Support for the Working Memory Model
Shallice and warrington (1974) - study of kf.
The working memory model is supported by evidence from brain damaged patients such as KF.


Research aim & method
- Aim: To investigate a patient KF who had suffered brain damage in a motorcycle accident.
- Method: A case study using numerous psychometric tests, experiments and observations.

- KF’s short term memory problems were much greater for auditory information than visual, suggesting his brain damage was restricted to the phonological loop.

- The case of KF supports both the MSM and the WMM as his LTM was unaffected by his injury, suggesting LTM and STM are different stores.
- His case supports the WMM as his visuospatial sketchpad seems unaffected by his injury, suggesting that resides in a different area of the brain to the phonological loop which was damaged.

- In depth and detailed.
- Cannot generalise from a case study.
Limitations of the Working Memory Model
Here are some limitations of the working memory model.

Central executive
- What does the central executive actually do?
- The model suggests that it allocates attention, but it is not fully explained why it is needed.

Lacks ecological validity
- Dual task experiments are very artificial – lacks ecological validity.

Lack of generalisability
- Cannot generalise from case studies on brain damaged patients.

Ambiguity about the LTM
- It is only a model of working memory and leaves many unanswered questions about the structure of LTM.
1 Social Influence
1.1 Social Influence
1.1.1 Conformity
1.1.2 Asch (1951)
1.1.3 Sherif (1935)
1.1.4 Conformity to Social Roles
1.1.5 BBC Prison Study
1.1.6 End of Topic Test - Conformity
1.1.7 Obedience
1.1.8 Analysing Milgram's Experiment
1.1.9 Agentic State & Legitimate Authority
1.1.10 Variables of Obedience
1.1.11 Resistance to Social Influence
1.1.12 Minority Influence & Social Change
1.1.13 Minority Influence & Social Impact Theory
1.1.14 End of Topic Test - Social Influences
1.1.15 Exam-Style Question - Conformity
1.1.16 Top Grade AO2/AO3 - Social Influence
2.1.1 Multi-Store Model of Memory
2.1.2 Short-Term vs Long-Term Memory
2.1.3 Long-Term Memory
2.1.4 Support for the Multi-Store Model of Memory
2.1.5 Duration Studies
2.1.6 Capacity Studies
2.1.7 Coding Studies
2.1.8 The Working Memory Model
2.1.9 The Working Memory Model 2
2.1.10 Support for the Working Memory Model
2.1.11 Explanations for Forgetting
2.1.12 Studies on Interference
2.1.13 Cue-Dependent Forgetting
2.1.14 Eye Witness Testimony - Loftus & Palmer
2.1.15 Eye Witness Testimony Loftus
2.1.16 Eyewitness Testimony - Post-Event Discussion
2.1.17 Eyewitness Testimony - Age & Misleading Questions
2.1.18 Cognitive Interview
2.1.19 Cognitive Interview - Geiselman & Fisher
2.1.20 End of Topic Test - Memory
2.1.21 Exam-Style Question - Memory
2.1.22 A-A* (AO3/4) - Memory
3 Attachment
3.1 Attachment
3.1.1 Caregiver-Infant Interaction
3.1.2 Condon & Sander (1974)
3.1.3 Schaffer & Emerson (1964)
3.1.4 Multiple Attachments
3.1.5 Studies on the Role of the Father
3.1.6 Animal Studies of Attachment
3.1.7 Explanations of Attachment
3.1.8 Attachment Types - Strange Situation
3.1.9 Cultural Differences in Attachment
3.1.10 Disruption of Attachment
3.1.11 Disruption of Attachment - Privation
3.1.12 Overcoming the Effects of Disruption
3.1.13 The Effects of Institutionalisation
3.1.14 Early Attachment
3.1.15 Critical Period of Attachment
3.1.16 End of Topic Test - Attachment
3.1.17 Exam-Style Question - Attachment
3.1.18 Top Grade AO2/AO3 - Attachment
4 Psychopathology
4.1 Psychopathology
4.1.1 Definitions of Abnormality
4.1.2 Definitions of Abnormality 2
4.1.3 Phobias, Depression & OCD
4.1.4 Phobias: Behavioural Approach
4.1.5 Evaluation of Behavioural Explanations of Phobias
4.1.6 Depression: Cognitive Approach
4.1.7 OCD: Biological Approach
4.1.8 Evidence for the Biological Approach
4.1.9 End of Topic Test - Psychopathy
4.1.10 Exam-Style Question - Phobias
4.1.11 Top Grade AO2/AO3 - Psychopathology
5 Approaches in Psychology
5.1 Approaches in Psychology
5.1.1 Psychology as a Science
5.1.2 Origins of Psychology
5.1.3 Reductionism & Problems with Introspection
5.1.4 The Behaviourist Approach - Classical Conditioning
5.1.5 Pavlov's Experiment
5.1.6 Little Albert Study
5.1.7 The Behaviourist Approach - Operant Conditioning
5.1.8 Social Learning Theory
5.1.9 The Cognitive Approach 1
5.1.10 The Cognitive Approach 2
5.1.11 The Biological Approach
5.1.12 Gottesman (1991) - Twin Studies
5.1.13 Brain Scanning
5.1.14 Structure of Personality & Little Hans
5.1.15 The Psychodynamic Approach (A2 only)
5.1.16 Humanistic Psychology (A2 only)
5.1.17 Aronoff (1957) (A2 Only)
5.1.18 Rogers' Client-Centred Therapy (A2 only)
5.1.19 End of Topic Test - Approaches in Psychology
5.1.20 Exam-Style Question - Approaches in Psychology
5.2 Comparison of Approaches (A2 only)
5.2.1 Psychodynamic Approach
5.2.2 Cognitive Approach
5.2.3 Biological Approach
5.2.4 Behavioural Approach
5.2.5 End of Topic Test - Comparison of Approaches
6 Biopsychology
6.1 Biopsychology
6.1.1 Nervous System Divisions
6.1.2 Neuron Structure & Function
6.1.3 Neurotransmitters
6.1.4 Endocrine System Function
6.1.5 Fight or Flight Response
6.1.6 The Brain (A2 only)
6.1.7 Localisation of Brain Function (A2 only)
6.1.8 Studying the Brain (A2 only)
6.1.9 CIMT (A2 Only) & Postmortem Examinations
6.1.10 Biological Rhythms (A2 only)
6.1.11 Studies on Biological Rhythms (A2 Only)
6.1.12 End of Topic Test - Biopsychology
6.1.13 Top Grade AO2/AO3 - Biopsychology
7 Research Methods
7.1 Research Methods
7.1.1 Experimental Method
7.1.2 Observational Techniques
7.1.3 Covert, Overt & Controlled Observation
7.1.4 Self-Report Techniques
7.1.5 Correlations
7.1.6 Exam-Style Question - Research Methods
7.1.7 End of Topic Test - Research Methods
7.2 Scientific Processes
7.2.1 Aims, Hypotheses & Sampling
7.2.2 Pilot Studies & Design
7.2.3 Questionnaires
7.2.4 Variables & Control
7.2.5 Demand Characteristics & Investigator Effects
7.2.6 Ethics
7.2.7 Limitations of Ethical Guidelines
7.2.8 Consent & Protection from Harm Studies
7.2.9 Peer Review & The Economy
7.2.10 Validity (A2 only)
7.2.11 Reliability (A2 only)
7.2.12 Features of Science (A2 only)
7.2.13 Paradigms & Falsifiability (A2 only)
7.2.14 Scientific Report (A2 only)
7.2.15 Scientific Report 2 (A2 only)
7.2.16 End of Topic Test - Scientific Processes
7.3 Data Handling & Analysis
7.3.1 Types of Data
7.3.2 Descriptive Statistics
7.3.3 Correlation
7.3.4 Evaluation of Descriptive Statistics
7.3.5 Presentation & Display of Data
7.3.6 Levels of Measurement (A2 only)
7.3.7 Content Analysis (A2 only)
7.3.8 Case Studies (A2 only)
7.3.9 Thematic Analysis (A2 only)
7.3.10 End of Topic Test - Data Handling & Analysis
7.4 Inferential Testing
7.4.1 Introduction to Inferential Testing
7.4.2 Sign Test
7.4.3 Piaget Conservation Experiment
7.4.4 Non-Parametric Tests
8 Issues & Debates in Psychology (A2 only)
8.1 Issues & Debates in Psychology (A2 only)
8.1.1 Culture Bias
8.1.2 Sub-Culture Bias
8.1.3 Gender Bias
8.1.4 Ethnocentrism
8.1.5 Cross Cultural Research
8.1.6 Free Will & Determinism
8.1.7 Comparison of Free Will & Determinism
8.1.8 Reductionism & Holism
8.1.9 Reductionist & Holistic Approaches
8.1.10 Nature-Nurture Debate
8.1.11 Interactionist Approach
8.1.12 Nature-Nurture Methods
8.1.13 Nature-Nurture Approaches
8.1.14 Idiographic & Nomothetic Approaches
8.1.15 Socially Sensitive Research
8.1.16 End of Topic Test - Issues and Debates
9 Option 1: Relationships (A2 only)
9.1 Relationships: Sexual Relationships (A2 only)
9.1.1 Sexual Selection & Human Reproductive Behaviour
9.1.2 Intersexual & Intrasexual Selection
9.1.3 Evaluation of Sexual Selection Behaviour
9.1.4 Factors Affecting Attraction: Self-Disclosure
9.1.5 Evaluation of Self-Disclosure Theory
9.1.6 Self Disclosure in Computer Communication
9.1.7 Factors Affecting Attraction: Physical Attributes
9.1.8 Matching Hypothesis Studies
9.1.9 Factors Affecting Physical Attraction
9.1.10 Factors Affecting Attraction: Filter Theory 1
9.1.11 Factors Affecting Attraction: Filter Theory 2
9.1.12 Evaluation of Filter Theory
9.1.13 End of Topic Test - Sexual Relationships
9.2 Relationships: Romantic Relationships (A2 only)
9.2.1 Social Exchange Theory
9.2.2 Evaluation of Social Exchange Theory
9.2.3 Equity Theory
9.2.4 Evaluation of Equity Theory
9.2.5 Rusbult’s Investment Model
9.2.6 Evaluation of Rusbult's Investment Model
9.2.7 Relationship Breakdown
9.2.8 Studies on Relationship Breakdown
9.2.9 Evaluation of Relationship Breakdown
9.2.10 End of Topic Test - Romantic relationships
9.3 Relationships: Virtual & Parasocial (A2 only)
9.3.1 Virtual Relationships in Social Media
9.3.2 Evaluation of Reduced Cues & Hyperpersonal
9.3.3 Parasocial Relationships
9.3.4 Attachment Theory & Parasocial Relationships
9.3.5 Evaluation of Parasocial Relationship Theories
9.3.6 End of Topic Test - Virtual & Parasocial Realtions
10 Option 1: Gender (A2 only)
10.1 Gender (A2 only)
10.1.1 Sex, Gender & Androgyny
10.1.2 Gender Identity Disorder
10.1.3 Biological & Social Explanations of GID
10.1.4 Biological Influences on Gender
10.1.5 Effects of Hormones on Gender
10.1.6 End of Topic Test - Gender 1
10.1.7 Kohlberg’s Theory of Gender Constancy
10.1.8 Evaluation of Kohlberg's Theory
10.1.9 Gender Schema Theory
10.1.10 Psychodynamic Approach to Gender Development 1
10.1.11 Psychodynamic Approach to Gender Development 2
10.1.12 Social Approach to Gender Development
10.1.13 Criticisms of Social Theory
10.1.14 End of Topic Test - Gender 2
10.1.15 Media Influence on Gender Development
10.1.16 Cross Cultural Research
10.1.17 Childcare & Gender Roles
10.1.18 End of Topic Test - Gender 3
11 Option 1: Cognition & Development (A2 only)
11.1 Cognition & Development (A2 only)
11.1.1 Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development 1
11.1.2 Piaget's Theory of Cognitive Development 2
11.1.3 Schema Accommodation Assimilation & Equilibration
11.1.4 Piaget & Inhelder’s Three Mountains Task (1956)
11.1.5 Conservation & Class Inclusion
11.1.6 Evaluation of Piaget
11.1.7 End of Topic Test - Cognition & Development 1
11.1.8 Vygotsky
11.1.9 Evaluation of Vygotsky
11.1.10 Baillargeon
11.1.11 Baillargeon's studies
11.1.12 Evaluation of Baillargeon
11.1.13 End of Topic Test - Cognition & Development 2
11.1.14 Sense of Self & Theory of Mind
11.1.15 Baron-Cohen Studies
11.1.16 Selman’s Five Levels of Perspective Taking
11.1.17 Biological Basis of Social Cognition
11.1.18 Evaluation of Biological Basis of Social Cognition
11.1.19 Important Issues in Social Neuroscience
11.1.20 End of Topic Test - Cognition & Development 3
11.1.21 Top Grade AO2/AO3 - Cognition & Development
12 Option 2: Schizophrenia (A2 only)
12.1 Schizophrenia: Diagnosis (A2 only)
12.1.1 Classification & Diagnosis
12.1.2 Reliability & Validity of Diagnosis
12.1.3 Gender & Cultural Bias
12.1.4 Pinto (2017) & Copeland (1971)
12.1.5 End of Topic Test - Scizophrenia Diagnosis
12.2 Schizophrenia: Treatment (A2 only)
12.2.1 Family-Based Psychological Explanations
12.2.2 Evaluation of Family-Based Explanations
12.2.3 Cognitive Explanations
12.2.4 Drug Therapies
12.2.5 Evaluation of Drug Therapies
12.2.6 Biological Explanations for Schizophrenia
12.2.7 Dopamine Hypothesis
12.2.8 End of Topic Test - Schizoprenia Treatment 1
12.2.9 Psychological Therapies 1
12.2.10 Psychological Therapies 2
12.2.11 Evaluation of Psychological Therapies
12.2.12 Interactionist Approach - Diathesis-Stress Model
12.2.13 Interactionist Approach - Triggers & Treatment
12.2.14 Evaluation of the Interactionist Approach
12.2.15 End of Topic Test - Scizophrenia Treatments 2
13 Option 2: Eating Behaviour (A2 only)
13.1 Eating Behaviour (A2 only)
13.1.1 Explanations for Food Preferences
13.1.2 Birch et al (1987) & Lowe et al (2004)
13.1.3 Control of Eating Behaviours
13.1.4 Control of Eating Behaviour: Leptin
13.1.5 Biological Explanations for Anorexia Nervosa
13.1.6 Psychological Explanations: Family Systems Theory
13.1.7 Psychological Explanations: Social Learning Theory
13.1.8 Psychological Explanations: Cognitive Theory
13.1.9 Biological Explanations for Obesity
13.1.10 Biological Explanations: Studies
13.1.11 Psychological Explanations for Obesity
13.1.12 Psychological Explanations: Studies
13.1.13 End of Topic Test - Eating Behaviour
14 Option 2: Stress (A2 only)
14.1 Stress (A2 only)
14.1.1 Physiology of Stress
14.1.2 Role of Stress in Illness
14.1.3 Role of Stress in Illness: Studies
14.1.4 Social Readjustment Rating Scales
14.1.5 Hassles & Uplifts Scales
14.1.6 Stress, Workload & Control
14.1.7 Stress Level Studies
14.1.8 End of Topic Test - Stress 1
14.1.9 Physiological Measures of Stress
14.1.10 Individual Differences
14.1.11 Stress & Gender
14.1.12 Drug Therapy & Biofeedback for Stress
14.1.13 Stress Inoculation Therapy
14.1.14 Social Support & Stress
14.1.15 End of Topic Test - Stress 2
15 Option 3: Aggression (A2 only)
15.1 Aggression: Physiological (A2 only)
15.1.1 Neural Mechanisms
15.1.2 Serotonin
15.1.3 Hormonal Mechanisms
15.1.4 Genetic Factors
15.1.5 Genetic Factors 2
15.1.6 End of Topic Test - Aggression: Physiological 1
15.1.7 Ethological Explanation
15.1.8 Innate Releasing Mechanisms & Fixed Action Pattern
15.1.9 Evolutionary Explanations
15.1.10 Buss et al (1992) - Sex Differences in Jealousy
15.1.11 Evaluation of Evolutionary Explanations
15.1.12 End of Topic Test - Aggression: Physiological 2
15.2 Aggression: Social Psychological (A2 only)
15.2.1 Social Psychological Explanation
15.2.2 Buss (1963) - Frustration/Aggression
15.2.3 Social Psychological Explanation 2
15.2.4 Social Learning Theory (SLT) 1
15.2.5 Social Learning Theory (SLT) 2
15.2.6 Limitations of Social Learning Theory (SLT)
15.2.7 Deindividuation
15.2.8 Deindividuation 2
15.2.9 Deindividuation - Diener et al (1976)
15.2.10 End of Topic Test - Aggression: Social Psychology
15.2.11 Institutional Aggression: Prisons
15.2.12 Evaluation of Dispositional & Situational
15.2.13 Influence of Computer Games
15.2.14 Influence of Television
15.2.15 Evaluation of Studies on Media
15.2.16 Desensitisation & Disinhibition
15.2.17 Cognitive Priming
15.2.18 End of Topic Test - Aggression: Social Psychology
16 Option 3: Forensic Psychology (A2 only)
16.1 Forensic Psychology (A2 only)
16.1.1 Defining Crime
16.1.2 Measuring Crime
16.1.3 Offender Profiling
16.1.4 Evaluation of Offender Profiling
16.1.5 John Duffy Case Study
16.1.6 Biological Explanations 1
16.1.7 Biological Explanations 2
16.1.8 Evaluation of the Biological Explanation
16.1.9 Cognitive Explanations
16.1.10 Moral Reasoning
16.1.11 Psychodynamic Explanation 1
16.1.12 Psychodynamic Explanation 2
16.1.13 End of Topic Test - Forensic Psychology 1
16.1.14 Differential Association Theory
16.1.15 Custodial Sentencing
16.1.16 Effects of Prison
16.1.17 Evaluation of the Effects of Prison
16.1.18 Recidivism
16.1.19 Behavioural Treatments & Therapies
16.1.20 Effectiveness of Behavioural Treatments
16.1.21 Restorative Justice
16.1.22 End of Topic Test - Forensic Psychology 2
17 Option 3: Addiction (A2 only)
17.1 Addiction (A2 only)
17.1.1 Definition
17.1.2 Brain Neurochemistry Explanation
17.1.3 Learning Theory Explanation
17.1.4 Evaluation of a Learning Theory Explanation
17.1.5 Cognitive Bias
17.1.6 Griffiths on Cognitive Bias
17.1.7 Evaluation of Cognitive Theory (A2 only)
17.1.8 End of Topic Test - Addiction 1
17.1.9 Gambling Addiction & Learning Theory
17.1.10 Social Influences on Addiction 1
17.1.11 Social Influences on Addiction 2
17.1.12 Personal Influences on Addiction
17.1.13 Genetic Explanations of Addiction
17.1.14 End of Topic Test - Addiction 2
17.2 Treating Addiction (A2 only)
17.2.1 Drug Therapy
17.2.2 Behavioural Interventions
17.2.3 Cognitive Behavioural Therapy
17.2.4 Theory of Reasoned Action
17.2.5 Theory of Planned Behaviour
17.2.6 Six Stage Model of Behaviour Change
17.2.7 End of Topic Test - Treating Addiction
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
The Working Memory Model 2
Explanations for Forgetting
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Psychology news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Psychology Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Study Notes
Working Memory Model
Last updated 7 Nov 2023
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
Baddeley and Hitch (1974) developed the Working Memory Model (WMM), which focuses specifically on the workings of short-term memory (STM).
Atkinson and Shiffrin’s Multi-Store Model of memory (MSM) was criticised for over-simplifying STM (as well as LTM) as a single storage system, so the WMM alternative proposed that STM is composed of three, limited capacity stores:
- Central Executive – this manages attention, and controls information from the two ‘slave stores’ [below]
- An articulatory rehearsal process (‘inner voice’) of language, including any language presented visually to convert to a phonological state, for storage in the:
- Phonological store (‘inner ear’), which holds auditory speech information and the order in which it was heard (or any visually-presented language converted by the articulatory process)
- Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad – this temporarily retains visual and spatial information
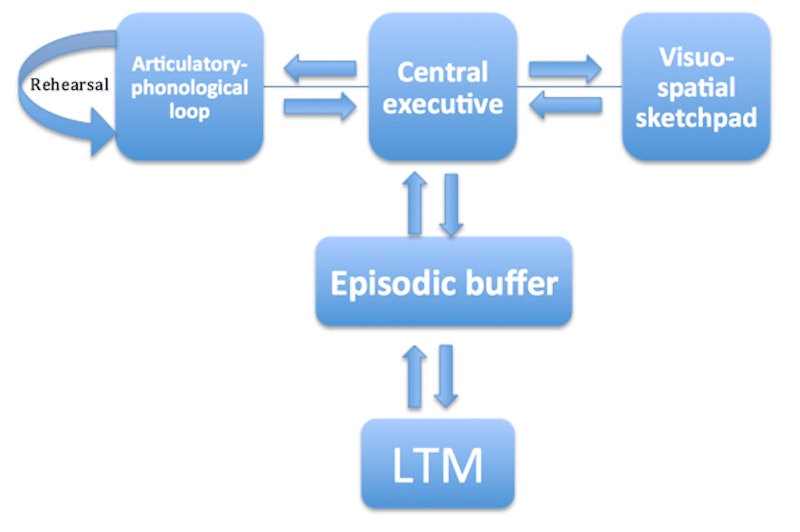
A later addition was the episodic buffer which facilitates communication between the central executive and long term memory.
The three-store STM stemmed from research using a ‘dual-task technique’ (or ‘interference tasks’), whereby performance is measured as participants perform two tasks simultaneously. The following observations provided evidence to suggest different, limited-capacity STM stores process different types of memory:
- If one store is utilised for both tasks, then task performance is poorer than when they are completed separately, due to the store’s limited capacity e.g. repeating “the the the” aloud and reading some text silently would use the articulatory-phonological loop for both tasks, slowing performance.
- If the tasks require different stores, performance would be unaffected when performing them simultaneously e.g. repeating “the the the” aloud whilst performing a reasoning task (requiring attention, i.e. the central executive), or whilst following a mobile stimulus with your eyes (using the visuo-spatial sketchpad).
Evaluation of the Working Memory Model
- The WMM provides an explanation for parallel processing (i.e. where processes involved in a cognitive task occur at once), unlike Atkinson and Shiffrin’s MSM.
- A Shallice and Warrington (1974) case study reported that brain-damaged patient KF could recall verbal but not visual information immediately after its presentation, which supports the WMM’s claim that separate short-term stores manage short-term phonological and visual memories.
- The model was developed based on evidence from laboratory experiments, so confounding variables could be carefully controlled to produce reliable results (that can be replicated).
- Despite providing more detail of STM than the multi-store model, the WMM has been criticized for being too simplistic and vague, e.g. it is unclear what the central executive is, or its exact role in attention.
- Results from laboratory experiments researching the WMM will often have low ecological validity (i.e. may not relate to real life), as tasks such as repeating ‘the the the’ are arguably not representative of our everyday activities.
- Working memory model
- Baddeley and Hitch (1974)
You might also like
duration of short-term memory, types of long term memory.
Quizzes & Activities
Multi-Store Model of Memory
Memory - key term "conundrum" activity, memory: mcq revision test 1 for aqa a level psychology.
Topic Videos

Example Answers for Memory: A Level Psychology, Paper 1, June 2018 (AQA)
Exam Support
Memory - "Connection Wall" activity
Related products.

Psychopathology Exam Buster Revision Guide for AQA A-Level Psychology
03-4130-30107-03

Aggression Exam Buster Revision Guide for AQA A Level Psychology
03-4130-30566-03

Schizophrenia Exam Buster Revision Guide for AQA A Level Psychology
03-4130-30548-03
- View full selection ›
Our subjects
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
Up Learn – A Level Psychology (AQA) – Memory
Evaluating the multi-store model of memory: patient kf case study.
The multi-store model predicts that if people have damage to their short-term memory, then they will also have damage to their long-term memory. But patients like patient KF have damage to their short-term memory without damage to their long-term memory. So, the first limitation of the multi-store model is that it isn’t supported by findings from case studies.
A*/A guaranteed or your money back
Really? Yes, really. Find out more about our A*/A Guarantee below.
Want to see the whole course?
No payment info required!
More videos on The Working Memory Model
Introduction (free trial)
Limitations of the Multi-store Model: Patient KF Case Study
Limitations of the Multi-store Model: Short-term Memory Stores (free trial)
Limitations of the Multi-store Model: the Role of Rehearsal (free trial)
Progress Quiz: Limitations of the Multi-store Model (free trial)
The Working Memory Model
Phonological Loop (free trial)
Sub-components of the Phonological Loop (free trial)
Rehearsal and the Word-length Effect (free trial)
Visuo-spatial Sketchpad (free trial)
Sub-components of the Visuo-spatial Sketchpad (free trial)
Episodic Buffer (free trial)
What is Memory?
Types of memory, types of long-term memory, memory accuracy: how good is our memory, exam questions: memory.
Last time we saw the story of patient KF, a man with impaired short-term memory but no damage to his long-term memory, whose condition challenged the multi-store model of memory.
Now, we already saw earlier, that the multi-store model says…
The multi-store model says that we have three memory stores: the sensory register, the short-term memory store, and the long-term memory store.
Information flows unidirectionally through the stores. To pass into short-term memory, information in the sensory register has to be paid attention to.
And to pass into the long-term memory store, information in short-term memory has to be rehearsed.
So, according to the multi-store model, to be stored in long-term memory, information has to first go through short-term memory. If it’s rehearsed, the information is then transferred to long-term memory.
But if it isn’t rehearsed in short-term memory, the information simply fades away.
So, the multi-store model predicts that…
The multi-store model predicts that a person can have damage to their long-term memory without their short-term memory being affected…
…But if a person’s short-term memory is damaged, they lose both their short and their long-term memories… because without being able to rehearse information in short-term memory, it can’t be transferred to long-term memory!
But, we also saw last time that patient KF’s motorbike accident impaired his short-term memory, but left his long-term memory intact.
And later case studies of other patients like KF also revealed similar findings: patients can damage their short-term memory without damaging their long-term memory!
So, a first limitation of the multi-store model is that it isn’t supported by findings from case studies of patients like KF.
Now, we’ll look at two more limitations of the multi-store model next.
But first, to sum up…
To sum it up, the multi-store model predicts that if people have damage to their short-term memory, then they will also have damage to their long-term memory.
But patients like patient KF have damage to their short-term memory without damage to their long-term memory.
So, the first limitation of the multi-store model is that it isn’t supported by findings from case studies.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Shallice and Warrington (1974) - Study of KF. The working memory model is supported by evidence from brain damaged patients such as KF. Research aim & method. Aim: To investigate a patient KF who had suffered …
These studies were mainly in a lab environment so there is low ecological validity. These studies also lacked mundane realism. Low levels of replicability because this data is only specific to …
A Shallice and Warrington (1974) case study reported that brain-damaged patient KF could recall verbal but not visual information immediately after its presentation, which …
The KF Case Study supports Working Memory. KF suffered brain damage from a motorcycle accident that damaged his short-term memory. KF struggled to process verbal information but …
Example Study: The Case of KF - Warrington and Shallice (1969) Aim: To investigate the possibility that short memory can be damaged without damage to the long-term
Evaluating the Multi-Store Model of Memory: Patient KF Case Study. The multi-store model predicts that if people have damage to their short-term memory, then they will also have …
Shallice and Warrington (1974) studied KF, a man whose brain had been injured in a motorcycle accident. KF’s LTM functioned normally, but his STM was severely impaired. Instead of around …
K.F. case. A patient described by Shallice & Warrington (1969 ; 1970) who suffered from short-term memory impairment (reduced digit span, no recency effect) with …