Procedure, Example Solved Problem | Operations Research - Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method) | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
Chapter: 12th business maths and statistics : chapter 10 : operations research.
Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method)
First check whether the number of rows is equal to the numbers of columns, if it is so, the assignment problem is said to be balanced.
Step :1 Choose the least element in each row and subtract it from all the elements of that row.
Step :2 Choose the least element in each column and subtract it from all the elements of that column. Step 2 has to be performed from the table obtained in step 1.
Step:3 Check whether there is atleast one zero in each row and each column and make an assignment as follows.
Step :4 If each row and each column contains exactly one assignment, then the solution is optimal.
Example 10.7
Solve the following assignment problem. Cell values represent cost of assigning job A, B, C and D to the machines I, II, III and IV.
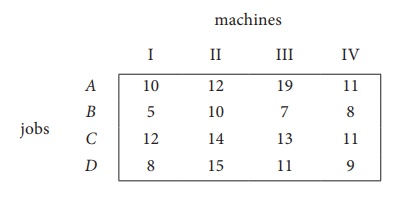
Here the number of rows and columns are equal.
∴ The given assignment problem is balanced. Now let us find the solution.
Step 1: Select a smallest element in each row and subtract this from all the elements in its row.
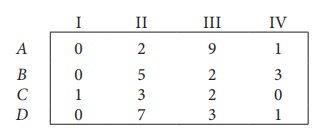
Look for atleast one zero in each row and each column.Otherwise go to step 2.
Step 2: Select the smallest element in each column and subtract this from all the elements in its column.
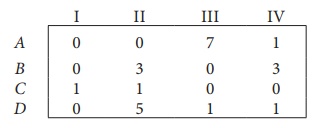
Since each row and column contains atleast one zero, assignments can be made.
Step 3 (Assignment):
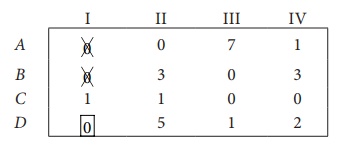
Thus all the four assignments have been made. The optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
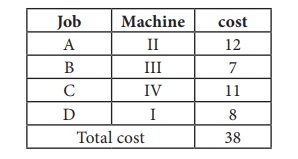
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost
Example 10.8
Consider the problem of assigning five jobs to five persons. The assignment costs are given as follows. Determine the optimum assignment schedule.
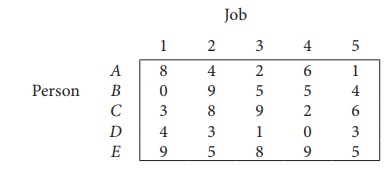
∴ The given assignment problem is balanced.
Now let us find the solution.
The cost matrix of the given assignment problem is
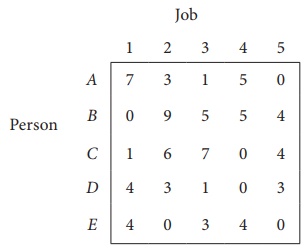
Column 3 contains no zero. Go to Step 2.
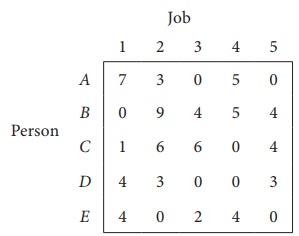
Thus all the five assignments have been made. The Optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
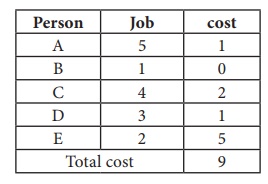
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ` 9
Example 10.9
Solve the following assignment problem.
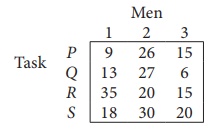
Since the number of columns is less than the number of rows, given assignment problem is unbalanced one. To balance it , introduce a dummy column with all the entries zero. The revised assignment problem is
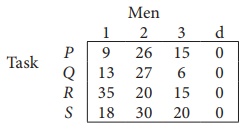
Here only 3 tasks can be assigned to 3 men.
Step 1: is not necessary, since each row contains zero entry. Go to Step 2.
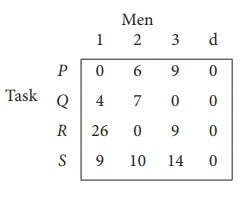
Step 3 (Assignment) :
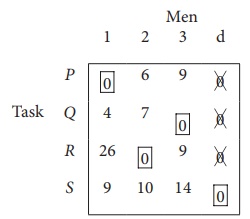
Since each row and each columncontains exactly one assignment,all the three men have been assigned a task. But task S is not assigned to any Man. The optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
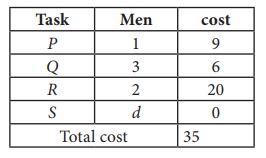
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ₹ 35
Related Topics
Privacy Policy , Terms and Conditions , DMCA Policy and Compliant
Copyright © 2018-2023 BrainKart.com; All Rights Reserved. Developed by Therithal info, Chennai.
Index Assignment problem Hungarian algorithm Solve online

Solve an assignment problem online
Fill in the cost matrix of an assignment problem and click on 'Solve'. The optimal assignment will be determined and a step by step explanation of the hungarian algorithm will be given.
Fill in the cost matrix ( random cost matrix ):
Don't show the steps of the Hungarian algorithm Maximize the total cost
HungarianAlgorithm.com © 2013-2024
- Practice Mathematical Algorithm
- Mathematical Algorithms
- Pythagorean Triplet
- Fibonacci Number
- Euclidean Algorithm
- LCM of Array
- GCD of Array
- Binomial Coefficient
- Catalan Numbers
- Sieve of Eratosthenes
- Euler Totient Function
- Modular Exponentiation
- Modular Multiplicative Inverse
- Stein's Algorithm
- Juggler Sequence
- Chinese Remainder Theorem
- Quiz on Fibonacci Numbers
Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- For each row of the matrix, find the smallest element and subtract it from every element in its row.
- Do the same (as step 1) for all columns.
- Cover all zeros in the matrix using minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines.
- Test for Optimality: If the minimum number of covering lines is n, an optimal assignment is possible and we are finished. Else if lines are lesser than n, we haven’t found the optimal assignment, and must proceed to step 5.
- Determine the smallest entry not covered by any line. Subtract this entry from each uncovered row, and then add it to each covered column. Return to step 3.
Try it before moving to see the solution
Explanation for above simple example:
An example that doesn’t lead to optimal value in first attempt: In the above example, the first check for optimality did give us solution. What if we the number covering lines is less than n.
Time complexity : O(n^3), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm implements the Hungarian algorithm, which is known to have a time complexity of O(n^3).
Space complexity : O(n^2), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm uses a 2D cost matrix of size n x n to store the costs of assigning each worker to a job, and additional arrays of size n to store the labels, matches, and auxiliary information needed for the algorithm.
In the next post, we will be discussing implementation of the above algorithm. The implementation requires more steps as we need to find minimum number of lines to cover all 0’s using a program. References: http://www.math.harvard.edu/archive/20_spring_05/handouts/assignment_overheads.pdf https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQDZNHwuuOY
Similar Reads
- Mathematical
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Hungarian Method

The Hungarian method is a computational optimization technique that addresses the assignment problem in polynomial time and foreshadows following primal-dual alternatives. In 1955, Harold Kuhn used the term “Hungarian method” to honour two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry. Let’s go through the steps of the Hungarian method with the help of a solved example.
Hungarian Method to Solve Assignment Problems
The Hungarian method is a simple way to solve assignment problems. Let us first discuss the assignment problems before moving on to learning the Hungarian method.
What is an Assignment Problem?
A transportation problem is a type of assignment problem. The goal is to allocate an equal amount of resources to the same number of activities. As a result, the overall cost of allocation is minimised or the total profit is maximised.
Because available resources such as workers, machines, and other resources have varying degrees of efficiency for executing different activities, and hence the cost, profit, or loss of conducting such activities varies.
Assume we have ‘n’ jobs to do on ‘m’ machines (i.e., one job to one machine). Our goal is to assign jobs to machines for the least amount of money possible (or maximum profit). Based on the notion that each machine can accomplish each task, but at variable levels of efficiency.

Hungarian Method Steps
Check to see if the number of rows and columns are equal; if they are, the assignment problem is considered to be balanced. Then go to step 1. If it is not balanced, it should be balanced before the algorithm is applied.
Step 1 – In the given cost matrix, subtract the least cost element of each row from all the entries in that row. Make sure that each row has at least one zero.
Step 2 – In the resultant cost matrix produced in step 1, subtract the least cost element in each column from all the components in that column, ensuring that each column contains at least one zero.
Step 3 – Assign zeros
- Analyse the rows one by one until you find a row with precisely one unmarked zero. Encircle this lonely unmarked zero and assign it a task. All other zeros in the column of this circular zero should be crossed out because they will not be used in any future assignments. Continue in this manner until you’ve gone through all of the rows.
- Examine the columns one by one until you find one with precisely one unmarked zero. Encircle this single unmarked zero and cross any other zero in its row to make an assignment to it. Continue until you’ve gone through all of the columns.
Step 4 – Perform the Optimal Test
- The present assignment is optimal if each row and column has exactly one encircled zero.
- The present assignment is not optimal if at least one row or column is missing an assignment (i.e., if at least one row or column is missing one encircled zero). Continue to step 5. Subtract the least cost element from all the entries in each column of the final cost matrix created in step 1 and ensure that each column has at least one zero.
Step 5 – Draw the least number of straight lines to cover all of the zeros as follows:
(a) Highlight the rows that aren’t assigned.
(b) Label the columns with zeros in marked rows (if they haven’t already been marked).
(c) Highlight the rows that have assignments in indicated columns (if they haven’t previously been marked).
(d) Continue with (b) and (c) until no further marking is needed.
(f) Simply draw the lines through all rows and columns that are not marked. If the number of these lines equals the order of the matrix, then the solution is optimal; otherwise, it is not.
Step 6 – Find the lowest cost factor that is not covered by the straight lines. Subtract this least-cost component from all the uncovered elements and add it to all the elements that are at the intersection of these straight lines, but leave the rest of the elements alone.
Step 7 – Continue with steps 1 – 6 until you’ve found the highest suitable assignment.
Hungarian Method Example
Use the Hungarian method to solve the given assignment problem stated in the table. The entries in the matrix represent each man’s processing time in hours.
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix} & I & II & III & IV & V \\1 & 20 & 15 & 18 & 20 & 25 \\2 & 18 & 20 & 12 & 14 & 15 \\3 & 21 & 23 & 25 & 27 & 25 \\4 & 17 & 18 & 21 & 23 & 20 \\5 & 18 & 18 & 16 & 19 & 20 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
With 5 jobs and 5 men, the stated problem is balanced.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}20 & 15 & 18 & 20 & 25 \\18 & 20 & 12 & 14 & 15 \\21 & 23 & 25 & 27 & 25 \\17 & 18 & 21 & 23 & 20 \\18 & 18 & 16 & 19 & 20 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Subtract the lowest cost element in each row from all of the elements in the given cost matrix’s row. Make sure that each row has at least one zero.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 0 & 3 & 5 & 10 \\6 & 8 & 0 & 2 & 3 \\0 & 2 & 4 & 6 & 4 \\0 & 1 & 4 & 6 & 3 \\2 & 2 & 0 & 3 & 4 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Subtract the least cost element in each Column from all of the components in the given cost matrix’s Column. Check to see if each column has at least one zero.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 0 & 3 & 3 & 7 \\6 & 8 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 2 & 4 & 4 & 1 \\0 & 1 & 4 & 4 & 0 \\2 & 2 & 0 & 1 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
When the zeros are assigned, we get the following:
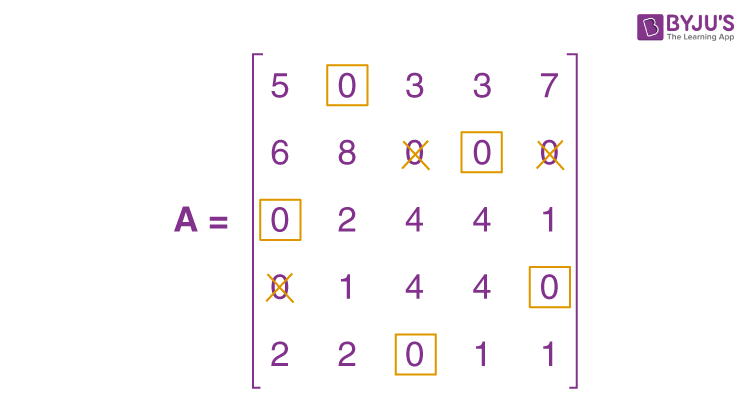
The present assignment is optimal because each row and column contain precisely one encircled zero.
Where 1 to II, 2 to IV, 3 to I, 4 to V, and 5 to III are the best assignments.
Hence, z = 15 + 14 + 21 + 20 + 16 = 86 hours is the optimal time.
Practice Question on Hungarian Method
Use the Hungarian method to solve the following assignment problem shown in table. The matrix entries represent the time it takes for each job to be processed by each machine in hours.
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix}J/M & I & II & III & IV & V \\1 & 9 & 22 & 58 & 11 & 19 \\2 & 43 & 78 & 72 & 50 & 63 \\3 & 41 & 28 & 91 & 37 & 45 \\4 & 74 & 42 & 27 & 49 & 39 \\5 & 36 & 11 & 57 & 22 & 25 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Stay tuned to BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app to explore all Maths-related topics.
Frequently Asked Questions on Hungarian Method
What is hungarian method.
The Hungarian method is defined as a combinatorial optimization technique that solves the assignment problems in polynomial time and foreshadowed subsequent primal–dual approaches.
What are the steps involved in Hungarian method?
The following is a quick overview of the Hungarian method: Step 1: Subtract the row minima. Step 2: Subtract the column minimums. Step 3: Use a limited number of lines to cover all zeros. Step 4: Add some more zeros to the equation.
What is the purpose of the Hungarian method?
When workers are assigned to certain activities based on cost, the Hungarian method is beneficial for identifying minimum costs.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ₹ 38. Example 10.8. Consider the problem of assigning five jobs to five persons. The assignment costs are given as follows. Determine the optimum assignment schedule. Solution: Here the number of rows and columns are equal. ∴ The given assignment problem is balanced. Now let us find the solution.
Solve an assignment problem online. Fill in the cost matrix of an assignment problem and click on 'Solve'. The optimal assignment will be determined and a step by step explanation of the hungarian algorithm will be given. Fill in the cost matrix (random cost matrix):
matrix. The assignment schedule corresponding to there zeros is the optimum (maximal) assignment. Note: the above procedure for assignment is Hungarian assignment method Problem 1. Three jobs A B C are to be assigned to three machines x Y Z. The processing costs are as given in the matrix shown below.
The Hungarian Method: The following algorithm applies the above theorem to a given n × n cost matrix to find an optimal assignment. Step 1. Subtract the smallest entry in each row from all the entries of its ... assignment with the smallest possible cost is called an optimal assignment. 30. The Hungarian Method: The Hungarian method (see
The Hungarian algorithm, aka Munkres assignment algorithm, utilizes the following theorem for polynomial runtime complexity (worst case O(n 3)) and guaranteed optimality: If a number is added to or subtracted from all of the entries of any one row or column of a cost matrix, then an optimal assignment for the resulting cost matrix is also an ...
The Hungarian method is a computational optimization technique that addresses the assignment problem in polynomial time and foreshadows following primal-dual alternatives. In 1955, Harold Kuhn used the term "Hungarian method" to honour two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry. Let's go through the steps of the Hungarian method with the help of a solved example.
Hungarian method for assignment problem Step 1. Subtract the entries of each row by the row minimum. Step 2. Subtract the entries of each column by the column minimum. Step 3. Make an assignment to the zero entries in the resulting matrix. A = M 17 10 15 17 18 M 6 10 20 12 5 M 14 19 12 11 15 M 7 16 21 18 6 M −10
The Hungarian method, also known as the Kuhn-Munkres algorithm, is a computational technique used to solve the assignment problem in polynomial time.It's a precursor to many primal-dual methods used today. The method was named in honor of Hungarian mathematicians Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry by Harold Kuhn in 1955.
The assignment problem can be solved by the following four methods: a) Complete enumeration method . b) Simplex Method . c) Transportation method . d) Hungarian method . 9.2.1 Complete enumeration method. In this method, a list of all possible assignments among the given resources and activities is prepared. Then an assignment involving the ...
We consider an example where four jobs (J1, J2, J3, and J4) need to be executed by four workers (W1, W2, W3, and W4), one job per worker. The matrix below shows the cost of assigning a certain worker to a certain job. The objective is to minimize the total cost of the assignment.