- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Sean is a fact-checker and researcher with experience in sociology, field research, and data analytics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sean-Blackburn-1000-a8b2229366944421bc4b2f2ba26a1003.jpg)
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Application
- Improvement
From deciding what to eat for dinner to considering whether it's the right time to buy a house, problem-solving is a large part of our daily lives. Learn some of the problem-solving strategies that exist and how to use them in real life, along with ways to overcome obstacles that are making it harder to resolve the issues you face.
What Is Problem-Solving?
In cognitive psychology , the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
A problem exists when there is a goal that we want to achieve but the process by which we will achieve it is not obvious to us. Put another way, there is something that we want to occur in our life, yet we are not immediately certain how to make it happen.
Maybe you want a better relationship with your spouse or another family member but you're not sure how to improve it. Or you want to start a business but are unsure what steps to take. Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires.
The problem-solving process involves:
- Discovery of the problem
- Deciding to tackle the issue
- Seeking to understand the problem more fully
- Researching available options or solutions
- Taking action to resolve the issue
Before problem-solving can occur, it is important to first understand the exact nature of the problem itself. If your understanding of the issue is faulty, your attempts to resolve it will also be incorrect or flawed.
Problem-Solving Mental Processes
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are:
- Perceptually recognizing the problem
- Representing the problem in memory
- Considering relevant information that applies to the problem
- Identifying different aspects of the problem
- Labeling and describing the problem
Problem-Solving Strategies
There are many ways to go about solving a problem. Some of these strategies might be used on their own, or you may decide to employ multiple approaches when working to figure out and fix a problem.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that, by following certain "rules" produces a solution. Algorithms are commonly used in mathematics to solve division or multiplication problems. But they can be used in other fields as well.
In psychology, algorithms can be used to help identify individuals with a greater risk of mental health issues. For instance, research suggests that certain algorithms might help us recognize children with an elevated risk of suicide or self-harm.
One benefit of algorithms is that they guarantee an accurate answer. However, they aren't always the best approach to problem-solving, in part because detecting patterns can be incredibly time-consuming.
There are also concerns when machine learning is involved—also known as artificial intelligence (AI)—such as whether they can accurately predict human behaviors.
Heuristics are shortcut strategies that people can use to solve a problem at hand. These "rule of thumb" approaches allow you to simplify complex problems, reducing the total number of possible solutions to a more manageable set.
If you find yourself sitting in a traffic jam, for example, you may quickly consider other routes, taking one to get moving once again. When shopping for a new car, you might think back to a prior experience when negotiating got you a lower price, then employ the same tactics.
While heuristics may be helpful when facing smaller issues, major decisions shouldn't necessarily be made using a shortcut approach. Heuristics also don't guarantee an effective solution, such as when trying to drive around a traffic jam only to find yourself on an equally crowded route.
Trial and Error
A trial-and-error approach to problem-solving involves trying a number of potential solutions to a particular issue, then ruling out those that do not work. If you're not sure whether to buy a shirt in blue or green, for instance, you may try on each before deciding which one to purchase.
This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options using another problem-solving technique can be helpful before attempting trial and error.
In some cases, the solution to a problem can appear as a sudden insight. You are facing an issue in a relationship or your career when, out of nowhere, the solution appears in your mind and you know exactly what to do.
Insight can occur when the problem in front of you is similar to an issue that you've dealt with in the past. Although, you may not recognize what is occurring since the underlying mental processes that lead to insight often happen outside of conscious awareness .
Research indicates that insight is most likely to occur during times when you are alone—such as when going on a walk by yourself, when you're in the shower, or when lying in bed after waking up.
How to Apply Problem-Solving Strategies in Real Life
If you're facing a problem, you can implement one or more of these strategies to find a potential solution. Here's how to use them in real life:
- Create a flow chart . If you have time, you can take advantage of the algorithm approach to problem-solving by sitting down and making a flow chart of each potential solution, its consequences, and what happens next.
- Recall your past experiences . When a problem needs to be solved fairly quickly, heuristics may be a better approach. Think back to when you faced a similar issue, then use your knowledge and experience to choose the best option possible.
- Start trying potential solutions . If your options are limited, start trying them one by one to see which solution is best for achieving your desired goal. If a particular solution doesn't work, move on to the next.
- Take some time alone . Since insight is often achieved when you're alone, carve out time to be by yourself for a while. The answer to your problem may come to you, seemingly out of the blue, if you spend some time away from others.
Obstacles to Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include:
- Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions. Thus, they may not even try some potential options.
- Functional fixedness : This term refers to the tendency to view problems only in their customary manner. Functional fixedness prevents people from fully seeing all of the different options that might be available to find a solution.
- Irrelevant or misleading information: When trying to solve a problem, it's important to distinguish between information that is relevant to the issue and irrelevant data that can lead to faulty solutions. The more complex the problem, the easier it is to focus on misleading or irrelevant information.
- Mental set: A mental set is a tendency to only use solutions that have worked in the past rather than looking for alternative ideas. A mental set can work as a heuristic, making it a useful problem-solving tool. However, mental sets can also lead to inflexibility, making it more difficult to find effective solutions.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
In the end, if your goal is to become a better problem-solver, it's helpful to remember that this is a process. Thus, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, following these steps can help lead you to your solution:
- Recognize that a problem exists . If you are facing a problem, there are generally signs. For instance, if you have a mental illness , you may experience excessive fear or sadness, mood changes, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists.
- Decide to solve the problem . Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution.
- Seek to fully understand the issue . Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides. If your problem is relationship-related, for instance, ask yourself how the other person may be interpreting the issue. You might also consider how your actions might be contributing to the situation.
- Research potential options . Using the problem-solving strategies mentioned, research potential solutions. Make a list of options, then consider each one individually. What are some pros and cons of taking the available routes? What would you need to do to make them happen?
- Take action . Select the best solution possible and take action. Action is one of the steps required for change . So, go through the motions needed to resolve the issue.
- Try another option, if needed . If the solution you chose didn't work, don't give up. Either go through the problem-solving process again or simply try another option.
You can find a way to solve your problems as long as you keep working toward this goal—even if the best solution is simply to let go because no other good solution exists.
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
Dunbar K. Problem solving . A Companion to Cognitive Science . 2017. doi:10.1002/9781405164535.ch20
Stewart SL, Celebre A, Hirdes JP, Poss JW. Risk of suicide and self-harm in kids: The development of an algorithm to identify high-risk individuals within the children's mental health system . Child Psychiat Human Develop . 2020;51:913-924. doi:10.1007/s10578-020-00968-9
Rosenbusch H, Soldner F, Evans AM, Zeelenberg M. Supervised machine learning methods in psychology: A practical introduction with annotated R code . Soc Personal Psychol Compass . 2021;15(2):e12579. doi:10.1111/spc3.12579
Mishra S. Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology . Personal Soc Psychol Rev . 2014;18(3):280-307. doi:10.1177/1088868314530517
Csikszentmihalyi M, Sawyer K. Creative insight: The social dimension of a solitary moment . In: The Systems Model of Creativity . 2015:73-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
Chrysikou EG, Motyka K, Nigro C, Yang SI, Thompson-Schill SL. Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality . Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts . 2016;10(4):425‐435. doi:10.1037/aca0000050
Huang F, Tang S, Hu Z. Unconditional perseveration of the short-term mental set in chunk decomposition . Front Psychol . 2018;9:2568. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02568
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Warning signs and symptoms .
Mayer RE. Thinking, problem solving, cognition, 2nd ed .
Schooler JW, Ohlsson S, Brooks K. Thoughts beyond words: When language overshadows insight. J Experiment Psychol: General . 1993;122:166-183. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.2.166
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Identifying Barriers to Problem-Solving in Psychology

Problem-solving is a key aspect of psychology, essential for understanding and overcoming challenges in our daily lives. There are common barriers that can hinder our ability to effectively solve problems. From mental blocks to confirmation bias, these obstacles can impede our progress.
In this article, we will explore the various barriers to problem-solving in psychology, as well as strategies to overcome them. By addressing these challenges head-on, we can unlock the benefits of improved problem-solving skills and mental agility.
- Identifying and overcoming barriers to problem-solving in psychology can lead to more effective and efficient solutions.
- Some common barriers include mental blocks, confirmation bias, and functional fixedness, which can all limit critical thinking and creativity.
- Mindfulness techniques, seeking different perspectives, and collaborating with others can help overcome these barriers and lead to more successful problem-solving.
- 1 What Is Problem-Solving in Psychology?
- 2 Why Is Problem-Solving Important in Psychology?
- 3.1 Mental Blocks
- 3.2 Confirmation Bias
- 3.3 Functional Fixedness
- 3.4 Lack of Creativity
- 3.5 Emotional Barriers
- 3.6 Cultural Influences
- 4.1 Divergent Thinking
- 4.2 Mindfulness Techniques
- 4.3 Seeking Different Perspectives
- 4.4 Challenging Assumptions
- 4.5 Collaborating with Others
- 5 What Are the Benefits of Overcoming These Barriers?
- 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Problem-Solving in Psychology?
Problem-solving in psychology refers to the cognitive processes through which individuals identify and overcome obstacles or challenges to reach a desired goal, drawing on various mental processes and strategies.
In the realm of cognitive psychology, problem-solving is a key area of study that delves into how people use algorithms and heuristics to tackle complex issues. Algorithms are systematic step-by-step procedures that guarantee a solution, whereas heuristics are mental shortcuts or rules of thumb that provide efficient solutions, albeit without certainty. Understanding these mental processes is crucial in exploring how individuals approach different types of problems and make decisions based on their problem-solving strategies.
Why Is Problem-Solving Important in Psychology?
Problem-solving holds significant importance in psychology as it facilitates the discovery of new insights, enhances understanding of complex issues, and fosters effective actions based on informed decisions.
Assumptions play a crucial role in problem-solving processes, influencing how individuals perceive and approach challenges. By challenging these assumptions, individuals can break through mental barriers and explore creative solutions.
Functional fixedness, a cognitive bias where individuals restrict the use of objects to their traditional functions, can hinder problem-solving. Overcoming functional fixedness involves reevaluating the purpose of objects, leading to innovative problem-solving strategies.
Through problem-solving, psychologists uncover underlying patterns in behavior, delve into subconscious motivations, and offer practical interventions to improve mental well-being.
What Are the Common Barriers to Problem-Solving in Psychology?
In psychology, common barriers to problem-solving include mental blocks , confirmation bias , functional fixedness, lack of creativity, emotional barriers, and cultural influences that hinder the application of knowledge and resources to overcome challenges.
Mental blocks refer to the difficulty in generating new ideas or solutions due to preconceived notions or past experiences. Confirmation bias, on the other hand, is the tendency to search for, interpret, or prioritize information that confirms existing beliefs or hypotheses, while disregarding opposing evidence.
Functional fixedness limits problem-solving by constraining individuals to view objects or concepts in their traditional uses, inhibiting creative approaches. Lack of creativity impedes the ability to think outside the box and consider unconventional solutions.
Emotional barriers such as fear, stress, or anxiety can halt progress by clouding judgment and hindering clear decision-making. Cultural influences may introduce unique perspectives or expectations that clash with effective problem-solving strategies, complicating the resolution process.
Mental Blocks
Mental blocks in problem-solving occur when individuals struggle to consider all relevant information, fall into a fixed mental set, or become fixated on irrelevant details, hindering progress and creative solutions.
For instance, irrelevant information can lead to mental blocks by distracting individuals from focusing on the key elements required to solve a problem effectively. This could involve getting caught up in minor details that have no real impact on the overall solution. A fixed mental set, formed by previous experiences or patterns, can limit one’s ability to approach a problem from new perspectives, restricting innovative thinking.
Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias, a common barrier in problem-solving, leads individuals to seek information that confirms their existing knowledge or assumptions, potentially overlooking contradictory data and hindering objective analysis.
This cognitive bias affects decision-making and problem-solving processes by creating a tendency to favor information that aligns with one’s beliefs, rather than considering all perspectives.
- One effective method to mitigate confirmation bias is by actively challenging assumptions through critical thinking.
- By questioning the validity of existing beliefs and seeking out diverse viewpoints, individuals can counteract the tendency to only consider information that confirms their preconceptions.
- Another strategy is to promote a culture of open-mindedness and encourage constructive debate within teams to foster a more comprehensive evaluation of data.
Functional Fixedness
Functional fixedness restricts problem-solving by limiting individuals to conventional uses of objects, impeding the discovery of innovative solutions and hindering the application of insightful approaches to challenges.
For instance, when faced with a task that requires a candle to be mounted on a wall to provide lighting, someone bound by functional fixedness may struggle to see the potential solution of using the candle wax as an adhesive instead of solely perceiving the candle’s purpose as a light source.
This mental rigidity often leads individuals to overlook unconventional or creative methods, which can stifle their ability to find effective problem-solving strategies.
To combat this cognitive limitation, fostering divergent thinking, encouraging experimentation, and promoting flexibility in approaching tasks can help individuals break free from functional fixedness and unlock their creativity.
Lack of Creativity
A lack of creativity poses a significant barrier to problem-solving, limiting the potential for improvement and hindering flexible thinking required to generate novel solutions and address complex challenges.
When individuals are unable to think outside the box and explore unconventional approaches, they may find themselves stuck in repetitive patterns without breakthroughs.
Flexibility is key to overcoming this hurdle, allowing individuals to adapt their perspectives, pivot when necessary, and consider multiple viewpoints to arrive at innovative solutions.
Encouraging a culture that embraces experimentation, values diverse ideas, and fosters an environment of continuous learning can fuel creativity and push problem-solving capabilities to new heights.
Emotional Barriers
Emotional barriers, such as fear of failure, can impede problem-solving by creating anxiety, reducing risk-taking behavior, and hindering effective collaboration with others, limiting the exploration of innovative solutions.
When individuals are held back by the fear of failure, it often stems from a deep-seated worry about making mistakes or being judged negatively. This fear can lead to hesitation in decision-making processes and reluctance to explore unconventional approaches, ultimately hindering the ability to discover creative solutions. To overcome this obstacle, it is essential to cultivate a positive emotional environment that fosters trust, resilience, and open communication among team members. Encouraging a mindset that embraces failure as a stepping stone to success can enable individuals to take risks, learn from setbacks, and collaborate effectively to overcome challenges.
Cultural Influences
Cultural influences can act as barriers to problem-solving by imposing rigid norms, limiting flexibility in thinking, and hindering effective communication and collaboration among diverse individuals with varying perspectives.
When individuals from different cultural backgrounds come together to solve problems, the ingrained values and beliefs they hold can shape their approaches and methods.
For example, in some cultures, decisiveness and quick decision-making are highly valued, while in others, a consensus-building process is preferred.
Understanding and recognizing these differences is crucial for navigating through the cultural barriers that might arise during collaborative problem-solving.
How Can These Barriers Be Overcome?
These barriers to problem-solving in psychology can be overcome through various strategies such as divergent thinking, mindfulness techniques, seeking different perspectives, challenging assumptions, and collaborating with others to leverage diverse insights and foster critical thinking.
Engaging in divergent thinking , which involves generating multiple solutions or viewpoints for a single issue, can help break away from conventional problem-solving methods. By encouraging a free flow of ideas without immediate judgment, individuals can explore innovative paths that may lead to breakthrough solutions. Actively seeking diverse perspectives from individuals with varied backgrounds, experiences, and expertise can offer fresh insights that challenge existing assumptions and broaden the problem-solving scope. This diversity of viewpoints can spark creativity and unconventional approaches that enhance problem-solving outcomes.
Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking enhances problem-solving by encouraging creative exploration of multiple solutions, breaking habitual thought patterns, and fostering flexibility in generating innovative ideas to address challenges.
When individuals engage in divergent thinking, they open up their minds to various possibilities and perspectives. Instead of being constrained by conventional norms, a person might ideate freely without limitations. This leads to out-of-the-box solutions that can revolutionize how problems are approached. Divergent thinking sparks creativity by allowing unconventional ideas to surface and flourish.
For example, imagine a team tasked with redesigning a city park. Instead of sticking to traditional layouts, they might brainstorm wild concepts like turning the park into a futuristic playground, a pop-up art gallery space, or a wildlife sanctuary. Such diverse ideas stem from divergent thinking and push boundaries beyond the ordinary.
Mindfulness Techniques
Mindfulness techniques can aid problem-solving by promoting present-moment awareness, reducing cognitive biases, and fostering a habit of continuous learning that enhances adaptability and open-mindedness in addressing challenges.
Engaging in regular mindfulness practices encourages individuals to stay grounded in the current moment, allowing them to detach from preconceived notions and biases that could cloud judgment. By cultivating a non-judgmental attitude towards thoughts and emotions, people develop the capacity to observe situations from a neutral perspective, facilitating clearer decision-making processes. Mindfulness techniques facilitate the development of a growth mindset, where one acknowledges mistakes as opportunities for learning and improvement rather than failures.
Seeking Different Perspectives
Seeking different perspectives in problem-solving involves tapping into diverse resources, engaging in effective communication, and considering alternative viewpoints to broaden understanding and identify innovative solutions to complex issues.
Collaboration among individuals with various backgrounds and experiences can offer fresh insights and approaches to tackling challenges. By fostering an environment where all voices are valued and heard, teams can leverage the collective wisdom and creativity present in diverse perspectives. For example, in the tech industry, companies like Google encourage cross-functional teams to work together, harnessing diverse skill sets to develop groundbreaking technologies.
To incorporate diverse viewpoints, one can implement brainstorming sessions that involve individuals from different departments or disciplines to encourage out-of-the-box thinking. Another effective method is to conduct surveys or focus groups to gather input from a wide range of stakeholders and ensure inclusivity in decision-making processes.
Challenging Assumptions
Challenging assumptions is a key strategy in problem-solving, as it prompts individuals to critically evaluate preconceived notions, gain new insights, and expand their knowledge base to approach challenges from fresh perspectives.
By questioning established beliefs or ways of thinking, individuals open the door to innovative solutions and original perspectives. Stepping outside the boundaries of conventional wisdom enables problem solvers to see beyond limitations and explore uncharted territories. This process not only fosters creativity but also encourages a culture of continuous improvement where learning thrives. Daring to challenge assumptions can unveil hidden opportunities and untapped potential in problem-solving scenarios, leading to breakthroughs and advancements that were previously overlooked.
- One effective technique to challenge assumptions is through brainstorming sessions that encourage participants to voice unconventional ideas without judgment.
- Additionally, adopting a beginner’s mindset can help in questioning assumptions, as newcomers often bring a fresh perspective unburdened by past biases.

Collaborating with Others
Collaborating with others in problem-solving fosters flexibility, encourages open communication, and leverages collective intelligence to navigate complex challenges, drawing on diverse perspectives and expertise to generate innovative solutions.
Effective collaboration enables individuals to combine strengths and talents, pooling resources to tackle problems that may seem insurmountable when approached individually. By working together, team members can break down barriers and silos that often hinder progress, leading to more efficient problem-solving processes and better outcomes.
Collaboration also promotes a sense of shared purpose and increases overall engagement, as team members feel valued and enableed to contribute their unique perspectives. To foster successful collaboration, it is crucial to establish clear goals, roles, and communication channels, ensuring that everyone is aligned towards a common objective.
What Are the Benefits of Overcoming These Barriers?
Overcoming the barriers to problem-solving in psychology leads to significant benefits such as improved critical thinking skills, enhanced knowledge acquisition, and the ability to address complex issues with greater creativity and adaptability.
By mastering the art of problem-solving, individuals in the field of psychology can also cultivate resilience and perseverance, two essential traits that contribute to personal growth and success.
When confronting and overcoming cognitive obstacles, individuals develop a deeper understanding of their own cognitive processes and behavioral patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions and overcome challenges more effectively.
Continuous learning and adaptability play a pivotal role in problem-solving, allowing psychologists to stay updated with the latest research, techniques, and methodologies that enhance their problem-solving capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Similar posts.
Exploring the Concept of Social Scripts in Psychology
The article was last updated by Marcus Wong on February 5, 2024. Have you ever found yourself acting in a certain way in social situations…
Uncovering the Meaning of Blind Spots in Psychology
The article was last updated by Dr. Emily Tan on February 8, 2024. Ever find yourself making decisions that seem irrational in hindsight? Or perhaps…
Unveiling Memory Stages: Psychology Experts and the Second Stage
The article was last updated by Rachel Liu on February 5, 2024. Have you ever wondered how your memory works and the different stages it…
Exploring Stress Tests in Evolutionary Psychology
The article was last updated by Ethan Clarke on February 8, 2024. Have you ever wondered why humans behave the way they do? Evolutionary psychology…
Informed Consent in Psychology: Understanding its Gestures and Limitations
The article was last updated by Julian Torres on February 5, 2024. In psychology, informed consent plays a crucial role in ensuring ethical practices and…
Exploring Dr. Spellman’s Contributions to Psychology: What Did He Study?
The article was last updated by Lena Nguyen on February 9, 2024. Have you ever wondered who Dr. Spellman is and what contributions he made…

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.5 Identifying and Overcoming Problem-Solving Barriers
The 9 dot problem.
Here is another popular type of puzzle that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper (Mayer, 1992).
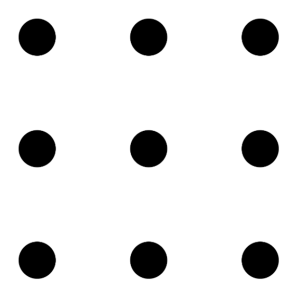
Did you figure it out?
Solve the puzzle with 4 contiguous segments:

Now, solve the puzzle with just 3 contiguous segments!
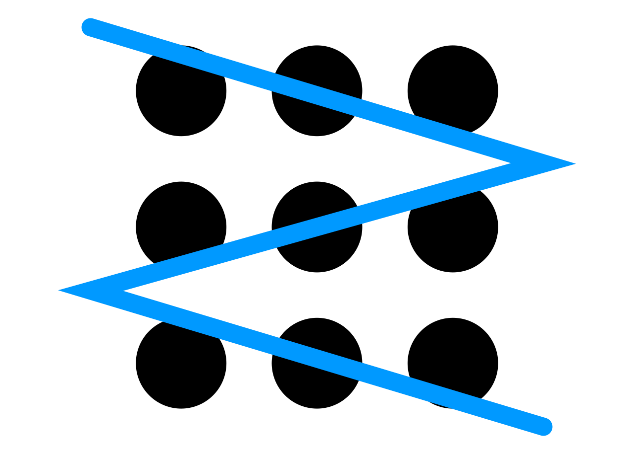
Remember, the way that a person understands and organizes information provided in a problem or represents a problem often facilitates or hinders problem solving. If information is misunderstood, thought about, or used inappropriately, then mistakes are likely – if indeed the problem can be solved at all.
So we not only metaphorically, but sometimes literally, want to “think outside the box” to facilitate creative problem solving. Until we had this insight with the problem, we were having “ representation failure . ”
Put differently, there were obstacles in problem representation, the way that a person understands and organizes information provided in a problem. Initially, we were understanding and organizing information the information in a manner that hindered successful problem solving.
Likely related to our initial representation failure, we likely made the unwarranted assumption or unwarranted expectation that we needed to stay inside some imaginary box. Note that in some contexts, we do want to stay inside some imaginary box. Further, we often have a history of parents and teachers encouraging us to stay inside the lines, leading to a negative transfer of learning in which past learning or training negatively impacts performance on new tasks.
If information is misunderstood or used inappropriately and/or unwarranted assumptions are made, then mistakes are likely – if indeed the problem can be solved at all. With the nine-dot matrix problem, for example, construing the instruction to draw four lines as meaning “draw four lines entirely within the imaginary box matrix” means that the problem simply could not be solved.
A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now .
In the example of the Nine-Dot Problem described above, students often tried one solution after another, but each solution was constrained by being stuck or set in their way of thinking about and response not to extend any line beyond the matrix of an imaginary box.
Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked . The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway , keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck , but she just needs to go to another doorway instead of trying to get out through the locked door.
Functional Fixedness
Fu nctional fixedness is a type of mental set where you do not consider using something for a purpose other than what it was designed for or is typically used for.
Functional fixedness concerns the solution of object-use problems. The basic idea is that when the usual way of using an object is emphasized , it will be far more difficult for a person to use that object in a novel manner . An example of this effect of being fixed on the typical use of objects is Duncker’s (194 5 ) candle problem .
Imagine you are given a box of matches, some candles and tacks. On the wall of the room there is a corkboard. Your task is to fix the candle to the corkboard in such a way that no wax will drop on the floor when the candle is lit. – Got an idea?
Explanation: The clue is just the following. When people are confronted with a problem and given certain objects to solve it, it is difficult for them to figure out that they could use them in a different (not so familiar or obvious) way s .
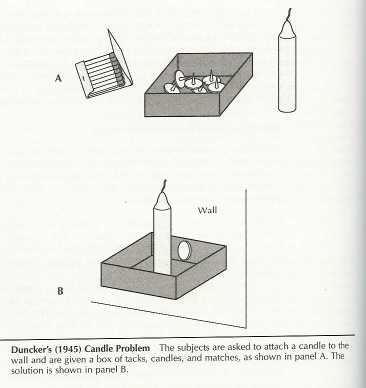
In this example the box needs to be recognized as a support for the candle rather than as a container. People tend to be stuck or fixed on the box as a container, and not think of or notice other uses or functions (like to support a candle).
Until we had this insight with the Candle Problem, we were having “ representation failure ”, or we were understanding and organizing information the information in a manner that hindered successful problem solving.
Likely related to our initial representation failure, we likely made the unwarranted assumption or unwarranted expectation that we needed to think about and use the box as a container (only).
Finally, check this link as an interesting way to review some of these concepts and relate them to your life. https://prezi.com/3o1o7yqdsabl/functional-fixedness/
A process in which previous learning obstructs or interferes with present learning. For instance, tennis players who learn racquetball must often unlearn their tendency to take huge, muscular swings with the shoulder and upper arm.
A temporary readiness to perform certain psychological functions that influences the response to a situation or stimulus, such as the tendency to apply a previously successful technique in solving a new problem.
The tendency to perceive an object only in terms of its most common (or intended) use.
Cognitive Psychology Copyright © by Robert Graham and Scott Griffin. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book

- Trending Categories

- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Barriers to Problem Solving
From solving a basic mathematical equation to deciding to buy a house, problem−solving is an integral part of our daily life. These problems can range from minor to major ones, like planning one's future career. The word "problem−solving" in cognitive psychology refers to the mental process that humans go through to identify, evaluate, and resolve difficulties. It is a complex process involving various steps like identifying and understanding the problem, researching appropriate strategies, and taking effective action to solve the problem and reach desired goals.

What is the Meaning of Barriers to Problem Solving?
Understanding the precise nature of the problem is crucial before problem−solving can start. One's odds of successfully resolving an issue increase if their knowledge of the problem is inaccurate. People approach problems in various ways and may utilize various methods, like algorithms, heuristics, insight, etc., to identify and resolve problems. An algorithm is a systematic process that always yields the right outcome. An excellent example of a problem−solving algorithm is a mathematical formula. Although an algorithm ensures accuracy, it is not necessarily the most effective method for addressing problems. Due to how time−consuming this method may be, it is not useful in many circumstances. For instance, it would take a very long time to use an algorithm to discover all potential number combinations for a lock.
Heuristics are mental shortcuts that may or may not be effective in particular circumstances. Heuristics do not necessarily ensure a proper answer, in contrast to algorithms. However, by employing this approach to problem-solving, individuals are able to simplify difficult issues and narrow the field of potential answers to a more manageable group.
Another method of problem−solving is the trial−and−error approach which entails testing a variety of options and eliminating the ones that do not work. This strategy could be a decent choice if you have a small selection of possibilities. Before undertaking trial−and−error, it is preferable to reduce the available possibilities using another problem-solving strategy if there are several options.
Lastly, in some cases, the answer to an issue immediately comes to individuals. This might happen when they recognize that the issue at hand is just a rehash of earlier struggles. However, the fundamental mental processes that result in insight take place unnoticed.
What are Barriers to Problem Solving?
It goes without saying that problem−solving is not a foolproof process. Our capacity to rapidly and effectively address a problem may be hampered by a variety of impediments. These mental barriers include functional fixedness, irrelevant information, assumptions, etc.

Assumptions − People frequently make assumptions about the limitations and barriers that impede specific solutions while addressing an issue or solving a problem.
Functional Fixedness − Functional fixedness is the propensity to perceive issues exclusively in their predetermined ways. Functional fixedness prohibits individuals from completely understanding all of the potential possibilities for a solution.
Unnecessary Constraints − A related barrier is unnecessary constraints that impose arbitrary limitations on an issue or problem. It relates to trying to use past experiences of what has worked in a circumstance to solve an issue and trying to force it to work in the present situation, rather than seeking a new solution. This limits inventiveness. With insight, the obstacle may be removed. The majority of problem−solving techniques center on gaining an understanding of a situation through data collection, analysis, and assessment. Unnecessary restrictions might result from an intellectual or emotional impediment that makes us rely too much on the familiar. An illustration would be trying to enhance a service utilizing the present procedures and processes as opposed to coming up with a solution and creating new procedures and processes.
Irrelevant or Misleading Information − It is critical to discriminate between knowledge that will help one solve the problem and information that won't, as the latter might result in poor solutions. Concentrating on false or unrelated information is simpler when a subject is extremely complicated.
Mental Set − When someone has a mental set, they are more likely to stick with past−effective solutions than consider new ones. An effective tool for problem-solving, a mental set frequently serves as a heuristic. Thought patterns can also be rigid, making it more difficult to develop workable answers.
Confirmation Bias −This is about establishing bias by not using the problem-solving approach. This may be caused by either skipping steps or failing to use them properly. Confirmation When a method is used to support a preconceived conclusion, bias results. In essence, one would have discovered the issue's solution prior to discovering the issue, and one would see the approach to problem-solving from this perspective.
Problem−solving is hindered by a variety of cognitive limitations as well as practical social and physical tasks. Perceptional, emotional, intellectual, expressive, environmental, and cultural factors might all be involved. Cognitive barriers are the patterns of thought and emotion we have. These influence how we approach and solve problems, creating hurdles. They typically provide biased, flawed, and incomplete answers. These obstacles may be overcome by becoming aware of the problems with issue solving and receiving instruction on how to use a solution strategy properly.

- Related Articles
- Attention and Problem Solving
- Reasoning and Problem Solving
- Problem Solving: Meaning, Theory, and Strategies
- Problem Solving - Steps, Techniques, & Best Practices
- Facilitating and Hindering Factors in Problem Solving
- How Can Leaders Improve Problem-Solving Abilities?
- Tips for Effective Problem-solving in Quality Management
- Problem-solving on Boolean Model and Vector Space Model
- Explain The Scientific Method Used By A Scientist In Solving Problem?
- What are the Barriers to IoT Adoption?
- Solving Cryptarithmetic Puzzles
- Sudoku Solving algorithms
- Portable applications in Cloud and their barriers in C++
- C++ program for Solving Cryptarithmetic Puzzles
- Breaking Down Barriers: The Power of Network Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Kickstart Your Career
Get certified by completing the course

Psych 256: Cognitive Psychology FA16 – 002
Making connections between theory and reality, problem solving.

Image Credit: www.slideshare.net
As depicted in the illustration above, a dilemma such as saving the world would certainly be considered an ill-defined problem. This is because a problem of this magnitude would not have its goals or steps clearly laid out. Additionally it is highly likely, or at least we would hope so for the sake of mankind, that there may be more than one approach or correct answers to solve the problem. Although, I believe that Einstein brings up a valid point, which is that in order to effectively solve a problem it is imperative to first fully understand exactly what the nature of the obstacle(s) is that is in the way of the goal. (Penn State, n.d.)
In the article Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles , Cherry (2016) writes about challenges that make problem solving difficult, which are similar to the barriers outlined in the lesson 13 commentary. According to Cherry, we are presented with a host of problems in our lives each day. These problems can range from minor issues such as, which route to take to work to avoid morning rush hour traffic to much larger issues like developing a five-year plan for your life and career path. In cognitive psychology, the act of problem solving is a mental process one uses to identify, analyze and find answers (Cherry, 2016) when it is not obvious how to overcome the obstacles that prevent you from achieving a goal, otherwise known as a problem (Goldstein, 2015).
The mental processes that are work during problem solving include; recognizing the problem, making a mental representation of the problem, considering the pertinent information applicable to the problem, identifying various facets of the problem and lastly describing or labeling it. Problem solving strategies may include; algorithms or a step-by step process to generate the correct answer (ex: mathematical formula), heuristics or a mental “rule of thumb” that may be applicable to certain scenarios but do not guarantee a correct solution, trial and error that is similar to the generate and test method described in the lesson where you try different solutions to see what works and insight in which a problem is similar to something you dealt with previously, like an analogy. (Cherry, 2016)
The obstacles to problem solving in which we encounter are mental set, functional fixedness, irrelevant or misleading information and Cherry also adds in assumptions. Mental set occurs when we only refer to solutions we have used in the past rather than attempting to identify new ideas that may be more effective. Functional fixedness is when we perceive problems in their usual manner that interferes with our ability to quickly solve the issue. The lesson indicates several examples of people failing to think of ways to use objects other than their primary or common purpose. Misleading information can lead to faulty solutions, which makes it important to have accurate and relevant information during the problem solving process. Lastly, assumptions regarding constraints can hinder the ability of a person to produce viable solutions. (Cherry, 2016)
So whether you are attempting to solve a math problem, a riddle or saving the world it is useful to keep in mind the strategies to effect problem solving while being aware of the obstacles you may face to finding an effective solution.
References
Cherry, K. (2016, August 31). Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles . Retrieved November 19, 2016 from https://www.verywell.com/problem-solving-2795008
Goldstein, E. B. (2015). Cognitive psychology: Connecting mind, research, and everyday experience (4th ed.). Australia: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Penn State World Campus (n.d.). Lesson 13: Problem Solving . Retrieved November 19, 2016 from https://psu.instructure.com/courses/1804143/modules/items/21169401
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
study guides for every class
That actually explain what's on your next test, problem-solving, from class:, cognitive psychology.
Problem-solving is the cognitive process of identifying a challenge or obstacle and systematically working through potential solutions to resolve it. This process involves critical thinking, creativity, and the application of knowledge, which connects to various aspects of how we think, learn, and make decisions.
congrats on reading the definition of Problem-Solving . now let's actually learn it.
5 Must Know Facts For Your Next Test
- Problem-solving can be categorized into two main types: well-defined problems with clear solutions and ill-defined problems that require more creative thinking.
- Effective problem-solving often relies on working memory to hold and manipulate information as potential solutions are evaluated.
- People's approach to problem-solving can be influenced by their intelligence, prior experiences, and even emotional states.
- Cognitive modeling helps researchers understand how individuals approach problem-solving by simulating thought processes and behaviors.
- Mindfulness practices can enhance problem-solving abilities by improving focus, reducing stress, and fostering a clearer perspective on challenges.
Review Questions
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that help streamline the problem-solving process by allowing individuals to make quick decisions without exhaustive analysis. They can facilitate faster conclusions, especially when dealing with complex situations. However, reliance on heuristics can sometimes lead to biases or errors in judgment, impacting the effectiveness of the solution reached.
- Working memory is essential for effective problem-solving as it enables individuals to hold multiple pieces of information simultaneously while they analyze potential solutions. This cognitive resource allows for the manipulation of data and integration of new information as one evaluates different strategies. Limitations in working memory capacity can hinder one's ability to solve complex problems efficiently.
- Insight plays a critical role in creative problem-solving as it represents a moment of clarity where an individual suddenly grasps the solution to a challenge. This contrasts with algorithmic approaches, which rely on systematic procedures to reach a solution. The spontaneity of insight can lead to innovative solutions that may not be accessible through traditional methods, highlighting the importance of both creativity and structured thinking in effective problem-solving.
Related terms
Mental shortcuts or rules of thumb that simplify decision-making and problem-solving by reducing the complexity of information.
A step-by-step procedure or formula for solving a problem that guarantees a solution if followed correctly.
A sudden realization or understanding of a problem's solution that often occurs after a period of contemplation or incubation.
" Problem-Solving " also found in:
Subjects ( 85 ).
- 2D Animation
- AP Psychology
- Adolescent Development
- Adult Nursing Care
- Advanced Public Speaking
- Animal Behavior
- Art Direction
- Business Cognitive Bias
- Business Communication
- Business Model Canvas
- Business Process Optimization
- Business Storytelling
- Causes and Prevention of Violence
- Children's Television
- Classroom Management
- Communication Technologies
- Communication for Leaders
- Contemporary Health Issues
- Creative Producing I
- Creative Video Development
- Crisis Management
- Critical Thinking
- Cross-Cultural Management
- Curriculum Development
- Design Strategy and Software
- Developmental Psychology
- Documentary Photography
- Early Childhood Curriculum
- Education in American Culture
- Educational Psychology
- Emotional Intelligence in Business
- English and Language Arts Education
- Entrepreneurship
- Film Industry
- Foundations of Education
- Foundations of Social Work Practice
- Graphic Design
- History of Education
- History of Modern Philosophy
- Human Social Behavior I
- Improvisational Leadership
- Innovation Management
- International Business Negotiations
- Intrapreneurship
- Intro to Acting
- Intro to Brain and Behavior
- Intro to Business
- Intro to Chemical Engineering
- Intro to Cognitive Science
- Intro to Creative Development
- Intro to Education
- Intro to Flight
- Intro to International Business
- Intro to Paleoanthropology
- Intro to Stage Directing
- Intro to Theatre Arts
- Investigative Reporting
- Leadership and Personal Development
- Literacy Instruction
- Management of Human Resources
- Market Dynamics and Technical Change
- Mathematics Education
- Negotiation and Conflict Resolution
- News Photography
- Organization Design
- Organizational Behavior
- Outsider Art
- Philosophy of Education
- Physiology of Motivated Behaviors
- Police and Society
- Principles of Management
- Professional Selling
- Public Health Policy and Administration
- Risk Assessment and Management
- Science Education
- Sculpture Techniques
- Set Design for Theater and Film
- Stage Management
- Strategic Improvisation in Business
- Thinking Like a Mathematician
- Topics in Entrepreneurship
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
Ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website..

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jan 3, 2023 · Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include: Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions.
Feb 26, 2024 · Problem-solving in psychology refers to the cognitive processes through which individuals identify and overcome obstacles or challenges to reach a desired goal, drawing on various mental processes and strategies. In the realm of cognitive psychology, problem-solving is a key area of study that delves into how people use algorithms and ...
The inability to see a problem from a new perspective. Mental Set A tendency to approach a problem in a particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past.
Barriers to Problem-solving There are numerous obstacles to solving a problem. Generally, these obstacles are mental constructs that impede the ability to correctly solve problems. Some barriers do not prevent us from finding a solution, but do prevent us from finding the most efficient solution. Four of the most common
Put differently, there were obstacles in problem representation, the way that a person understands and organizes information provided in a problem. Initially, we were understanding and organizing information the information in a manner that hindered successful problem solving.
Nov 8, 2022 · The word "problem−solving" in cognitive psychology refers to the mental process that humans go through to identify, evaluate, and resolve difficulties. It is a complex process involving various steps like identifying and understanding the problem, researching appropriate strategies, and taking effective action to solve the problem and reach ...
This is a barrier that shows up in problem solving that causes people to unconsciously place boundaries on the task at hand. A famous example of this barrier to problem solving is the dot problem. In this problem, there are nine dots arranged in a 3 x 3 square.
problem-solving Adapted their problem-solving approach from perception. Perception inherently involves restructuring. •Two views of Necker cube seen by restructuring image to see as “right” or “left” Person often has to restructure a problem in order to gain insight into its solution Van Selst (Reed Chapter 12)
Nov 19, 2016 · In cognitive psychology, the act of problem solving is a mental process one uses to identify, analyze and find answers (Cherry, 2016) when it is not obvious how to overcome the obstacles that prevent you from achieving a goal, otherwise known as a problem (Goldstein, 2015).
Problem-solving is the cognitive process of identifying a challenge or obstacle and systematically working through potential solutions to resolve it. This process involves critical thinking, creativity, and the application of knowledge, which connects to various aspects of how we think, learn, and make decisions.