- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both

Writing objectively How and when to use an impersonal tone
For another look at the same content, check out the video on YouTube (also available on Youku ). There is a worksheet (with answers and teacher's notes) for this video.
Academic writing is generally impersonal and objective in tone. This section considers what objective writing is , how objective academic writing is , then presents several ways to make your writing more objective . There is also an academic article , to show authentic examples of objective language, and a checklist at the end, that you can use to check the objectivity of your own writing.
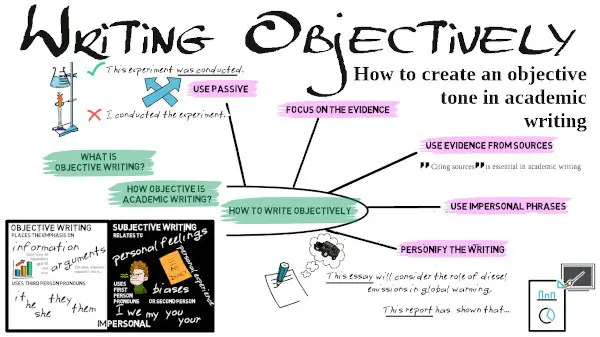
What is objective writing?
Objective writing places the emphasis on facts, information and arguments, and can be contrasted with subjective writing which relates to personal feelings and biases. Objective writing uses third person pronouns (it, he, she, they), in contrast to subjective writing which uses first person pronouns (I, we) or second person pronoun (you).
How objective is academic writing?
Although many academic writers believe that objectivity is an essential feature of academic writing, conventions are changing and how much this is true depends on the subject of study. An objective, impersonal tone remains essential in the natural sciences (chemistry, biology, physics), which deal with quantitative (i.e. numerical) methods and data. In such subjects, the research is written from the perspective of an impartial observer, who has no emotional connection to the research. Use of a more subjective tone is increasingly acceptable in areas such as naturalist research, business, management, literary studies, theology and philosophical writing, which tend to make greater use of qualitative rather than quantitative data. Reflective writing is increasingly used on university courses and is highly subjective in nature.
How to write objectively
There are many aspects of writing which contribute to an objective tone. The following are some of the main ones.
Use passive
Objective tone is most often connected with the use of passive, which removes the actor from the sentence. For example:
- The experiment was conducted.
- I conducted the experiment.
- The length of the string was measured using a ruler.
- I measured the length of the string with a ruler.
Most academic writers agree that passive should not be overused, and it is generally preferrable for writing to use the active instead, though this is not always possible if the tone is to remain impersonal without use of I or other pronouns. There is, however, a special group of verbs in English called ergative verbs , which are used in the active voice without the actor of the sentence. Examples are dissolve, increase, decrease, lower, and start . For example:
- The white powder dissolved in the liquid.
- I dissolved the white powder in the liquid.
- The white powder was dissolved in the liquid.
- The tax rate increased in 2010.
- We increased the tax rate in 2010.
- The tax rate was increased in 2010.
- The building work started six months ago.
- The workers started the building work six months ago.
- The building work was started six months ago.
Focus on the evidence
Another way to use active voice while remaining objective is to focus on the evidence, and make this the subject of the sentence. For example:
- The findings show...
- The data illustrate...
- The graph displays...
- The literature indicates...

Use evidence from sources
Evidence from sources is a common feature of objective academic writing. This generally uses the third person active. For example:
- Newbold (2021) shows that... He further demonstrates the relationship between...
- Greene and Atwood (2013) suggest that...
Use impersonal constructions
Impersonal constructions with It and There are common ways to write objectively. These structures are often used with hedges (to soften the information) and boosters (to strengthen it) . This kind of language allows the writer to show how strongly they feel about the information, without using emotive language, which should be avoided in academic writing.
- It is clear that... (booster)
- It appears that... (hedge)
- I believe that...
- There are three reasons for this.
- I have identified three reasons for this.
- There are several disadvantages of this approach.
- This is a terrible idea.
Personify the writing
Another way to write objectively is to personify the writing (essay, report, etc.) and make this the subject of the sentence.
- This essay considers the role of diesel emissions in global warming.
- I will discuss the role of diesel emissions in global warming.
- This report has shown that...
- I have shown that...
In short, objective writing means focusing on the information and evidence. While it remains a common feature of academic writing, especially in natural sciences, a subjective tone is increasingly acceptable in fields which make use of qualitative data, as well as in reflective writing. Objectivity in writing can be achieved by:
- using passive;
- focusing on the evidence ( The findings show... );
- referring to sources ( Newbold (2021) shows... );
- using impersonal constructions with It and There ;
- using hedges and boosters to show strength of feeling, rather than emotive language;
- personifying the writing ( This report shows... ).
Bailey, S. (2000). Academic Writing. Abingdon: RoutledgeFalmer
Bennett, K. (2009) 'English academic style manuals: A survey', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 8 (2009) 43-54.
Cottrell, S. (2013). The Study Skills Handbook (4th ed.) , Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan.
Hinkel, E. (2004). Teaching Academic ESL Writing: Practical Techniques in Vocabulary and Grammar . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc Publishers.
Hyland, K. (2006) English for Academic Purposes: An advanced resource book . Abingdon: Routledge.
Jordan, R. R. (1997) English for academic purposes: A guide and resource book for teachers . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Example article
Below is an authentic academic article. It has been abbreviated by using the abstract and extracts from the article; however, the language is unchanged from the original. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes) to highlight the different objective features.
Title: Obesity bias and stigma, attitudes and beliefs among entry-level physiotherapy students in the Republic of Ireland: a cross sectional study. Source: : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031940621000353

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for using objectivity in academic writing. Use it to check your writing, or as a peer to help. Note: you do not need to use all the ways given here.
Next section
Read more about writing critically in the next section.
- Critical writing
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about using complex grammar .
- Complex grammar

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 05 February 2024.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.

IMAGES
VIDEO