It is a frequent type of task encountered in US colleges and universities, both in humanitarian and exact sciences, which is due to how important it is to teach students to properly ...
Sep 4, 2024 · Examples of Article Summary for Research Example 1: Title: Advances in Renewable Energy Technologies Author: Dr. Maria Gonzalez Publication Date: September 12, 2023 Main Idea: The article explores recent innovations in renewable energy technologies and their potential to combat climate change. Key Points:
Nov 4, 2024 · Remember, the purpose of the summary is to communicate the research’s essence without all the extra details, so focus on the “big picture” points. Example. Instead of writing: “The research explores the multifaceted relationships between demographic variables and the reported instances of subjective well-being.”
Sep 5, 2024 · What goes in a research paper summary is the main topic or the main plot of your research paper. However, what is and should never be included are any new discoveries, arguments and new leads that help your research. The purpose of the summary is to simply give out the general point of view or the outline of your research paper and nothing else.
purpose of the summary is to take notes to later remind yourself about the article you may want to write a longer summary. However, if the purpose of summarizing the article is to include it in a paper you are writing, the summary should focus on how the articles relates specifically to your paper. Reading the Article Allow enough time.