Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456

Parts of Speech: An Overview of Grammar Fundamentals
- Parts Of Speech

Understanding Parts of Speech Definitions, Types, Examples and Usage
Understanding the parts of speech is essential for mastering English grammar . Parts of speech are the building blocks of sentences, and each plays a specific role in conveying meaning. This guide covers the fundamental parts of speech, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. By learning how these parts function and interact, you'll be able to write clearer and more effective sentences. Whether you’re a student looking to improve your grammar or skill, this guide provides simple explanations and practical examples to help you grasp the basics of English grammar .

What are Parts of Speech?
Parts of speech are categories of words based on their function in a sentence. Each part of speech plays a specific role in sentence structure and helps convey meaning.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
There are eight categories, and they are as follows:
Preposition
Conjunction.
Interjection
Now let us discuss each of these one by one
The noun is the name of any person, place, or thing. The noun "thing" includes all the things which have a name and can be seen, tasted, heard, touched, or smelled by you. It also includes anything that we could think of, but our feelings cannot comprehend.
For Example:
Rey is a good girl. Here Rey is the name of a person; hence, it is a noun.
Switzerland is breathtaking. Here Switzerland is the name of a place. Hence it is a noun.
My dog's name is Dobby. Here Dog and Dobby are both names of animals; hence it is a noun.
I love books. Here books are the name of a thing; hence it is a noun.
The noun is further divided into a common noun, proper noun, countable and uncountable noun. The common nouns include abstract nouns and collective nouns.
Proper Noun - It is the name of a particular person or place. For example, Rey is a good girl. Here Rey is a proper noun.
Common Noun - The name of any generalised group or community, class or kind. The name shared by a common type of person or person is a common noun. For example, Rey is a good girl. Here the girl is a common noun. My dog's name is Dobby. Here the dog is a common noun and Dobby proper noun.
Collective Noun - It describes a collection of people or things. For example, The crowds in the market suffocate me. The crowd is a collective noun.
Abstract Noun - It is the name of quality, action, or state. E.g., honesty is important. Here honesty is an abstract noun.
Countable and Uncountable Noun - It describes if the name of objects or people is countable or not. For example, doctors are countable, but sugar and milk are uncountable entities.
The Pronoun is the word which we use instead of a noun. For say, if we keep using a person's name in writing or speech, it would be an inappropriate sentence and will take away the essence of the sentence. Hence instead of using the name, we use a pronoun to denote that person or thing. The pronoun's words include I, me, she, he, you, us, their, ours, etc. Following are the examples:
Roger is in my class. He is intelligent.
In the above sentence, we have to use He to denote Roger.
I love novels, and this is my book.
In the above sentence, I use I, myself, to denote ourselves instead of using our name.
The pronoun "it" is used to denote a neutral gender or unknown gender or to denote a lifeless thing. E.g.,
It is a library book. Here the book is denoted by it.
It is the word that describes or stresses the quality of the noun or person, place, or thing. The following example will help you understand better.
Ben is a clever boy.
Here, the adjective Clever describes Ben.
I do not like that book.
In the above sentence, if you say which book? "That" points out the book. Hence, that is an adjective here.
The adjective is divided into a descriptive or proper adjective, quantity, number, and demonstrative and interrogative adjectives. Some examples are as follows and darkened word adjectives:
Australia is the smallest continent. (descriptive or proper adjective).
She ate the whole food alone. (Adjective of quantity).
There were five boys. (Adjective of number).
Each person has to answer in class. (adjective of number).
He is such an honest man. (demonstrative adjective).
Which path is correct? (Interrogative adjective).
A verb is a word that describes the state of a person or thing. A verb tells us what a person or thing does, or what has been done to a person or thing. They are the action words that describe the action done by a person or thing. For example,
Sia is singing. (So singing is an activity performed by Sia. Hence, it is a verb)
The dog died. (The word died describes the state of the dog)
A verb is mainly of two types: transitive and intransitive.
He kicked the man. (Transitive verb)
He never kicks. (Intransitive verb)
It is a word that adds meaning or adjective to the verb. The word which describes the quality of the verb is an adverb. The following are examples to make you understand better, and darkened words are adverbs.
He quickly ran to buy medicines.
She sang beautifully.
They loved each other immensely.
It is a word that is used with a noun or pronoun to establish a relation between a noun or pronoun concerning something else. Following are the examples:
The monkeys sat under the tree.
She lives in a big city.
They were looking out the window.
A conjunction is a word that is used to join sentences or phrases. Read the below examples for a better understanding. Here, bold words are conjunctions.
Cat and dog are enemies.
Her courage and determination won.
It was sunny but cold.
She ran fast but missed the bus.
Interjection:
It is the word that expresses an exclamation that is a sudden reaction, feeling, or emotion of happiness, despair anger, etc. Follow the examples below:
Hurray! I won.
Alas! He is no more.
You are a courageous person. Bravo!
Parts of Speech Chart
10 sentences with all parts of speech.
Here are 10 sentences that include all the main parts of speech:
The (article) quick (adjective) brown (adjective) fox (noun) jumps (verb) over (preposition) the (article) lazy (adjective) dog (noun).
She (pronoun) happily (adverb) plays (verb) the (article) piano (noun) every (adjective) day (noun) in (preposition) the (article) evening (noun).
The (article) old (adjective) man (noun) gives (verb) his (pronoun) time (noun) to (preposition) help (verb) the (article) community (noun).
My (pronoun) sister (noun) often (adverb) reads (verb) interesting (adjective) books (noun) in (preposition) her (pronoun) spare (adjective) time (noun).
After (preposition) the (article) rain (noun), we (pronoun) went (verb) to (preposition) the (article) park (noun) and (conjunction) played (verb) a (article) game (noun).
He (pronoun) was (verb) extremely (adverb) happy (adjective) when (conjunction) he (pronoun) saw (verb) the (article) beautiful (adjective) sunset (noun).
They (pronoun) carefully (adverb) painted (verb) their (pronoun) house (noun) with (preposition) bright (adjective) colours (noun) for (preposition) the (article) festival (noun).
The (article) new (adjective) teacher (noun) explained (verb) the (article) complex (adjective) concept (noun) to (preposition) the (article) students (noun) clearly (adverb).
In (preposition) the (article) morning (noun), she (pronoun) usually (adverb) goes (verb) for (preposition) a (article) run (noun) around (preposition) the (article) neighbourhood (noun).
I (pronoun) have (verb) never (adverb) seen (verb) such (adjective) a (article) beautiful (adjective) painting (noun) in (preposition) my (pronoun) life (noun).
Parts of Speech With Examples
Exercise: identify the part of speech.
The cat sat on the mat.
She quickly finished her homework.
He is going to the store.
The beautiful flowers are in the garden.
We and them went to the concert.
Wow , that’s a great idea!
The book is on the table.
They are playing in the park.
She sang a lovely song.
Although it was raining, we went outside.
Adverb – quickly
Pronoun – He
Adjective – beautiful
Conjunction – and
Interjection – Wow
Preposition – on
Pronoun – They
Verb – sang
Conjunction – Although
Check Your Understanding of Parts of Speech
The cat is sleeping on the sofa.
She runs quickly in the morning.
He enjoys playing football on weekends.
The blue sky is very clear today.
They went to the park and played basketball.
Oh , I forgot to call her!
The keys are under the sofa.
We need to buy groceries.
She writes letters every day.
Because it was cold, we stayed inside.
Find Out if You Got them All Right from the Answers Below.
Article – The
Adjective – blue
Interjection – Oh
Preposition – under
Pronoun – We
Verb – writes
Conjunction – Because
Takeaway from the Page
Core Components : Parts of speech are fundamental to sentence construction and understanding. Each type—nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections—serves a unique role.
Sentence Structure : Mastery of parts of speech is crucial for creating well-structured sentences. Knowing how each part functions helps in forming clear and meaningful sentences.
Clarity and Precision : Using parts of speech correctly improves communication by making sentences more precise and less ambiguous.
Practical Application : Regular practice through exercises helps reinforce understanding and application of parts of speech, leading to better writing and speaking skills.
Comprehensive Understanding : A solid grasp of parts of speech contributes to overall language proficiency, enabling more effective and confident use of the language in various contexts.
FAQs on Parts of Speech: An Overview of Grammar Fundamentals
1. What are parts of speech?
Parts of speech are categories of words based on their function in a sentence. They include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
2. What are parts of the speech chart?
A part of a speech chart is a visual representation that categorises different types of words and their functions in sentences, often with examples.
3. Can you provide parts of speech with examples?
Yes, parts of speech with examples include nouns (dog), pronouns (he), verbs (run), adjectives (happy), adverbs (quickly), prepositions (under), conjunctions (and), and interjections (wow).
4. What are the 8 parts of speech definitions and examples?
The 8 parts of speech are:
Noun: A person, place, or thing (e.g., cat).
Pronoun: Replaces a noun (e.g., she).
Verb: Expresses action or state (e.g., run).
Adjective: Describes a noun (e.g., blue).
Adverb: Describes a verb, adjective, or adverb (e.g., quickly).
Preposition: Shows the relationship between words (e.g., under).
Conjunction: Connects words or clauses (e.g., and).
Interjection: Expresses emotion (e.g., wow).
5. What are some examples of parts of speech in sentences?
Examples in sentences: The dog (noun) quickly (adverb) runs (verb) through the park (noun) because (conjunction) it (pronoun) is fun (adjective).
6. How can I use parts of the speech chart?
Use parts of a speech chart to understand the function of each word type in a sentence, which helps in improving writing and grammar skills.
7. What is the importance of knowing the types of parts of speech?
Knowing the types of parts of speech helps in understanding sentence structure, improving communication, and mastering grammar.
8. Can you give 10 sentences with all parts of speech?
The (article) cat (noun) quickly (adverb) runs (verb) under (preposition) the (article) big (adjective) tree (noun).
She (pronoun) and (conjunction) I (pronoun) went (verb) to (preposition) the (article) store (noun).
Wow (interjection), that (pronoun) was (verb) an (article) amazing (adjective) performance (noun)!
They (pronoun) are (verb) very (adverb) happy (adjective) about (preposition) the (article) news (noun).
She (pronoun) saw (verb) him (pronoun) at (preposition) the (article) movie (noun) yesterday (adverb).
The (article) dog (noun) barked (verb) loudly (adverb) at (preposition) the (article) stranger (noun).
Although (conjunction) it (pronoun) was (verb) raining (verb), we (pronoun) went (verb) to (preposition) the (article) park (noun).
I (pronoun) cannot (verb) believe (verb) how (adverb) quickly (adverb) she (pronoun) finished (verb) the (article) task (noun).
They (pronoun) talked (verb) about (preposition) their (pronoun) plans (noun) for (preposition) the (article) weekend (noun).
Oh (interjection), the (article) team (noun) played (verb) well (adverb) and (conjunction) won (verb) the (article) game (noun).
9. What are the main parts of speech?
The main parts of speech are nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
10. How do parts of speech help in understanding sentences?
Parts of speech help in understanding sentences by identifying the function of each word, which clarifies the meaning and structure of the sentence.

- English Grammar
- Grammar Exercises
- Parts Of Speech Exercises
Parts of Speech Exercises with Answers
Every topic in English grammar requires good understanding and a lot of practice. A thorough knowledge of the various grammatical components and their application is necessary to master the English language . This article provides you with a few practice exercises for parts of speech . Check it out.
Table of Contents
Exercise 1 – identify the adverb, exercise 2 – use the appropriate pronoun.
- Exercise 3 – Underline the Preposition
Exercise 4 – Identify the Part of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech exercises.
Give below are a few exercises. Try them out and assess your understanding of the different parts of speech.
Go through the given sentences and identify the adverb.
- We have seen this before.
- The postman comes to her daily.
- The man repeated the same thing thrice.
- Your friend called again.
- Please walk forward.
- The horse ran away.
- My brother writes clearly.
- The army fought bravely.
- The mangoes are almost ripe.
- Are you keeping well?
Fill the blanks with correct pronouns.
- Shyam is my brother. ___ study in the same class
- Between Ritu and me, __ am the younger one.
- Do you see this book with my name on it? It is ___.
- Miss Gwen is our new class teacher. ___ is very sweet.
- While cutting vegetables, Mitu cut ___.
- The jury got divided among ___.
- I’m coming too. Please wait for __.
- Nobody but ___ was present.
- ___ book is better than the other.
- Is the mug ___? It was on your table.
Exercise 3 – Underline the Preposition
Identify the prepositions in the following passage.
Goldilocks used to live with her parents in a cabin near the forest. One day, she decided to go for a walk. She strolled down the lane that led to the forest and came across a cottage. Feeling intrigued, she decided to check whose house it was. She knocked on the door, but no one answered. Then she decided to go in and check. Once she came into the cottage, she saw three soup bowls kept on the table. Feeling hungry, she drank the soup out of the smallest bowl. She saw a flight of stairs that led to a room above. She decided to go and see the rooms. On reaching the rooms, she saw there were three beds. Feeling sleepy with all the walking and hot soup, she decided to take a nap and slept on the smallest bed. When she woke up, she saw three bears standing in front of her, and the smallest bear among them crying loudly. Terrified, she started screaming and ran past the bear family to reach her home.
Goldilocks used to live with her parents in a cabin near the forest. One day, she decided to go for a walk. She strolled down the lane that led to the forest and came across a cottage. Feeling intrigued, she decided to check whose house it was. She knocked on the door, but no one answered. Then she decided to go in and check. Once she came into the cottage, she saw three soup bowls kept on the table. Feeling hungry, she drank the soup out of the smallest bowl. She saw a flight of stairs that led to a room above . She decided to go and see the rooms. On reaching the rooms, she saw there were three beds. Feeling sleepy with all the walking and hot soup, she decided to take a nap and slept on the smallest bed. When she woke up, she saw three bears standing in front of her, and the smallest bear among them crying loudly. Terrified, she started screaming and ran past the bear family to reach her home.
Go through the following sentences and identify the part of speech of the underlined words.
- Namitha is not coming today.
- My mom will be leaving to Bangalore tomorrow .
- The teacher asked the students to stand.
- He is my brother.
- There is a cat under the table.
- The clothes did not dry as it was raining all night.
- Sheena and her sister dance well .
- I am wearing a green dress for the party.
- Oh ! That is really sad.
- She is coming with me.
- Verb, adverb
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Conjunction, adverb
- Interjection
What are parts of speech?
Words are classified into different classes called parts of speech depending on their usage.
What comes under parts of speech?
Noun, adjective, pronoun, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction and interjection come under parts of speech.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

Speech Writing Class 11 Format, Examples, Topics, Exercises
Basic English Grammar rules can be tricky. In this article, we’ll get you started with the basics of sentence structure, punctuation, parts of speech, and more.
We also providing Extra Questions for Class 11 English Chapter wise.
Speech Writing Class 11 Format, Examples, Topics, Exercises PDF
Purpose of making a speech:
- to convey information orally to a large gathering of people, forcefully and convincingly
- to convert the listeners to the speaker’s point of view
- to pass on a wide range of information to a wide range of audience orally
- to express an opinion, share a point of view, experience, observation etc.
- Salutation – speaker greets chief guests, fellow speakers, and listeners
- Key sentence carrying the central theme or issue of the speech
- Expressing one’s views – what you feel about the topic
- Compare and contrast – what others feel and why your views are better
- Summing up – conclude by summing up arguments that highlight your viewpoint.
- A speech must begin with a catchy introduction in the form of an anecdote, quotation, statistical data, or a thought-provoking question.
- A speech must reflect the speaker’s clarity of thought, accuracy of facts, and balanced view through a comparison and contrast with other viewpoints.
- Bring credibility to views by quoting of adequate supporting data.
- Infuse humour through anecdotes.
- Sum up or consolidate ideas/suggestions/measures to improve the situation, personal observations, and predictions.
- Use language that is persuasive and powerful.
- Include a vote of thanks to the audience.
The speech must be written in the appropriate format and style. Remember to keep within the word limit.
Speech Writing Sample Example for Class 11

A large number of advertisers are using children to sell their products. You are against the concept of children being used in advertisements. Write a speech to put forward your views. You are Dinesh/Divya of Government Model School, Karnal. Use the clues given.
Honourable judges, respected teachers, and my dear friends, a very good morning to all. Today I, Divya of Government Model School, Karnal (a) ………………………………… on ‘Should We Use Children to Advertise Goods?’ (b) ………………………………… all those advertisements which use children to target other children for marketing their products. There are two reasons for this. (c) ………………………………… . Advertisers show teenagers jumping from the bridge to pick up a bottle of a popular brand of soft drink or performing daredevil acts on motorcycles. Children try to emulate these models and often get hurt or, worse still, even lose their lives.
The second reason is that (d) ……………………………….. . They do not have access to information, so when their favourite actor says, “Yehi hai right choice, baby’, they’re ready to accept it as the right choice. Kids love a particular brand of juice because the girl in the advertisement says, “I love you juice.” It becomes the favoured drink though it does not have any nutritive value as it is not fruit – based. Monosodium glutamate, an essential ingredient of a popular brand of instant noodles, is known to cause brain damage and obesity. But the advertisements are so powerful that children will eat no other brand.
(e) ……………………………….. . They realise kids have ‘pester – power’. (f) ………………………………… till they buy them the branded shoes or jeans that they have seen children wearing in advertisements and (g) ……………………………….. .
The Advertising Standards Council of India lays down the code for advertising as follows, ‘Advertisements addressed to children shall not contain anything, whether in illustration or otherwise, which might result in their physical, mental or moral harm, or which exploits their vulnerability.’ (h) ………………………………… that this code is being flouted openly? I feel there should be a committee to review all advertisements using children. Answer: (a) stand before you to share with you my views (b) I strongly condemn as unethical (c) One is the fact that children are more vulnerable (d) it violates the right of informed choice (e) I feel that advertisers are exploiting children by using them in advertisements (f) They pester their parents (g) the manufacturers laugh all the way to the bank (h) But, friends, don’t you agree with me when I say
- The manufacturers laugh all the way to the bank
- But, friends, don’t you agree with me when I say I strongly condemn as unethical
- I feel that advertisers are exploiting children by using them in advertisements
- One is the fact that children are more vulnerable.
- stand before you to share with you my views
- They pester their parents
- It violates the right of informed choice.
Speech Writing Class 11 Practice Examples
1. You recently read the following newspaper article:
Shocked by the recent study that shows how computers are killing childhood by making redundant a host of skills which a child would otherwise acquire naturally, you decide to speak in the morning assembly at your school, advising students not to lose themselves in virtual reality. Write the speech in 150 – 200 words.
2. You are Ratan/Radha of Class XI. You have been asked to write a debate on the motion: ‘Extracurricular Activities Should Be Accorded Equal Importance as Academics’. Write a speech for the motion. (150 – 200 words)
35. Write a debate for the motion: ‘Politeness and Courtesy are Outdated in Today’s World’. You are Gautam/ Gargi of St Mary’s School.
3. While science is a good slave, it can be a bad master. Write a short speech to be delivered in the morning assembly of your school, advising students not to let gadgets and gizmos drive them, but to employ these to their advantage.
4. Write a speech against capital punishment.
5. You are Preeti/Pawan, Head Girl/Boy of your school. Write a speech to be delivered at the career counselling session for students of classes IX-XII of your school advising students on the benefits of thinking seriously about their goals and aptitudes before choosing a stream of study.

As a volunteer of the National AIDS Foundation, deliver a speech for the students of classes IX-XII on the causes, spread, and prevention of this disease. You are Uday Man Singh.
7. In the latter part of the 20th century, “Team Building’ became recognised by many companies as an important factor in providing a quality service and remaining competitive. What are the qualities required to be a good team member? Write a speech to be delivered to the students of classes IX-XII about the importance of team – building and how to be a team – member.
8. In a meeting of the World Water Forum at Kyoto, the 24,000 delegates from 182 countries focused on the escalating global water crisis. Global water consumption has increased tenfold in the last century, largely due to growing population, industrial development, and expansion of irrigated farming. The speakers said that water or Blue Gold will be the next object of conquest by the year 2020. You are Anamika/Anuj Sinha, Head Girl/Boy of Loyola School, Patna. Deliver a speech in the school assembly on the need to conserve water.

The Eight Parts of Speech in English (PDF)
In this article, we will provide a clear overview of the eight parts of speech in English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
What are the eight parts of speech?
Think of parts of speech as roles within a sentence. Just as people can have different job titles-such as soldier, teacher, or baker-words can serve different purposes depending on their function.
- Noun – dog, city, love
- Pronoun – I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Verb – run, be, have, do, take
- Adjective – blue, happy, tall, friendly
- Adverb – quickly, well, very, here
- Preposition – in, on, at, with, by
- Conjunction – and, but, or, yet, so
- Interjection – oh, wow, ouch, hurray
Down below, you will find downloadable worksheets, grammar poster PDFs with examples of each part of speech, and more. You can use them in your classroom activities.
Parts of Speech Grammar Table
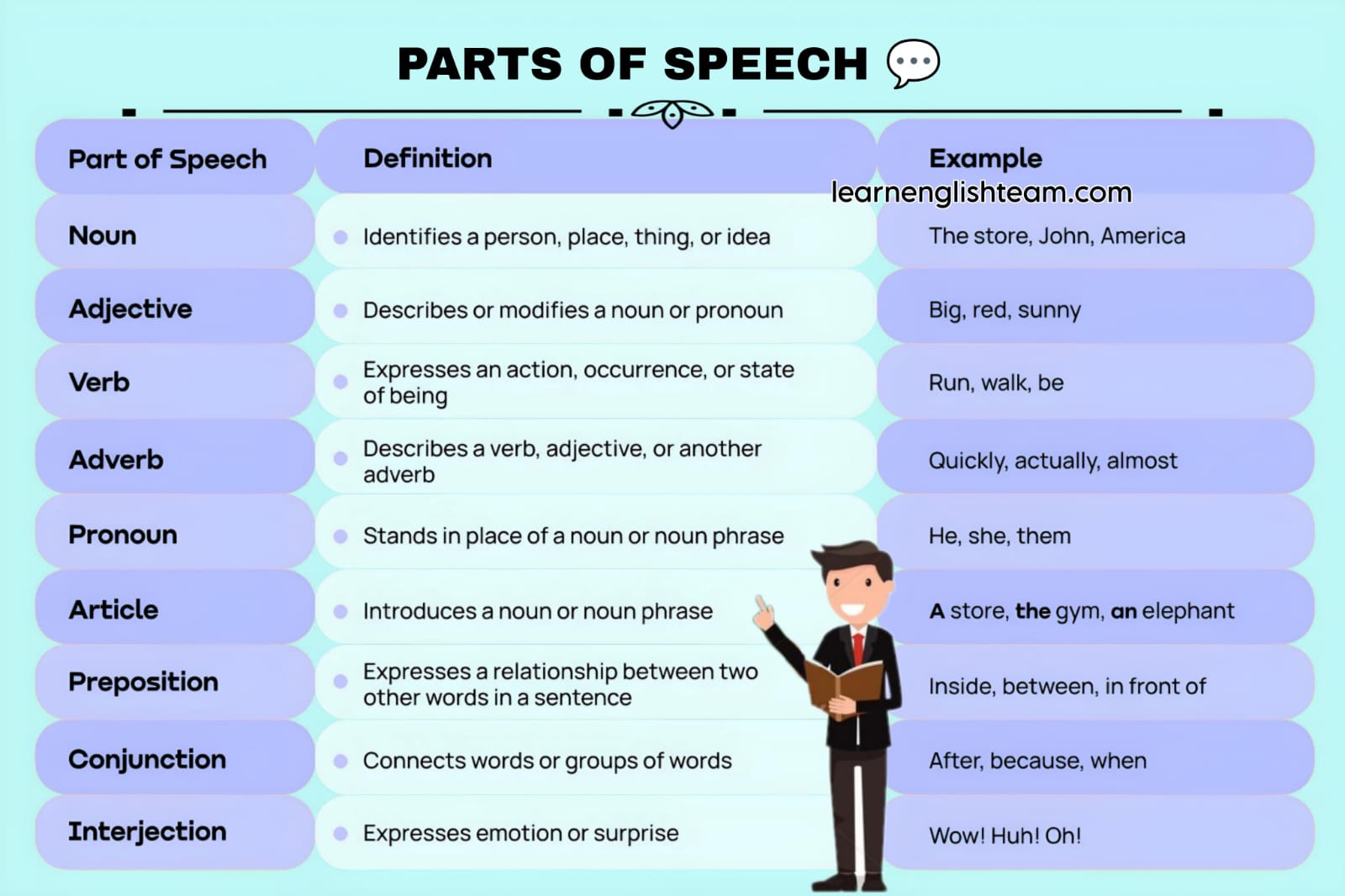
Parts of Speech PDF
Here you can download parts of speech poster, worksheet PDFs with examples.
- Parts of Speech in English PDF - download
- Simple Parts of Speech Worksheet - download
- Parts of Speech Grammar Poster - download
The 8 Parts of Speech

Nouns are separated into common nouns and proper nouns .
What is a common noun?
Common nouns are used for people, animals, places, or things.
Example: granny, mother, river, mountain, hotel, taxi, fox, camel.
He is an artist . Tom hates bananas . I love my mother . Her father is a doctor .
What is a proper noun?
Proper nouns are names for particular people, places or things. They always begin with a capital letter.
Example: Ali Baba, Harry Potter, Beethoven, Turkish, British, Malay, Hong Kong, India, The United Kingdom,the Pacific Ocean, the Eiffel Tower, Father’s Day, Ramadan, Halloween.
☛ The days of the week and months of the year are also proper nouns.
December is the last month of the year. Sunday is the last day of the week.
What is singular and plural noun?
When you are talking about one person, animal, place, or thing, use a singular noun .
Example: a ship, a teacher, a river, an apple, an umbrella.
When you are talking about two or more people, animals, places, or things, use plural nouns . Most nouns are made plural by adding -s at the end.
Example: ships, teachers, rivers, apples, umbrellas
Some exceptions: bus-buses. glass-glasses. watch-watches. brush-brushes. butterfly-butterflies. baby-babies. lady-ladies. story-stories.
☛ Nouns show possession by adding ‘s.
☛ Tom’s car. ☛ Car’s key.
What is concrete and abstract noun?
Concrete nouns are things you can experience (see, hear, smell, touch, or taste) with your senses. Here are some examples: tree, music, flowers, and chocolate.
Abstract nouns represent ideas, qualities, or states that cannot be perceived through the senses. Examples include love, honesty, joy, and freedom.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of nouns in English:
Check Also: Common and Proper Nouns Explained (Exercise and Examples) Masculine and Feminine Nouns in English 100 Most Common English Nouns A-Z List (PDF)

Personal Pronouns: The words I , you , he , she , it , we and they are called personal pronouns. He is a nice guy. You are welcome.
Possessive Pronouns: The words mine , yours , hers , his , its , theirs , ours , yours , theirs are called possessive pronouns. This car is mine . Time is yours .
Reflexive Pronouns: The words myself , yourself , himself , herself , itself , ourselves , yourselves and themselves are called reflexive pronouns. Maryam has hurt herself . Don’t cut yourself .
Demonstrative Pronouns: The words this , these , that and those are called demonstrative pronouns. This is my car. These are my flowers.
Interrogative Pronouns: The words who , whom , whose , what and which are called interrogative pronouns. We ask questions by using these pronouns. Who is she talking to? Which do you prefer?
Here’s a table with examples of different types of pronouns in English:
Check Also: Personal & Possessive Pronouns for English Learners Nobody, No one, None Difference & Examples Difference Between Who and Whom

Most verbs are action words. Verbs shows you what people, animals or things are doing.
Verbs can show actions or they can show states or situations.Those are the two types of verbs in English.
☛ I am eating. – verb (eat) shows an action. ☛ I am a student. verb (to be) shows a state.
☛ Verbs also change and take different forms to show tenses.
I drink a lot of water ☛ I drank a lot of water yesterday.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of verbs in English:
Check Also: 500+ English Verbs List (V1 V2 V3 Verb Forms) + PDF Most Common English Verbs & Synonyms List (PDF) All forms of the verb TO BE and Its Usage
4. ADJECTIVE

The red carpet. Deep thoughts. A busy street. She is beautiful today.
Here’s a table with examples of different types of adjectives in English:
Check Also: List of Opposite Adjectives in English (PDF) Positive Adjectives to Describe a Person (PDF) Comparative and Superlative Adjectives List + PDF

☛ A lot of adverbs end in -ly.
We are happily married. Tom calls me regularly . Suddenly , she knows. It’s love!
Here’s a table with examples of different types of adverbs in English:

Check Also: Types of Adverbs in English & Meaning and Examples (PDF) Common Suffixes in English (With Examples) & PDF
6. PREPOSITION

Prepositions tell us about time, position or place.
Some examples of prepositions are words like ‘ in ,’ ‘ at ,’ ‘ on ,’ ‘ of ,’ ‘ to ,’ ‘ from .’
She is in love. Book was on the table. I am from France. He is calling to you. Where are you at ?
Here’s a table categorizing types of prepositions with examples:
Check Also: Complete List of English Prepositions A-Z (Free PDF) Commonly Used Prepositions Lists in English Common Collocations in English With Prepositions (PDF) Prepositions of Location At, In & On (PDF)
7. CONJUNCTION

Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, and clauses together.
a teacher and students. a male or female?
☛ Words such as before , after , as , when , while , until , since , are conjunctions of time. Maryam could play guitar before she was four. She always brush her teeth after eating her meal.
There are four categories of conjunctions:
8.INTERJECTION
An interjection is a word that expresses an emotion, sudden, strong feeling such as surprise, pain, or pleasure.
☛ It is often followed by an exclamation point.
Check Also: Interjections in English Grammar & List Examples 1000+ Common Daily English Phrases for Beginners (PDF)

You May Also Like

How to Revise Multiple Science Essay Topics Within a Short Duration
There Is & There Are: Exercise and Test (Beginner)✅

CKA Exam Overview: Structure, Syllabus, and Certification Benefits
Parts of Speech – A Guide to Types and Real-World Examples That Inspire
Updated: 15 Oct 2024
Every word you use in English has a particular job, which we call a part of speech ! Imagine it like a team where each player has a unique role to play. Some words help us name things, some show action, and others describe how things are. Understanding parts of speech is like unlocking a secret code that makes sentences come alive and sparkle!
In this article, we’re going on a fun journey to explore what parts of speech are, the different types, and some superb examples that will help you become a superstar at expressing yourself. You’ll be amazed at how powerful words can be!
Table of Content
Definition:, types of noun, types of pronoun, types of verb, how do adjectives work, examples of adjectives, types of adjectives, examples of adverbs, types of adverbs, types of preposition:, types of conjunctions, types of interjections:, types of determiners:, types of articles:.
So, let’s jump in and unlock the magic of words together! First, we’ll learn the definition of parts of speech and discover why they’re so important. Get ready for an adventure in language!
What are Parts of Speech?

Parts of speech are one of the first exciting grammar topics we dive into when we start our journey in school or begin learning the English language. Think of parts of speech as the building blocks of sentences, where each word plays a unique role that brings our ideas to life!
- Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines parts of speech as “any of the classes of words that have similar grammatical properties; especially: a class (such as noun, verb, or adjective) that has a specific function in a sentence.”
- Collins English Dictionary defines parts of speech as “any of the categories into which words are classified according to their functions in a sentence, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.”
- Macmillan Dictionary defines parts of speech as “the different types of words in a language that have similar grammatical functions, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.”
So, based on these definitions, we can understand that parts of speech are categories of words that help us see how sentences are formed. They include names (nouns), action words (verbs), describing words (adjectives), and more. By learning about parts of speech, we gain the tools to express ourselves clearly and creatively!
Now, let’s move on to the different types of parts of speech and see some examples. This will help us understand how these words work together in sentences. Let’s explore!
Parts of Speech Types and Their Impactful Examples
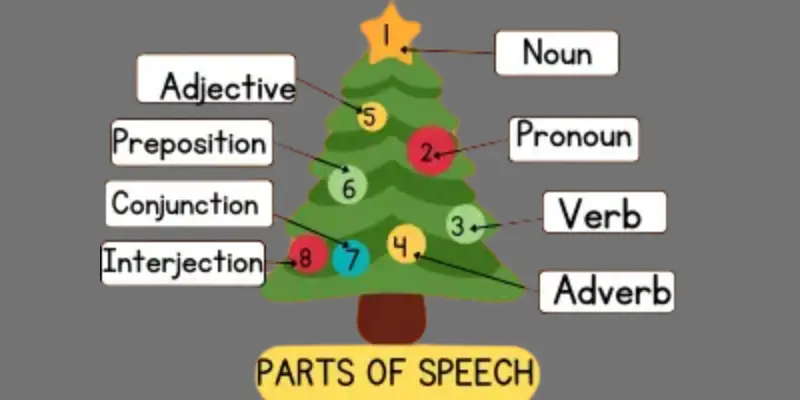
In English, eight parts of speech help us build sentences and express our ideas clearly. Here they are:
- Noun: Names a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Pronoun: Replaces a noun.
- Verb: Shows action or a state of being.
- Adjective: Describes a noun.
- Adverb: Describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb.
- Preposition: Shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words.
- Conjunction: Connects words, phrases, or clauses.
- Interjection: Expresses strong emotion or surprise.
Now, let’s discuss each type in detail, one by one!
A Noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are essential in our sentences because they help us know what we discuss! Think of nouns as the heroes of our sentences—they can be the subject , which means they do the action.
For example:
- “The dog barks.” The word “dog” is the hero who is barking!
- The cat chased the mouse.
(“The cat” is the subject noun doing the chasing.)
- Sarah loves to paint.
(“Sarah” is the subject noun who loves to paint.)
Nouns can also function as the object of a verb, which refers to the person or thing affected by the action.
For Example:
- Sara gave her brother a gift. (“Her brother” is the object noun receiving the gift.)
- They built a sandcastle at the beach. (“A sandcastle” is the object noun that was built.)
- The dog fetched the ball. (“The ball” is the object noun the dog fetched.)
Common Noun:
- A common noun refers to nonspecific people, places, things, or concepts. It’s like a general name that could apply to many things.
- Example: dog, city, book, happiness
- Sentence: “The dog barked loudly in the park.”
Proper Noun:
- A proper noun refers to specific people, places, things, or concepts. Proper nouns are always capitalized because they name unique entities.
- Example: Eiffel Tower, Sarah, London, January
- Sentence: “We visited the Eiffel Tower last summer.”
Collective Noun:
- A collective noun refers to a group of people or things considered a single unit. It’s like a particular word for a collection!
- Example: team, flock, class, family
- Sentence: “The team celebrated their victory together.”
Abstract Noun:
- An abstract noun is a word that describes ideas, qualities, or feelings that we can’t see or touch. These nouns represent things we can think about but not physically hold.
- Examples: love, freedom, bravery, sadness
- Sentence: “Her bravery inspired everyone around her.”
Another way to classify nouns is by whether they are countable or uncountable.
Countable Nouns:
- Countable nouns are things we can count easily. They have singular and plural forms, meaning you can say “one” or “two” or more!
- Examples: apple, book, car, child
- Sentence: “I have three apples in my bag.” (Here, you can count the apples!)
Uncountable Nouns:
- Uncountable nouns are things we cannot count individually because they are seen as a whole or a mass. These nouns usually don’t have a plural form.
- Examples: water, sugar, information, music
- Sentence: “I need some water after my run.” (Here, you don’t count water in individual units; it’s a mass.)
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun, which makes our sentences easier to read. Think of it like a helper!
For example, instead of saying, “Tom likes ice cream, and Tom eats ice cream,” we can say, “Tom likes ice cream, and he eats it.”
In this case, he is the pronoun that replaces Tom. Pronouns help us avoid repeating the exact words all the time. They can refer to places, people, things, or ideas.
For Example
- “James loves basketball, and he plays every weekend.” Here, “he” replaces James, so we don’t have to repeat his name.
- “Maria is a great artist, and she paints beautiful pictures.” In this sentence, “she” takes the place of Maria.
- “The cat is very playful. It loves to chase its tail.” “It” refers to the cat, helping us avoid repeating the word.
Here are some types of pronouns :
Personal Pronouns:
- These pronouns refer to specific people or things.
- Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Sentence: “I love reading books, and she enjoys them too.”
Possessive Pronouns:
- These show ownership or belonging.
- Examples: mine, yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs
- Sentence: “That book is mine , and this one is yours .”
Reflexive Pronouns:
- These refer back to the sentence’s subject and end in “-self” or “-selves.”
- Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, yourselves, themselves, ourselves
- Sentence: “I made the cake myself. “
Demonstrative Pronouns:
- These point to specific things or people.
- Examples: this, that, these, those
- Sentence: “This is my favorite toy, but that one is cool too.”
Interrogative Pronouns:
- These are used to ask questions.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, what
- Sentence: “ Who is your best friend?”
Relative Pronouns:
- These introduce a clause and relate to a noun mentioned before.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, that
- Sentence: “The book that I read was amazing.”
Indefinite Pronouns:
- These refer to nonspecific people or things.
- Examples: anyone, everyone, someone, nobody, all, some, few
- Sentence: “ Everyone is excited for the party!”
You may also Like these posts
- What is a Personal Pronoun? Everything You Need to Know
- Interjections Explained – Definition, Types, and Uses
- What is an Intensive Pronouns? Learn with Examples & Uses
- What Is an Adjective? Definition, Forms, Types, and Examples
- What is an Adverb? Everything You Need to Know
A verb is an exciting word that tells us what someone or something is doing! It can show an action (like “jump” or “run”), something that happens (like “become” or “change”), or a state of being (like “exist” or “feel”). Verbs are super crucial because every complete sentence needs at least one to make sense!
For example, in the sentence “The dog barks, ” the verb “barks” tells us what the dog is doing.
What’s cool about verbs is that they can change their form based on different things! They can change depending on the subject (like who or what is doing the action), the tense (when the action happens, like past or present), the mood (like asking a question), and the voice (like when the action is done to the subject).
- “She runs fast in the race.” (Action Verb)
- “He will become a great artist.” (Linking Verb)
- “He is playing soccer right now.” (Helping Verb)
- “I know the answer to the question.” (State of Being)
Here are some types of verbs :
Action Verbs:
- These verbs show what someone or something is doing. They can be physical actions or mental actions.
- Examples: run, jump, swim, think, laugh
- Sentence: “She jumps on the trampoline.”
Linking Verbs:
- These verbs connect the subject of a sentence to more information about that subject. They don’t show action but instead describe a state of being.
- Examples: am, is, are, was, were, seem, become
- Sentence: “He is my best friend.”
Helping Verbs (Auxiliary Verbs):
- These verbs help the main verb in a sentence by extending its meaning, often to indicate tense, mood, or voice.
- Examples: have, has, had, will, shall, can, may
- Sentence: “She has finished her homework.”
Transitive Verbs:
- These verbs require an object to receive the action. They transfer action from the subject to the object.
- Examples: give, send, make, eat
- Sentence: “He gave her a gift.”
Intransitive Verbs:
- These verbs do not require an object to complete their meaning. They express action or a state of being without an object.
- Examples: sleep, laugh, arrive, go
- Sentence: “The baby sleeps soundly.”
Regular Verbs:
- These verbs follow a standard pattern when changing tenses, typically adding “-ed” for the past tense.
- Examples: walk (walked), talk (talked), play (played)
- Sentence: “She walked to school yesterday.”
Irregular Verbs:
- These verbs have unique forms and do not follow standard patterns when changing tenses.
- Examples: go (went), eat (ate), have (had)
- Sentence: “He went to the park.”
Phrasal Verbs:
- These are combinations of a verb and one or more particles (prepositions or adverbs) that change the meaning of the original verb.
- Examples: give up, look after, run out
- Sentence: “She gave up trying to solve the puzzle.”
4. Adjective
An adjective is like a magical word that gives life to nouns and pronouns! It describes them by telling us more about them, such as their color, size, shape, or feelings. Think of adjectives as special paintbrushes that help us create a colorful picture in our minds!
Adjectives can appear in two ways:
- Attributive Adjectives: These adjectives come before a noun to describe it.
- Example: “I have a blue bicycle.” (Here, blue tells us what color the bicycle is!)
- Predicative Adjectives: These adjectives come after a linking verb (like “is”) to describe the subject.
- Example: “The sky is clear. ” (In this case, clear tells us what kind of sky it is!)
- The happy puppy wagged its tail.”
- “He is the tallest player on the team.”
- “She runs fast during the race.”
- “The shiny car caught everyone’s attention.”
Descriptive Adjectives:
- These adjectives describe qualities or features of a noun, helping us understand more about it.
- Examples: beautiful, tall, colorful
- Sentence: “She wore a beautiful dress.”
Quantitative Adjectives:
- These adjectives show how much or how much of something there is.
- Examples: some, many, few, three
- Sentence: “I have three apples.”
Demonstrative Adjectives:
- These adjectives point out specific nouns. They include “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those.”
- Sentence: “ This book is my favorite.”
Possessive Adjectives:
- These adjectives show ownership or possession. They include words like “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their.”
- Examples: my, your, his, their
- Sentence: “That is her bicycle.”
Interrogative Adjectives:
- These adjectives are used to ask questions about nouns. They include words like “which,” “what,” and “whose.”
- Examples: which, what, whose
- Sentence: “ Which movie do you want to watch?”
Indefinite Adjectives:
- These adjectives provide a general description of nouns without being specific. They include words like “some,” “any,” “few,” and “many.”
- Examples: some, any, several
- Sentence: “There are few cookies left.”
Comparative Adjectives:
- These adjectives compare two nouns, often ending in “-er” or using “more.”
- Examples: taller, faster, smarter
- Sentence: “My dog is taller than yours.”
Superlative Adjectives:
- These adjectives compare three or more nouns, often ending in “-est” or using “most.”
- Examples: tallest, fastest, smartest
- Sentence: Sara is the smartest student in the class.”
An adverb is a particular word that gives us more information about a verb, an adjective, or even another adverb! It tells us how, when, where, or to what extent something occurs.
For example, if you say someone runs fast, the word “ fast ” is an adverb because it describes how the person runs. Sometimes, adverbs are made by adding “ -ly ” to an adjective, like turning “ quick ” into “quickly. ” But remember, not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words that end in “ -ly ” are adverbs.
- She sings beautifully .
- He will come tomorrow .
- The cat is hiding inside .
Here are some types of adverbs with examples:

Adverbs of Manner:
- Describe how an action is done.
- Example: She dances gracefully.
Adverbs of Time:
- Tell us when something happens.
- Example: We will leave soon.
Adverbs of Place:
- Show where an action happens.
- Example: The dog ran outside.
Adverbs of Degree:
- Indicate the intensity or degree of an action, adjective, or adverb.
- Example: He is highly talented.
Adverbs of Frequency:
- Tell us how often something happens.
- Example: I always brush my teeth.
6. Preposition
A preposition is a word or phrase that helps us understand how different parts of a sentence relate to each other. Think of prepositions as little connectors that show us where something is, when something happens, or which direction it goes!
For example, in the sentence “The cat is on the table,” the word “on” is a preposition because it tells us where the cat is.
- The dog is under the bed.
- He fell asleep during the movie.
- The bird flew into the house.
Prepositions of Place:
- These prepositions tell us where something is located.
- The book is on the table.
- The cat is under the chair.
- She is sitting beside her friend.
Prepositions of Time:
- These prepositions indicate when something happens.
- We will meet at noon.
- The movie starts before dinner.
- She was born during the summer.
Prepositions of Direction:
- These prepositions show where something is going or the direction of an action.
- He walked to the park.
- The bird flew over the house.
- They ran into the store.
Prepositions of Manner:
- These prepositions describe how something is done.
- She spoke with confidence.
- He painted the picture in a hurry.
Compound Prepositions:
- These phrases comprise two or more words that act as a single preposition.
- The cat jumped on top of the fence.
- She is going in front of the class to present.
7. Conjunctions
A conjunction is a unique word that connects different parts of a sentence. Consider conjunctions the glue that holds words, phrases, or whole sentences together! They help our ideas flow smoothly and make our sentences more interesting.
For example, in the sentence “I want to play soccer, but it’s raining,” the word “but” is a conjunction because it connects two ideas.
- I wanted to eat pizza, but my sister chose sushi.
- Either we can watch a movie, or we can play a game.
Coordinating Conjunctions:
- Connect words, phrases, or independent clauses with a similar or equal structure.
- Examples: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (often remembered by the acronym FANBOYS).
Subordinating Conjunctions:
- Connect an independent clause with a dependent clause to highlight their relationship.
- Examples: because, although, since, unless, if, while, when.
Correlative Conjunctions:
- Work in pairs to connect balanced words or phrases.
- Examples: either…or, neither…nor, both…and, whether…or, not only…but also.
Conjunctive Adverbs:
- These act as conjunctions to connect independent clauses and often provide a transition or show the relationship between ideas.
- Examples: however, therefore, moreover, consequently, thus.
8. Interjections
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a strong emotion, feeling, or reaction. It is often used to convey excitement, surprise, happiness, anger, or other emotions. Interjections are unique in that they do not grammatically connect to the other parts of the sentence and can often stand alone without affecting the overall meaning.
- Surprise: “Wow! That’s incredible!”
- Happiness: “Yay! We won the game!”
- Disappointment: “Oh no! I lost my keys!”
- Greetings: “Hello! How are you today?”
- Command: “Stop! That’s dangerous!”
Emotion-based Interjections:
- These interjections express strong emotions and are often followed by an exclamation mark.
- Examples:
- “Wow!” (surprise)
- “Yay!” (joy)
- “Oh!” (realization or understanding)
Greeting Interjections:
- Used to greet someone, these exclamations can stand alone or be part of a more significant sentence.
- “Hello!” (greeting)
- “Hey!” (informal greeting)
- “Hi!” (friendly greeting)
Command Interjections:
- These interjections express commands or requests, usually followed by an exclamation mark.
- “Stop!” (command)
- “Wait!” (request for pausing)
- “Listen!” (call for attention)
Pain or Discomfort Interjections:
- These interjections convey reactions to physical sensations, often related to pain or discomfort.
- “Ouch!” (pain)
- “Yikes!” (fear or concern)
- “Phew!” (relief)
Surprise or Shock Interjections:
- Used to express shock, disbelief, or unexpected occurrences.
- “Oh my!” (astonishment)
- “Goodness!” (surprise)
- “Gosh!” (mild surprise)
Filler Interjections:
- These interjections fill pauses in conversation and do not express strong emotion but can indicate thought or hesitation.
- “Um” (hesitation)
- “Well” (transition)
- “You know” (informal filler)
Other Parts of Speech
While we often learn about the eight main parts of speech, language is rich and varied, and some words fit into categories beyond the traditional eight. Two important categories are determiners and articles.
Determiners
A determiner is a word that helps describe a noun by showing quantity, possession, or position. Think of determiners as guides that give us more information about nouns.
Demonstrative Determiners:
- “ This book is my favorite.”
- “ That tree is taller than the others.”
Possessive Determiners:
- “ My dog loves to play fetch.”
- “ Her dress is beautiful.”
Quantifiers:
- “I have some friends coming over.”
- “ Many students participated in the competition.”
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether the noun is specific or general. Articles help us understand if we’re talking about something unique or just an example of something.
Definite Article (the):
- “ The cat sat on the mat.”
- “I visited the Eiffel Tower last summer.”
Indefinite Articles (a and an):
- “I saw a bird in the garden.”
- “Sadia wants to be an artist when she grows up.”
Understanding the parts of speech is essential for everyone who wants to communicate better. They are like building blocks that help us express our thoughts and feelings. Nouns are the names of people, places, or things, while verbs show action. Adjectives describe nouns, making our sentences colorful, and adverbs tell us more about verbs.
Learning to use these parts of speech allows us to tell stories, share our ideas, and connect with others more easily. Each word we choose helps us express ourselves and make our conversations enjoyable.
So, keep practicing and using the parts of speech in your writing and speaking. They are tools that will help you share your thoughts clearly and creatively. Remember, your words have power; learning about them can make you a better communicator!
What are the 8 parts of speech?
The eight parts of speech—noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection—each play a unique and essential role in our sentences.
What is the definition of parts of speech?
A part of speech is a class of words that includes adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, interjections, nouns, prepositions, pronouns, and verbs. These words are grouped based on the types of ideas they express and how they function in a sentence.
How do we identify parts of speech?
Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs frequently have distinct word endings known as suffixes. Examining these suffixes allows you to easily differentiate the words from other parts of speech and understand their roles within a sentence. This simple approach clarifies the word’s meaning and enhances your overall comprehension of the sentence structure.
Why are parts of speech important?
Parts of speech are essential because they help us understand how words work together in sentences. This knowledge improves our writing and speaking skills, making communication more transparent and effective.
How do parts of speech work in a sentence?
Each part of speech has a specific role. For instance, nouns name things, verbs show action, adjectives describe nouns, and adverbs modify verbs. Understanding their roles helps us create meaningful sentences.
Please Write Your Comments
Englishal.com.
Congratulations!
You have subscribed for englishal.com Newsletter
You have subscribed for our SEO Tips & Tricks
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
Parts of Speech: Definitions, Examples & 8 Types
Every word is a part of speech playing a specific role in sentences or paragraphs. Parts of speech provide an organized way to align words and phrases, it is a fundamental meaning for a language to become more understandable and serve a specific purpose. Here, in this article, we will see what is Part of Speech, its types, and its uses. So let us dive in deeper to learn more about it!

Table of Content
What is Part of Speech?
Parts of speech chart.
- Different Types of Parts of Speech :
- Parts of Speech Examples Using Sentences
- Quiz to practice Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech – FAQs
The English language has thousands of words and every word has some function to perform. Some words are there to show action, some to join, and some to name something. There are 8 different parts of speech including nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunction, and interjection. And together, all the functions performed by words in the English language fall under Parts of speech.
Parts of Speech Definition
The parts of speech are the “traditional grammatical categories to which words are assigned in accordance with their syntactic functions, such as noun, verb, adjective, adverb, and so on.” In other words, they refer to the different roles that words can play in a sentence and how they relate to one another based on grammar and syntax.
All Parts of Speech with Examples
There are 8 different types of parts of speech i.e., Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverb, prepositions, Conjunction, and Interjection.
Noun –
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, state, or quality. It can be singular or plural. Nouns are a part of speech.
- Function: Refers to Things or person
- Examples: Pen, Chair, Ram, Honesty
- Sentences: Cars are expensive, This chair is made of wood, and Ram is a topper, Honesty is the best policy.
Pronoun –
The word used in place of a noun or a noun phrase is known as a pronoun. A pronoun is used in place of a noun to avoid the repetition of the noun.
- Function: Replaces a noun
- Examples: I, you, he, she, it, they
- Sentences: They are expensive, It is of wood, He is a topper, It is the best policy
Adjective –
A word that modifies a noun or a pronoun is an adjective. Generally, an adjective’s function is to further define and quantify a noun or pronoun.
- Function: Describes a noun
- Examples: Super, Red, Our, Big, Great, class
- Sentences: Supercars are expensive, The red chair is for kids, Ram is a class topper, and Great things take time.
Verb –
A word or a group of words that describes an action, a state, or an event is called a verb. A verb is a word that says what happens to somebody or what somebody or something does.
- Function: Describes action or state
- Sentences: I play football, I will be a doctor, I like to work, I love writing poems.
Adverb –
A verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence is typically modified by an adverb . Adverbs often answer questions like “how,” “in what way,” “when,” “where,” and “to what extent” by expressing things like method, place, time, frequency, degree, level of certainty, etc
- Function: Describes a verb, adjective, or adverb
- Examples: Silently, too, very
- Sentences: I love reading silently, It is too tough to handle, He can speak very fast.
Preposition –
A preposition is called a connector or linking word which has a very close relationship with the noun, pronoun or adjective that follows it . Prepositions show position in space, movement, direction, etc.
- Function: Links a noun to another word
- Examples: at, in, of, after, under,
- Sentences: The ball is under the table, I am at a restaurant, she is in trouble, I am going after her, It is so nice of him
Conjunction –
A conjunction is a word that connects clauses, sentences, or other words. Conjunctions can be used alone or in groups of two.
- Function: Joins clauses and sentences
- Examples: and, but, though, after
- Sentences: First, I will go to college and then I may go to Fest, I don’t have a car but I know how to drive, She failed the exam though she worked hard, He will come after he finishes his match.
Interjection –
An interjection is a word or phrase expressing some sudden feelings of sadness or emotions.
- Function: Shows exclamation
- Examples: oh! wow!, alas! Hurray!
- Sentences: Oh! I got fail again, Wow! I got the job, Alas! She is no more, Hurray! We are going to a party.
These are the main parts of speech, but there are additional subcategories and variations within each. Understanding the different parts of speech can help construct grammatically correct sentences and express ideas clearly.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Examples: Luggage, Cattle.
- Sentence: Never leave your luggage unattended.
- In some places, cattle are fed barely.
- Examples: who, either, themselves
- Sentence: I know a man who plays the guitar very well.
- Either of the two cars is for sale.
- They enjoyed themselves at the party.
- Examples: kind, moving, wounder.
- Sentence:
- She is a kind person.
- Boarding a moving bus can be dangerous.
- Never poke a wounded animal.
- Examples: Praise, Hate, Punish
- Sentence: She always praises her friends.
- I don’t hate anybody.
- The boy has been punished by his teacher
- Examples: Always, enough, immediately
- Sentence: we should always help each other.
- We should be wise enough to understand what is good for us.
- We should leave bad habits immediately.
Preposition
- Examples: Off, Below, From. to
- He plunged off the cliff
- I live below the 9th floor.
- I travel daily from Delhi to Noida.
Conjunction
- Examples: whereas, as well as, so,
- Sentence: The new software is fairly simple whereas the old one was a bit complicated.
- The finance company is not performing well as well as some of its competitors.
- He was ready so he may come.
Interjection
- Examples: oops! whoa! phew!
- Sentence: Oops! I forgot to mention her name.
- Whoa! you drive fast.
- Phew! That was a close call, we had a narrow escape.
Parts of Speech Exercise – Test your Knowledge of Part of speech
Choose the correct Parts of Speech of the BOLD word from the following questions.
1. Let us play, Shall We?
a. Conjunction b. Pronoun c. Verb
2. I t is a good practice to arrange books on shelves.
a. Verb b. Noun c. Adjective
3. Whose books are these?
a. Pronoun b. Preposition c. verb
4. Father, please get me that toy.
a. Pronoun b. Adverb c. Adjective
5. His mentality is rather obnoxious.
a. Adverb b. Adjective c. Noun
6. He is the guy whose money got stolen.
a. Pronoun b. Conjunction c. Adjective
7. I will have finished my semester by the end of this year.
a. Interjection b. Conjunction c. Preposition
8. Bingo! That’s the one I have been looking for
a. Interjection b. Conjunctio c. Preposition
Quiz Answers:
1. c, 2. b, 3. a, 4. c, 5. a, 6. b, 7. c, 8. a
Also Check:
- English Grammar
- Figures of Speech
- Learn English Grammar Online
- Difference Between Adjective and Verb
Q1. What are Parts of Speech?
A word is assigned to a category as per its function, and those categories are together known as Parts of Speech.
Q2. What are the 8 Parts of Speech?
Noun, Pronoun, Adjective, Verb, Adverb, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection.
Q3. How many Parts of Speech are there?
There are a total of 8 parts of Speech.
Q4. What Part of Speech is “our”?
“Our” is a adjective type of Part of Speech. Eg. Our car.
Q5. What Part of Speech is “Quickly”?
Adverb. let us understand it with this example – Milk sours quickly in warm weather.
Similar Reads
- English Grammar : Learn Rules of Grammar and Basics Whether you're just starting on your journey to learn the English language or you've been studying for some time and find yourself struggling with English grammar, with a little bit of perseverance, anyone can learn to speak and write English with confidence and accuracy. English grammar is a set of 9 min read
- Parts of Speech: Definitions, Examples & 8 Types Every word is a part of speech playing a specific role in sentences or paragraphs. Parts of speech provide an organized way to align words and phrases, it is a fundamental meaning for a language to become more understandable and serve a specific purpose. Here, in this article, we will see what is Pa 8 min read
- What is a Noun? Types, Definitions and Examples (List) In simple terms, a noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are one of the basic building blocks of language, and they help us identify and refer to the people, objects, and concepts in our everyday communication. Examples of nouns include "dog" (a thing), "teacher" (a person 15 min read
- Proper Noun - Definition, Examples, & Rules There are two primary categories of nouns: common and proper. Proper nouns are name words that are used to designate or categorize a particular person, place, or thing, whereas common nouns are generic. Make sure that the first letter of a proper noun is always capitalized. Read through the followin 6 min read
- Common Noun - Definition, Examples, List & Usage What is a common noun? and what is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns? You must have this question in your mind. In this article, we will explore more about common nouns and get to know about the differences between a common and proper noun. Table of Content What is a Common Noun?C 6 min read
- Plural Noun - Rules and Examples In English, there are different rules for forming plurals and some exceptions to the authorities. Therefore, it is essential to understand the rules and exceptions of plural nouns to use them correctly in written and spoken English. In this article, we will discuss its rules with examples in brief a 9 min read
- Possessive Noun - Meaning, Usage, Rules and Examples A possessive noun is an important part of the English language and writing. They play an important role to indicate ownership or possession. You can express relationships with people, things, and ideas. In this article, we will learn about the concepts of Possessive Noun, their meaning, usage, rules 7 min read
- What is Collective Noun? List of Examples, Uses and Exercises A collective noun refers to a group or collection of people, animals, or things. It represents a singular entity made up of multiple individuals. Examples of Collective nouns include Team (A team of players), Herd (A herd of cattle), School (A school of fish) etc. In this article, We have discussed 10 min read
- Abstract Nouns - Definition, Examples, List, Usage An abstract noun is a kind of noun that represents ideas, things, and experiences. It is an important part of Nouns. It is an important topic for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. One or more questions from this topic are asked in every competitive ex 4 min read
- What is a Compound Noun? Definition, Types & Examples Compound nouns are used to identify a class of people, places, things or a particular name. It is an important topic for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. One or more questions from this topic are asked in every competitive examination. This article 7 min read
- What are Countable Noun? Countable Noun includes all those things, we can count, whether it is in singular or plural form. A countable noun is used in the form of a singular or plural in a sentence. Because if we can count something then it can be either one or more than one. Do you want to know more about Countable Noun? G 11 min read
- What are Uncountable Noun - How to use them? According to English's grammar, we cannot divide them into separate elements, so for this reason, they are called uncountable nouns. The uncountable noun is another type of noun in traditional English Grammar. Uncountable nouns are such as oil, milk, sugar, salt, patience, juice, bravery, etc. Mater 7 min read
- Material Noun: Definition, Examples, Rules & Exercises Material NounThe noun is used mainly in five ways in English Grammar, in which all differences have their separate existence. Material Noun is one of those which addresses such a Noun that can only be measured or weighed but cannot be counted at all. A Material Noun is a special name given to things 7 min read
- Pronoun Definition - Rules and Types of Pronouns A strong command of Grammar is essential for Candidates for Competitive exams. So, concentrating on pronouns can also be quite beneficial as pronouns are one of the strongest and most important parts of speech. We will talk about the different types of Pronouns and their usage & rules in this ar 9 min read
- Reflexive Pronoun The term 'reflexive' refers to something aimed against oneself. The reflexive pronoun would be a form of pronoun that is accompanied by the predecessor, which must be positioned within a single phrase. A reflexive pronoun in English grammatical signifies that the individual doing the verb's behavior 5 min read
- Subject Pronouns - Definition, Example and Exercise Subject pronoun is an essential topic of parts of speech. In recent years, a number of tricky questions are asked in various competitive examinations on this topic. So it is very useful to learn this topic correctly. To know more about the subject Pronouns you must read through the article. What is 4 min read
- Relative Pronouns - Definition, Uses and Examples A Relative pronoun is a type of pronoun that introduces a subordinate clause and relates it to the main clause. A clause beginning with a relative pronoun is poised to answer questions such as Which one? How many? or What kind? Who, whom, what, which, etc. In this article, we will explore the concep 8 min read
- Demonstrative Pronouns - Definition and Examples The demonstrative pronoun is another main type or one kind of pronoun. which one uses noun place. demonstrative pronoun used to indicate particular things or persons or directions. Pronouns mainly work to stop the repetition of nouns, which makes sentences beautiful and meaningful. From this Pronoun 7 min read
- Possessive Pronouns - Definition, Usage and Examples Possessive Pronouns are used to indicate the possession or ownership or relation of a person/thing to another person/thing i.e. Possessive Pronouns are used to describe people, animals, or things that a person or be related to something. A possessive pronoun is another kind or type of pronoun. When 6 min read
- Indefinite Pronoun Any indeterminate pronoun is a term that lacks a particular familiar recipient. Indefinite pronouns vary from definite pronouns. Indefinite pronouns have the ability to indicate either count as well as non-count nouns. They frequently have associated forms across all these categories. An indefinite 6 min read
- Personal Pronoun - Definition, Rules and Examples Personal pronouns are short words that are used in place of a person's own name. Each English personal pronoun shows the person, gender, number, and case of the noun it replaces. I, you, he, she, it, we, they, me, him, her, us, and them are all personal pronouns. What are Personal Pronouns? Those Pr 8 min read
- Interrogative Pronoun The Pronoun is just a term that substitutes a noun. Many English phrases contain pronouns, which include inquiries. An interrogative pronoun is a form of pronoun that is continually asking for replies. When posing a question, an interrogative pronoun serves to replace a person and an object. What Is 5 min read
- Reciprocal Pronouns - Definition, Examples & Uses The pronoun, and particularly the reciprocal pronoun, will be the center of our attention. Let's start with an explanation of a pronoun. In a language, a pronoun is a term that replaces a noun, or another pronoun. A reciprocal pronoun is one that links two previously defined nouns that are both gett 6 min read
- What is a Verb? Types, Uses, Examples A verb is an important part of the English language and is classified under the Parts of Speech chapter. It is very important for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive exams. More than two questions are asked about this topic in every competitive examination. A verb is 13 min read
- Verb Forms Verbs are one of the most essential parts of speech in any language, as they express actions, states, or occurrences. Understanding the different forms of verbs is key to mastering grammar and effective communication. Verb forms can vary depending on tense, voice, and mood, and knowing how to use th 8 min read
- Main Verbs - Meaning, Types and Examples A verb is a part of speech used to show an action. There are several other sorts of verbs. The main verbs, on the contrary side, are the ones that explicitly describe an activity which the particular topic is conducting. These are the primary verbs in a phrase that carry the main meaning. Main Verbs 6 min read
- Helping Verb: Definition, Types and Examples In English grammar, a Helping verb is a verb that comes before a main verb or lexical verb in a sentence. An auxiliary/helping verb and a main verb together form a verb phrase. Helping verbs & auxiliary verbs are mostly equal. we often get confused about how to use main verbs and helping verbs i 7 min read
- Auxiliary Verbs: Definition, Examples & List Auxiliary verbs are needed to make our sentences more exciting and impressive. Auxiliary verbs are the first step in forming a complete sentence. When used with the main verb, auxiliary verbs finish sentences. Using auxiliary verbs is about expressing your feelings, making a statement, asking a ques 10 min read
- Irregular Verbs Irregular verbs are an important type of verb in the English language. It does not follow normal rules of grammar. It is an important topic for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. In this article, we will delve into the world of irregular verbs, and exp 9 min read
- What Are Modal Verbs? – Definition, Usage & Examples Any competitive government exam, including those for CGL, banking, and the armed services, assesses a candidate's command of the English language. There is a focus on testing the use of grammar in the English language section. As a result, understanding grammar rules becomes essential. One should be 8 min read
- What is A Gerund? Definition and Examples Understanding the difference between a gerund and other parts of speech is an important step in perfecting your grammar and writing skills. A gerund is a verb form used in the third person, meaning it's used as a noun. The form of the gerund is not that important, because this blog post is about how 8 min read
- Adjective - Definition, List, Types, Uses and Examples When we discuss Adjectives, it means those words which well describe a Noun or a Place, Person, Thing, or Idea. An adjective is the only word that can create a major difference between the two.Let's discuss this topic in detail and also bookmark it to get back to the article whenever we want to revi 10 min read
- Proper Adjectives Definition and Examples An appropriate adjective is a subcategory of the wider category of adjectives in particular. Adjectives are one of the eight fundamental parts of speech in English, and it is critical to understand and be able to distinguish which parts of speech make up a full sentence. Some pupils may already be f 6 min read
- Possessive Adjectives - Definition, Example and List How do possessive adjectives contribute to expressing ownership and help to indicate the relationship between people, ideas, and objects? Do you want to know more about Possessive adjectives? This article will help you to explore more about Possessive Adjectives along with their usage, examples, and 5 min read
- Interrogative Adjective - Meaning, Definition and Examples Understanding and learning about interrogative adjectives can greatly enhance your communication skills, helps you to seek information, and engages you in meaningful conversations. Here you will explore the importance of Interrogative along with rules and examples that will provide you valuable insi 5 min read
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, List & Examples In this article, we will learn about "Adverbs". A verb, adjective, another adverb, determiner, clause, preposition, or sentence is typically modified by an adverb. Adverbs often answer questions like "how," "in what way," "when," "where," and "to what extent" by expressing things like method, place, 10 min read
- Conjunctive Adverbs - Meaning, Examples and Exercises Are you having trouble with conjunctive adverbs? Have you ever wanted to express yourself more clearly and effectively, but just didn’t know where to start? In this article, we'll provide a comprehensive overview of the important role that conjunctive adverbs play in writing a great piece of literat 6 min read
- Adverbs of Time - Examples, Meaning, and Definition If you are looking for a guide that explains what is adverbs of time with suitable examples, then here in this blog post we will learn about adverbs of time and how to use them with examples. So without wasting time, let's dig into the article. Adverbs of Time inform us when an activity occurred. It 7 min read
- Adverbs of Frequency - Definition, Examples, and Usage Adverbs of Frequency are defined as words that modify verbs to tell us how often something happens Go through this blog post to get a detailed overview of adverbs of frequency, and how to use them with all suitable examples. What is adverb frequency? this question may arise in your mind when you hea 10 min read
- Adverbs of Place - Definition, List and Examples In the world of English grammar, adverbs of place specify where something happens. Basically, it can be used to describe a place, a direction, or a place in relation to something else. If you're looking for a detailed guide to adverbs of place, in this article we'll look at how adverbs of place work 7 min read
- What are Adverbs of Degree? Definition, List and Examples Adverbs are commonly used in English to explain the adjective, verb, or another adverb inside a paragraph. Among many of the different kinds of adverbs, a degree adverb assists speakers in expressing the concentration of a statement in a paragraph. The Adverb of degree answers the question, "How muc 8 min read
- Adverbs of Manner - Meaning, Definition and Examples Adverbs of manner are a type of parts of speech. It denotes the manner of action done by the Subject. It is an important topic for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. One or more questions from this topic are asked in every competitive examination. Tab 7 min read
- What is a Conjunction - Meaning, Definition, Types & Exercises Conjunctions are essential tools in the English language, used to connect words, phrases, or sentences to create more complex and meaningful statements. Without conjunctions, our sentences would be short and choppy, lacking flow and coherence. In the vast realm of language, there exists a small but 9 min read
- Subordinating Conjunction - Meaning, Definition, Types and Examples It is a very useful topic for joining two sentences in English and also important for all students, especially for those who are preparing for competitive examinations. A few questions on this topic are asked in every competitive examination. Table of Content What is a Subordinating Conjunction? De 6 min read
- Preposition Prepositions are considered one of the essential topics of the English language. They help in coordinating the usage of words and phrases. These are called prepositions because they relate to something before the word they follow. The below article will deal with the rules of prepositions in the Eng 11 min read
- Interjections - Definition, Types, Rules and Examples An interjection is a word or phrase expressing some kind of sudden feelings of sadness or emotions. Interjections are a type of part of speech, but in a sentence, they are not grammatically connected to other parts of a sentence. Interjections are those common words which use in everyday speech and 11 min read
- Definite and Indefinite Articles ( A, An, The) Table of ContentWhat is an Article? Definite and Indefinite ArticlesWhat are Definite Articles?What are Indefinite Articles?Definite and Indefinite Articles ExamplesDifference Between Definite and Indefinite Articles Definite and Indefinite Articles QuestionsFAQ's on Definite and Indefinite Articles 9 min read
- Subject-Verb Agreement Rules: Examples & Exercises Have you ever heard of the term subject-verb agreement? This is your chance to discover what subject-verb agreement is, what is meant by "concord," and the guidelines that will assist you in comprehending how it functions. In this article, we'll understand the rules of subject-verb agreement, exampl 11 min read
- Active and Passive Voice Rules for Competitive Exams Active and Passive voice is a particularly essential grammatical structure used in the English language. Understanding the rules governing their usage is crucial for effective communication. In this article, we will delve into the fundamentals of the active and passive voice. we will also explore th 8 min read
- What is Tense? Types, Definitions & Examples Earlier we have already discussed how important tenses are in English Grammar as the very basis of English Grammar is built on tenses. Once you complete the tenses then you will understand every part and use of tenses. You already know that there are three tenses- past, present, and future; and four 8 min read
- Tense Chart in English - Rules, Examples, Types & Mind map Tense Chart: The Tense Chart is a visual representation of the various verb tenses in English. It organizes the verb tenses in English. It outlines the various forms of the verb according to their uses. By using a tense chart, one can easily understand the relationship between the various forms of v 10 min read
- SSC/Banking
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech: We use thousands of words every day and would you believe if I tell you that every single one of them can be categorized into 8 categories that we call Parts of speech. These 8 parts of speech literally encompass each and every word you use in your English. How amazing is that! In this chapter, we will cover all of the 8 parts of speech with loads of fun example. In essence, everything else in grammar is based on Parts of speech, so we really recommend you to use this as your holy grail and get it absolutely soaked in.
Suggested Videos

Parts of Speech: The eight pillars of english grammar:
Let us start by enlisting the 8 parts of speech first: Noun , pronoun, verb, adverb , adjective , conjunction , preposition and interjection. Now let’s look at each one of these one by one:
Simply put: Nouns are names of people, things, places or ideas. They are simply the names you use to refer to a thing, person, place or idea. Nouns could be proper nouns or common nouns or abstract nouns or collective nouns or possessive nouns or compound nouns.
- Common nouns: Just generic names, starting with a small letter. Examples – bees, yard, cycle, pasta.
- Proper nouns: Specific names, starting with capital letter always. Examples – Geeta, Shashank, Joe’s pasta, Harry Potter, Nancy Drew
- Abstract nouns: Usually names of ideas or emotions. Examples – Happiness, joy, excitement
- Collective nouns: These are nouns that are used to count something in a union or a group. Examples – team, jury, school, clan, class, pride
- Possessive nouns: Sometimes you want to show the possession of something with the noun. That’s when you add an apostrophe s to the noun and it becomes a possessive noun. Examples – Sheela’s, Juno’s pizza
- Compound nouns: As simple as it sounds, when two nouns come together they form a compound noun. Examples – daughter-in-law, tooth-paste, eight-pack
A pronoun is a word used instead of the noun. The meaning stays the same, it’s just instead of repeatedly using the noun, you have something shorter that is the pronoun. To list a few- I, her, she, them, theirs, they, and so on.
A few examples:
- Sheela is a great singer. She is performing at the city centre mall today.
- My parents are in town. They will visit me day after tomorrow.
- Joe’s pizza is a great place to eat at. It’s right around the corner.
All the fun of the sentence is the verb. Verb is the action in a sentence. It could be a physical or mental action or just the state of being in a sentence . Let’s see a quick few examples:
- The Sun rises from the East.
- Children are playing on the playground.
- My cat jumps on me when I’m sleeping.
- She was with the choir group last summer.
Notice how the verbs am, is, are, was, were show the state of being.
An adverb aids the verb in showing how the action was done. Adverbs describe the verbs in the sentence. There are different kinds of Adverbs that we have covered before:
- Adverbs of time: These show the time of the action. They answer the question of when? Example – She walked in today .
- Adverbs of manner: These adverbs show the manner of action. they usually are the common adverb type. They answer the question of how? Example – The turtle walked slowly.
- Adverbs of place: This kind of adverbs show the place of the action, essentially answering the question of where? Example – We looked for mushrooms everywhere in the marshy land.
- Adverbs of degree: This kind shows the degree of the verb , essentially answering the question of how much? Example – This escalated very quickly.
This part of speech adds what we can call color to the sentence. An adjective describes the noun or a pronoun. It could be a quality or shape or size or number. let’s understand this with the help of a few examples:
- My grandfather has a beautiful house in San Francisco.
- She is a clever girl.
- My house is situated in a quaint place in the village.
Preposition:
Prepositions are simply words that connect different elements in a sentence to define a relation between them. Some prepositions are- with, to, from, on, in, beneath, between and so on.
- The cat is sitting on the table.
- Please put a layer of caramel inside my roll.
Conjunction:
Conjunction are words that join two clauses, phrases or words in a single sentence. Let’s see a few examples:
- This meditation technique is very clam and healing.
- I wanted to backpack across Europe, but I have to wait until March end till the weather gets better.
- We are going to Puerto Rico next year because of my brother’s wedding there.
Interjection:
Interjections are usually words that express strong emotions usually followed by an exclamation mark. For example:
- Hurray! We will be seeing the space very soon.
- Ouch! That sting ray really hurt!
- Bravo! Well done!
Now that we hope you have some idea of the different parts of speech, you know what would be great? If you could just pick up a few sentences, sit with your teacher and identify all these parts of speech one by one in a few sample sentences. Learning is always by doing, remember this. Only when you do it for yourself will you truly learn anything. Trust yourself and go for it. You are on your way to becoming a grammar guru. Have fun!
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Transformation of Sentences
- Types of Sentences
- Reported Speech
- Active and Passive voice
37 responses to “Active and Passive voice”
Simple but very nice explanation and helpfull too.
What is the voice change of ” I have endeavoured to understand the fundamental truths.”
ENDEAVOUR HAS BEEN MADE BY ME TO UNDERSTAND THE FUNDAMENTAL TRUTH.
The fundamental truths have been endeavoured to be understood by me
The fundamental truths to understand had been endeavoured by him
The fundamental truths have endeavoured to be understood by me
The fundamental truths has been understood endeavoured to by me
How to change the voice for the following sentence – the books will be received by tomorrow
By whom? We need a subject. If the subject was for example “The library”, then the sentence in active voice would read “The library will receive the books by tomorrow”.
You will receive the books by tomorrow.
Tomorrow you will receive the book
You will receive the books (by) tomorrow.
Someone will receive the books by tomorrow
Tomorrow will be receive the books
HE WILL RECEIVE THE BOOKS BY TOMORROW.
By tomorrow the books will be received.
By tomorrow, you will receive the books
Tomorrow received the book
Change this “take right and turn left” into passive voice
Let the right be taken amd left be turned
‘amd’ is “and” 😅
You are advised to take right and turn left
Very helpful information thanks
Very well explained all basics that can lead to gain further knowledge very easily
What is in this box change into passive
what is the voice change of,” some people think nuclear is the best, because it doesnt add to global warming “….
Brilliant stuff!! – Rishabh
A kite was made by Ravi . What is the active form of this statement???
how to change into passive this sentence “when they were shifting the patient to the I.C.U.,he died
change into passive voice this sentence “when they were shifting the patient to I.C.U.,he died .
May you tell us tense conversion in voice.
Sentences without action like…. Jim is a doctor . Is it active or passive and if any how would you decide without having a main verb ?
It is named after the name of its principal tree ‘sundari'(passive)
how can ocean be object 🙄???
They made a bag
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Understanding the parts of speech is essential for mastering English grammar. Parts of speech are the building blocks of sentences, and each plays a specific role in conveying meaning. This guide covers the fundamental parts of speech, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Exercise 4 – Identify the Part of Speech; Frequently Asked Questions on Parts of Speech Exercises; Parts of Speech Exercises with Answers. Give below are a few exercises. Try them out and assess your understanding of the different parts of speech. Exercise 1 – Identify the Adverb. Go through the given sentences and identify the adverb.
Feb 20, 2023 · Basic English Grammar rules can be tricky. In this article, we’ll get you started with the basics of sentence structure, punctuation, parts of speech, and more. We also providing Extra Questions for Class 11 English Chapter wise.
Parts of Speech in English Definition with Examples The 8 Parts of Speech 1. NOUN. noun is a word (other than a pronoun) used to identify any of a class of people, animals, places, things, ideas. Nouns in English – Types with Examples
Oct 15, 2024 · Every word you use in English has a particular job, which we call a part of speech! Imagine it like a team where each player has a unique role to play. Some words help us name things, some show action, and others describe how things are. Understanding parts of speech is like unlocking a secret code that makes sentences come alive and sparkle!
6 days ago · Approach English is a free educational platform offering in-depth English grammar tutorials, worksheets, and notes for NCERT, CBSE, ICSE, ISC, WBBSE, and HS. From Kindergarten to Class 12, we provide composition practice, quizzes, education updates, and ESL resources to support students and educators globally.
Nov 16, 2023 · A word is assigned to a category as per its function, and those categories are together known as Parts of Speech. Q2. What are the 8 Parts of Speech? Noun, Pronoun, Adjective, Verb, Adverb, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection. Q3. How many Parts of Speech are there? There are a total of 8 parts of Speech. Q4. What Part of Speech is “our”?
English. Linguistics; Parts of Speech--grade 11. 3.5 (2 reviews) Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Get a hint. a sentence. Contains a subject, predicate and is ...
Sep 26, 2019 · Parts of Speech: We use thousands of words every day and would you believe if I tell you that every single one of them can be categorized into 8 categories that we call Parts of speech. These 8 parts of speech literally encompass each and every word you use in your English. How amazing is that! In this chapter, we will cover all of the 8 parts ...
Review 13.1 Parts of Speech and Sentence Structure for your test on Unit 13 – Grammar and Mechanics. For students taking English 11