The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Nonprofit Business Plan
A business plan can be an invaluable tool for your nonprofit. Even a short business plan pushes you to do research, crystalize your purpose, and polish your messaging. This blog shares what it is and why you need it, ten steps to help you write one, and the dos and don’ts of creating a nonprofit business plan.
Nonprofit business plans are dead — or are they?
For many nonprofit organizations, business plans represent outdated and cumbersome documents that get created “just for the sake of it” or because donors demand it.
But these plans are vital to organizing your nonprofit and making your dreams a reality! Furthermore, without a nonprofit business plan, you’ll have a harder time obtaining loans and grants , attracting corporate donors, meeting qualified board members, and keeping your nonprofit on track.
Even excellent ideas can be totally useless if you cannot formulate, execute, and implement a strategic plan to make your idea work. In this article, we share exactly what your plan needs and provide a nonprofit business plan template to help you create one of your own.

What is a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan describes your nonprofit as it currently is and sets up a roadmap for the next three to five years. It also lays out your goals and plans for meeting your goals. Your nonprofit business plan is a living document that should be updated frequently to reflect your evolving goals and circumstances.
A business plan is the foundation of your organization — the who, what, when, where, and how you’re going to make a positive impact.
The best nonprofit business plans aren’t unnecessarily long. They include only as much information as necessary. They may be as short as seven pages long, one for each of the essential sections you will read about below and see in our template, or up to 30 pages long if your organization grows.
Why do we need a Nonprofit Business Plan?
Regardless of whether your nonprofit is small and barely making it or if your nonprofit has been successfully running for years, you need a nonprofit business plan. Why?
When you create a nonprofit business plan, you are effectively creating a blueprint for how your nonprofit will be run, who will be responsible for what, and how you plan to achieve your goals.
Your nonprofit organization also needs a business plan if you plan to secure support of any kind, be it monetary, in-kind , or even just support from volunteers. You need a business plan to convey your nonprofit’s purpose and goals.
It sometimes also happens that the board, or the administration under which a nonprofit operates, requires a nonprofit business plan.
To sum it all up, write a nonprofit business plan to:
- Layout your goals and establish milestones.
- Better understand your beneficiaries, partners, and other stakeholders.
- Assess the feasibility of your nonprofit and document your fundraising/financing model.
- Attract investment and prove that you’re serious about your nonprofit.
- Attract a board and volunteers.
- Position your nonprofit and get clear about your message.
- Force you to research and uncover new opportunities.
- Iron out all the kinks in your plan and hold yourself accountable.
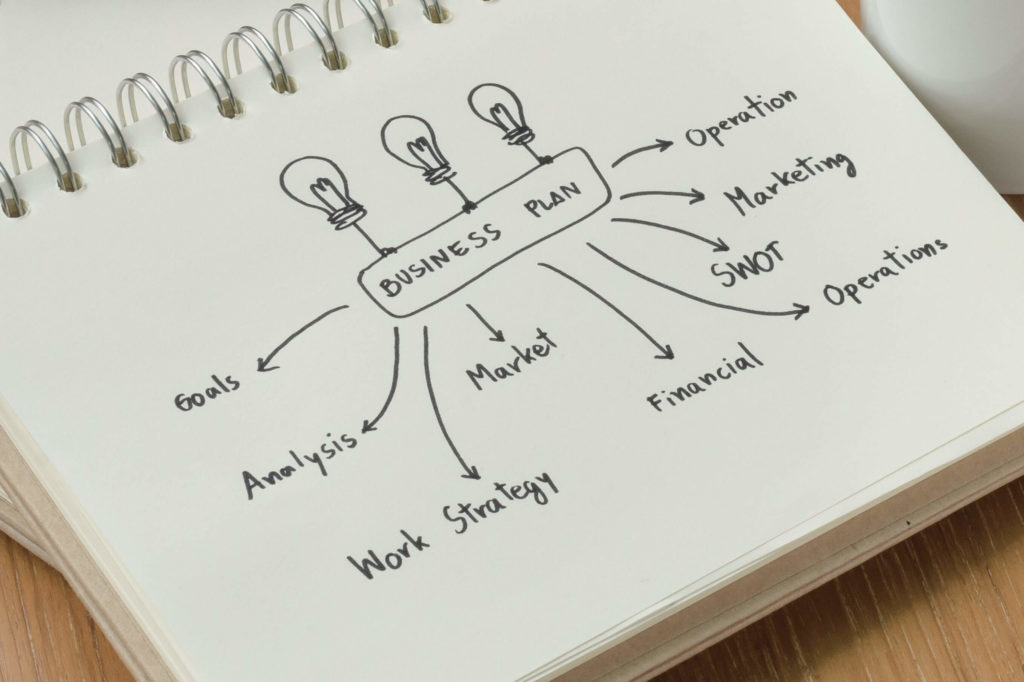
Before starting your nonprofit business plan, it is important to consider the following:
- Who is your audience? E.g. If you are interested in fundraising, donors will be your audience. If you are interested in partnerships, potential partners will be your audience.
- What do you want their response to be? Depending on your target audience, you should focus on the key message you want them to receive to get the response that you want.
10-Step Guide on Writing a Business Plan for Nonprofits
Note: Steps 1, 2, and 3 are in preparation for writing your nonprofit business plan.
Step 1: Data Collection
Before even getting started with the writing, collect financial, operating, and other relevant data. If your nonprofit is already in operation, this should at the very least include financial statements detailing operating expense reports and a spreadsheet that indicates funding sources.
If your nonprofit is new, compile materials related to any secured funding sources and operational funding projections, including anticipated costs.
Step 2: Heart of the Matter
You are a nonprofit after all! Your nonprofit business plan should start with an articulation of the core values and your mission statement . Outline your vision, your guiding philosophy, and any other principles that provide the purpose behind the work. This will help you to refine and communicate your nonprofit message clearly.
Your nonprofit mission statement can also help establish your milestones, the problems your organization seeks to solve, who your organization serves, and its future goals.
Check out these great mission statement examples for some inspiration. For help writing your statement, download our free Mission & Vision Statements Worksheet .
Step 3: Outline
Create an outline of your nonprofit business plan. Write out everything you want your plan to include (e.g. sections such as marketing, fundraising, human resources, and budgets).
An outline helps you focus your attention. It gives you a roadmap from the start, through the middle, and to the end. Outlining actually helps us write more quickly and more effectively.
An outline will help you understand what you need to tell your audience, whether it’s in the right order, and whether the right amount of emphasis is placed on each topic.
Pro tip: Use our Nonprofit Business Plan Outline to help with this step! More on that later.
Step 4: Products, Programs, and Services
In this section, provide more information on exactly what your nonprofit organization does.
- What products, programs, or services do you provide?
- How does your nonprofit benefit the community?
- What need does your nonprofit meet and what are your plans for meeting that need?
E.g. The American Red Cross carries out its mission to prevent and relieve suffering with five key services: disaster relief, supporting America’s military families, lifesaving blood, health and safety services, and international service.
Don’t skimp out on program details, including the functions and beneficiaries. This is generally what most readers will care most about.
However, don’t overload the reader with technical jargon. Try to present some clear examples. Include photographs, brochures, and other promotional materials.
Step 5: Marketing Plan
A marketing plan is essential for a nonprofit to reach its goals. If your nonprofit is already in operation, describe in detail all current marketing activities: any outreach activities, campaigns, and other initiatives. Be specific about outcomes, activities, and costs.
If your nonprofit is new, outline projections based on specific data you gathered about your market.
This will frequently be your most detailed section because it spells out precisely how you intend to carry out your business plan.
- Describe your market. This includes your target audience, competitors, beneficiaries, donors, and potential partners.
- Include any market analyses and tests you’ve done.
- Outline your plan for reaching your beneficiaries.
- Outline your marketing activities, highlighting specific outcomes.
Step 6: Operational Plan
An operational plan describes how your nonprofit plans to deliver activities. In the operational plan, it is important to explain how you plan to maintain your operations and how you will evaluate the impact of your programs.
The operational plan should give an overview of the day-to-day operations of your organization such as the people and organizations you work with (e.g. partners and suppliers), any legal requirements that your organization needs to meet (e.g. if you distribute food, you’ll need appropriate licenses and certifications), any insurance you have or will need, etc.
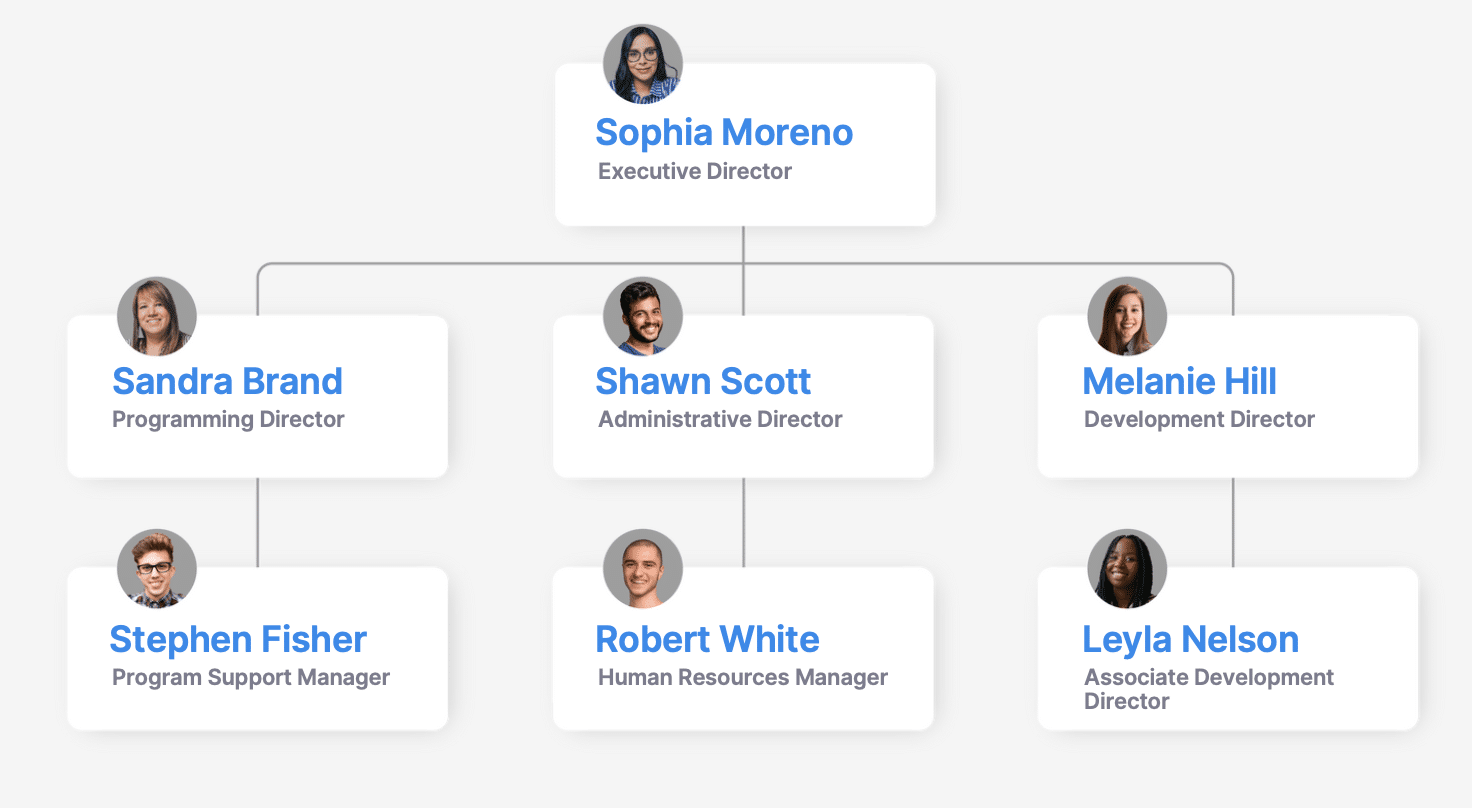
In the operational plan, also include a section on the people or your team. Describe the people who are crucial to your organization and any staff changes you plan as part of your business plan.
Pro tip: If you have an organizational chart, you can include it in the appendix to help illustrate how your organization operates. Learn more about the six types of nonprofit organizational charts and see them in action in this free e-book .
Step 7: Impact Plan
For a nonprofit, an impact plan is as important as a financial plan. A nonprofit seeks to create social change and a social return on investment, not just a financial return on investment.
Your impact plan should be precise about how your nonprofit will achieve this step. It should include details on what change you’re seeking to make, how you’re going to make it, and how you’re going to measure it.
This section turns your purpose and motivation into concrete accomplishments your nonprofit wants to make and sets specific goals and objectives.
These define the real bottom line of your nonprofit, so they’re the key to unlocking support. Funders want to know for whom, in what way, and exactly how you’ll measure your impact.
Answer these in the impact plan section of your business plan:
- What goals are most meaningful to the people you serve or the cause you’re fighting for?
- How can you best achieve those goals through a series of specific objectives?
E.g. “Finding jobs for an additional 200 unemployed people in the coming year.”
Step 8: Financial Plan
This is one of the most important parts of your nonprofit business plan. Creating a financial plan will allow you to make sure that your nonprofit has its basic financial needs covered.
Every nonprofit needs a certain level of funding to stay operational, so it’s essential to make sure your organization will meet at least that threshold.
To craft your financial plan:
- Outline your nonprofit’s current and projected financial status.
- Include an income statement, balance sheet , cash flow statement, and financial projections.
- List any grants you’ve received, significant contributions, and in-kind support.
- Include your fundraising plan .
- Identify gaps in your funding, and how you will manage them.
- Plan for what will be done with a potential surplus.
- Include startup costs, if necessary.
If your nonprofit is already operational, use established accounting records to complete this section of the business plan.
Knowing the financial details of your organization is incredibly important in a world where the public demands transparency about where their donations are going.
Pro tip : Leverage startup accelerators dedicated to nonprofits that can help you with funding, sponsorship, networking, and much more.
Step 9: Executive Summary
Normally written last but placed first in your business plan, your nonprofit executive summary provides an introduction to your entire business plan. The first page should describe your non-profit’s mission and purpose, summarize your market analysis that proves an identifiable need, and explain how your non-profit will meet that need.
The Executive Summary is where you sell your nonprofit and its ideas. Here you need to describe your organization clearly and concisely.
Make sure to customize your executive summary depending on your audience (i.e. your executive summary page will look different if your main goal is to win a grant or hire a board member).
Step 10: Appendix
Include extra documents in the section that are pertinent to your nonprofit: organizational chart , current fiscal year budget, a list of the board of directors, your IRS status letter, balance sheets, and so forth.
The appendix contains helpful additional information that might not be suitable for the format of your business plan (i.e. it might unnecessarily make it less readable or more lengthy).

Do’s and Dont’s of Nonprofit Business Plans – Tips
- Write clearly, using simple and easy-to-understand language.
- Get to the point, support it with facts, and then move on.
- Include relevant graphs and program descriptions.
- Include an executive summary.
- Provide sufficient financial information.
- Customize your business plan to different audiences.
- Stay authentic and show enthusiasm.
- Make the business plan too long.
- Use too much technical jargon.
- Overload the plan with text.
- Rush the process of writing, but don’t drag it either.
- Gush about the cause without providing a clear understanding of how you will help the cause through your activities.
- Keep your formatting consistent.
- Use standard 1-inch margins.
- Use a reasonable font size for the body.
- For print, use a serif font like Times New Roman or Courier. For digital, use sans serifs like Verdana or Arial.
- Start a new page before each section.
- Don’t allow your plan to print and leave a single line on an otherwise blank page.
- Have several people read over the plan before it is printed to make sure it’s free of errors.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
To help you get started we’ve created a nonprofit business plan outline. This business plan outline will work as a framework regardless of your nonprofit’s area of focus. With it, you’ll have a better idea of how to lay out your nonprofit business plan and what to include. We have also provided several questions and examples to help you create a detailed nonprofit business plan.
Download Your Free Outline

At Donorbox, we strive to make your nonprofit experience as productive as possible, whether through our donation software or through our advice and guides on the Nonprofit Blog . Find more free, downloadable resources in our Library .
Many nonprofits start with passion and enthusiasm but without a proper business plan. It’s a common misconception that just because an organization is labeled a “nonprofit,” it does not need to operate in any way like a business.
However, a nonprofit is a type of business, and many of the same rules that apply to a for-profit company also apply to a nonprofit organization.
As outlined above, your nonprofit business plan is a combination of your marketing plan , strategic plan, operational plan, impact plan, and financial plan. Remember, you don’t have to work from scratch. Be sure to use the nonprofit business plan outline we’ve provided to help create one of your own.
It’s important to note that your nonprofit should not be set in stone—it can and should change and evolve. It’s a living organism. While your vision, values, and mission will likely remain the same, your nonprofit business plan may need to be revised from time to time. Keep your audience in mind and adjust your plan as needed.
Finally, don’t let your plan gather dust on a shelf! Print it out, put up posters on your office walls, and read from it during your team meetings. Use all the research, data, and ideas you’ve gathered and put them into action!
If you want more help with nonprofit management tips and fundraising resources, visit our Nonprofit Blog . We also have dedicated articles for starting a nonprofit in different states in the U.S., including Texas , Minnesota , Oregon , Arizona , Illinois , and more.
Learn about our all-in-one online fundraising tool, Donorbox, and its simple-to-use features on the website here .

Raviraj heads the sales and marketing team at Donorbox. His growth-hacking abilities have helped Donorbox boost fundraising efforts for thousands of nonprofit organizations.
Join the fundraising movement!
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to receive the latest blogs, news, and more in your inbox.

- Insights & Analysis
- Nonprofit Jobs
Business Planning for Nonprofits
Business planning is a way of systematically answering questions such as, “What problem(s) are we trying to solve?” or “What are we trying to achieve?” and also, “Who will get us there, by when, and how much money and other resources will it take?”
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit’s mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising.
Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit’s operating environment. What if the sources of income that exist today change in the future? Is the nonprofit too reliant on one foundation for revenue? What happens if there’s an economic downturn?
A business plan can help the nonprofit and its board be prepared for future risks. What is the likelihood that the planned activities will continue as usual, and that revenue will continue at current levels – and what is Plan B if they don't?
Narrative of a business plan
You can think of a business plan as a narrative or story explaining how the nonprofit will operate given its activities, its sources of revenue, its expenses, and the inevitable changes in its internal and external environments over time. Ideally, your plan will tell the story in a way that will make sense to someone not intimately familiar with the nonprofit’s operations.
According to Propel Nonprofits , business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure.
A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine running – how much will be earned, how much from government grants or contracts, how much will be contributed? Within each of those broad categories, how much diversification exists, and should they be further diversified? Are there certain factors that need to be in place in order for today’s income streams to continue flowing?
The plan should address the everyday costs needed to operate the organization, as well as costs of specific programs and activities.
The plan may include details about the need for the organization's services (a needs assessment), the likelihood that certain funding will be available (a feasibility study), or changes to the organization's technology or staffing that will be needed in the future.
Another aspect of a business plan could be a "competitive analysis" describing what other entities may be providing similar services in the nonprofit's service and mission areas. What are their sources of revenue and staffing structures? How do their services and capacities differ from those of your nonprofit?
Finally, the business plan should name important assumptions, such as the organization's reserve policies. Do your nonprofit’s policies require it to have at least six months of operating cash on hand? Do you have different types of cash reserves that require different levels of board approval to release?
The idea is to identify the known, and take into consideration the unknown, realities of the nonprofit's operations, and propose how the nonprofit will continue to be financially healthy. If the underlying assumptions or current conditions change, then having a plan can be useful to help identify adjustments that must be made to respond to changes in the nonprofit's operating environment.
Basic format of a business plan
The format may vary depending on the audience. A business plan prepared for a bank to support a loan application may be different than a business plan that board members use as the basis for budgeting. Here is a typical outline of the format for a business plan:
- Table of contents
- Executive summary - Name the problem the nonprofit is trying to solve: its mission, and how it accomplishes its mission.
- People: overview of the nonprofit’s board, staffing, and volunteer structure and who makes what happen
- Market opportunities/competitive analysis
- Programs and services: overview of implementation
- Contingencies: what could change?
- Financial health: what is the current status, and what are the sources of revenue to operate programs and advance the mission over time?
- Assumptions and proposed changes: What needs to be in place for this nonprofit to continue on sound financial footing?
More About Business Planning
Budgeting for Nonprofits
Strategic Planning
Contact your state association of nonprofits for support and resources related to business planning, strategic planning, and other fundamentals of nonprofit leadership.
Additional Resources
- Components of transforming nonprofit business models (Propel Nonprofits)
- The matrix map: a powerful tool for nonprofit sustainability (Nonprofit Quarterly)
- The Nonprofit Business Plan: A Leader's Guide to Creating a Successful Business Model (David La Piana, Heather Gowdy, Lester Olmstead-Rose, and Brent Copen, Turner Publishing)
- Nonprofit Earned Income: Critical Business Model Considerations for Nonprofits (Nonprofit Financial Commons)
- Nonprofit Sustainability: Making Strategic Decisions for Financial Viability (Jan Masaoka, Steve Zimmerman, and Jeanne Bell)
Disclaimer: Information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is neither intended to be nor should be construed as legal, accounting, tax, investment, or financial advice. Please consult a professional (attorney, accountant, tax advisor) for the latest and most accurate information. The National Council of Nonprofits makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein.
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to write a nonprofit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan ensures your organization’s fundraising and activities align with your core mission.

Every nonprofit needs a mission statement that demonstrates how the organization will support a social cause and provide a public benefit. A nonprofit business plan fleshes out this mission statement in greater detail. These plans include many of the same elements as a for-profit business plan, with a focus on fundraising, creating a board of directors, raising awareness, and staying compliant with IRS regulations. A nonprofit business plan can be instrumental in getting your organization off the ground successfully.
Start with your mission statement
The mission statement is foundational for your nonprofit organization. The IRS will review your mission statement in determining whether to grant you tax-exempt status. This statement also helps you recruit volunteers and staff, fundraise, and plan activities for the year.
[Read more: Writing a Mission Statement: A Step-by-Step Guide ]
Therefore, you should start your business plan with a clear mission statement in the executive summary. The executive summary can also cover, at a high level, the goals, vision, and unique strengths of your nonprofit organization. Keep this section brief, since you will be going into greater detail in later sections.
Identify a board of directors
Many business plans include a section identifying the people behind the operation: your key leaders, volunteers, and full-time employees. For nonprofits, it’s also important to identify your board of directors. The board of directors is ultimately responsible for hiring and managing the CEO of your nonprofit.
“Board members are the fiduciaries who steer the organization towards a sustainable future by adopting sound, ethical, and legal governance and financial management policies, as well as by making sure the nonprofit has adequate resources to advance its mission,” wrote the Council of Nonprofits.
As such, identify members of your board in your business plan to give potential donors confidence in the management of your nonprofit.
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain.
Describe your organization’s activities
In this section, provide more information about what your nonprofit does on a day-to-day basis. What products, training, education, or other services do you provide? What does your organization do to benefit the constituents identified in your mission statement? Here’s an example from the American Red Cross, courtesy of DonorBox :
“The American Red Cross carries out their mission to prevent and relieve suffering with five key services: disaster relief, supporting America’s military families, lifesaving blood, health and safety services, and international service.”
This section should be detailed and get into the operational weeds of how your business delivers on its mission statement. Explain the strategies your team will take to service clients, including outreach and marketing, inventory and equipment needs, a hiring plan, and other key elements.
Write a fundraising plan
This part is the most important element of your business plan. In addition to providing required financial statements (e.g., the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), identify potential sources of funding for your nonprofit. These may include individual donors, corporate donors, grants, or in-kind support. If you are planning to host a fundraising event, put together a budget for that event and demonstrate the anticipated impact that event will have on your budget.

Create an impact plan
An impact plan ties everything together. It demonstrates how your fundraising and day-to-day activities will further your mission. For potential donors, it can make a very convincing case for why they should invest in your nonprofit.
“This section turns your purpose and motivation into concrete accomplishments your nonprofit wants to make and sets specific goals and objectives,” wrote DonorBox . “These define the real bottom line of your nonprofit, so they’re the key to unlocking support. Funders want to know for whom, in what way, and exactly how you’ll measure your impact.”
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain. Revisit your business plan as your organization grows to make sure the goals you’ve set both align with your mission and continue to be within reach.
[Read more: 8 Signs It's Time to Update Your Business Plan ]
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
6 ways to support your local chamber of commerce, what is a pricing markup, a complete guide to starting a b corp.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
- Sample Business Plans
- Nonprofit & Community
Charity Business Plan
Starting a charity business is a huge responsibility. To make a positive impact in society, you will need to build your charity business strong, for which you will need a detailed business plan.
Need help writing a business plan for your charity business? You’re at the right place. Our charity business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free charity business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write A Charity Business Plan?
Writing a charity business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
- Introduce your Business: Start your executive summary by briefly introducing your business to your readers.This section may include the name of your charity business, its location, when it was founded, the type of charity business (E.g., humanitarian charities, environmental charities, community development charities), etc.
- Market Opportunity: Summarize your market research, including market size, growth potential, and marketing trends. Highlight the opportunities in the market and how your business will fit in to fill the gap.
- Programs: Highlight the charity programs you offer your clients. The USPs and differentiators you offer are always a plus.For instance, you may include direct assistance, healthcare & medical services, social services, community development, etc.
- Marketing & Sales Strategies: Outline your sales and marketing strategies—what marketing platforms you use, how you plan on acquiring customers, etc.
- Financial Highlights: Briefly summarize your financial projections for the initial years of business operations. Include any capital or investment requirements, associated startup costs, projected revenues, and profit forecasts.
- Call to Action: Summarize your executive summary section with a clear CTA, for example, inviting angel investors to discuss the potential business investment.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your company. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
- Humanitarian charities
- Public charity
- Private charity
- Health charities
- Educational charities
- Environmental charities
- Animal welfare charities
- Describe the legal structure of your charity company, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
- Owners: List the names of your charity company’s founders or owners. Describe what shares they own and their responsibilities for efficiently managing the business.
- Mission Statement: Summarize your business’ objective, core principles, and values in your mission statement. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
- Business History: If you’re an established charity service provider, briefly describe your business history, like—when it was founded, how it evolved over time, etc.Additionally, If you have received any awards or recognition for excellent work, describe them.
- Future Goals: It’s crucial to convey your aspirations and vision. Mention your short-term and long-term goals; they can be specific targets for revenue, market share, or expanding your services.
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
- Target market: Start this section by describing your target market. Define your ideal customer and explain what types of services they prefer. Creating a buyer persona will help you easily define your target market to your readers.For instance, individual donors, corporate donors, government agencies, etc would be an ideal target audience for a charity business.
- Conduct SWOT analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) to determine the internal and external factors that may have an impact on the success of the charity.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and analyze your direct and indirect competitors. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and describe what differentiates your charity from them. Point out how you have a competitive edge in the market.
- Market Trends: Analyze emerging trends in the industry, such as technology disruptions, changes in customer behavior or preferences, etc. Explain how your business will cope with all the trends.For instance, there is a rise in online and digital giving has a booming market; explain how you plan on dealing with this potential growth opportunity.
- Regulatory Environment: List regulations and licensing requirements that may affect your charity company, such as legal structure & registration, tax-exempt status, reporting & financial transparency, fundraising regulations, etc.
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your charity business plan:
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products of Your Bicycle Shop
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
- Direct assistance
- Education and training
- Healthcare & medical services
- Social services
- Advocacy and awareness
- Describe the objectives behind programs: Give a brief description of the main aims and objectives of each program or service your charity provides. Explain in detail how these programs are created to meet the needs of your intended recipients and advance your overall purpose.
- Supportive services: Describe these services and how they support your primary programs if your charity offers them in addition to your core offerings, such as counseling, advocacy, or educational resources.
In short, this section of your charity plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Define your business’s USPs depending on the market you serve, the equipment you use, and the unique services you provide. Identifying USPs will help you plan your marketing strategies.For example, a clear mission & impact, innovative approach, specialized expertise, collaborations & partnership, etc could be some of the great USPs for a charity company.
- Marketing Mix: Describe your marketing mix to reach your target audience, including product, price, promotion, and place elements of your marketing strategy. Your strategy should consider how you will create and deliver value, how you will price your offerings, how you will communicate and persuade, and how you will distribute and deliver your offerings.
- Marketing channels: Describe how your organization intends to reach its target audience. In addition to social media, email marketing, public relations, events, webinars, partnerships, and direct email, you may use other marketing channels to promote your offerings.
- Fundraising Strategies: Describe the fundraising strategies you plan on implementing to generate revenue for your nonprofit. Your nonprofit may generate income from grants, major gifts, individual giving, charity events, online fundraising, corporate sponsorship, etc.Identify fundraising strategies that align with the nonprofit’s mission, vision, and values.
- Donor Retention: Describe how your nonprofit will retain donors and build loyalty. Your donor retention strategies may involve sending regular updates and impact reports, creating donor recognition programs, or asking for feedback and input.
Overall, this section of your charity business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your charity business, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
- Staffing & Training: Mention your business’s staffing requirements, including the number of employees or fundraising coordinator, program manager, or other staff needed. Include their qualifications, the training required, and the duties they will perform.
- Operational Process: Outline the processes and procedures you will use to run your charity business. Your operational processes may include program development & management, fundraising & donor management, financial management, marketing & communications, etc.
- Equipment & Software: Include the list of equipment and software required for charity, such as office equipment, software & IT infrastructure, communication & presentation tools, fundraising equipment, vehicles & transportation, etc.Explain how these technologies help you maintain quality standards and improve the efficiency of your business operations.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your charity business’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Founders/CEO: Mention the founders and CEO of your charity company, and describe their roles and responsibilities in successfully running the business.
- Key managers: Introduce your management and key members of your team, and explain their roles and responsibilities.It should include, key executives(e.g. COO, CMO.), senior management, and other department managers (e.g. operations manager, finance manager, customer services manager.) involved in the charity business operations, including their education, professional background, and any relevant experience in the industry.
- Organizational structure: Explain the organizational structure of your management team. Include the reporting line and decision-making hierarchy.
- Compensation Plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management and staff. Include their salaries, incentives, and other benefits.
- Advisors/Consultants: Mentioning advisors or consultants in your business plans adds credibility to your business idea.So, if you have any advisors or consultants, include them with their names and brief information consisting of roles and years of experience.
This section should describe the key personnel for your charity, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
- Profit & loss statement: Describe details such as projected revenue, operational costs, and service costs in your projected profit and loss statemen t. Make sure to include your business’s expected net profit or loss.
- Cash flow statement: The cash flow for the first few years of your operation should be estimated and described in this section. This may include billing invoices, payment receipts, loan payments, and any other cash flow statements.
- Balance Sheet: Create a projected balance sheet documenting your charity business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-even point: Determine and mention your business’s break-even point—the point at which your business costs and revenue will be equal.This exercise will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to sustain or be profitable.
- Financing Needs: Calculate costs associated with starting a charity business, and estimate your financing needs and how much capital you need to raise to operate your business. Be specific about your short-term and long-term financing requirements, such as investment capital or loans.
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your charity business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample charity business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful charity plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our charity business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Youth Mentoring Program Business
Nonprofit Business Plan
How to Write a Business Plan for a Small Business
Best Top Business Planner Tools
Business Location Selection Process
Business Plan Cover Page Crafting Steps
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do you need a charity business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful charity business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your charity company.
How to get funding for your charity business?
There are several ways to get funding for your charity business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your charity business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and ideas better than you, so we recommend you write your charity business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your charity business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any charity business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
How do I write a good market analysis in a charity business plan?
Market analysis is one of the key components of your business plan that requires deep research and a thorough understanding of your industry. We can categorize the process of writing a good market analysis section into the following steps:
- Stating the objective of your market analysis—e.g., investor funding.
- Industry study—market size, growth potential, market trends, etc.
- Identifying target market—based on user behavior and demographics.
- Analyzing direct and indirect competitors.
- Calculating market share—understanding TAM, SAM, and SOM.
- Knowing regulations and restrictions
- Organizing data and writing the first draft.
Writing a marketing analysis section can be overwhelming, but using ChatGPT for market research can make things easier.
How detailed should the financial projections be in my charity business plan?
The level of detail of the financial projections of your charity business may vary considering various business aspects like direct and indirect competition, pricing, and operational efficiency. However, your financial projections must be comprehensive enough to demonstrate a complete view of your financial performance.
Generally, the statements included in a business plan offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
What key components should a charity business plan include?
The following are the key components your charity business plan must include:
- Executive summary
- Business Overview
- Market Analysis
- Products and services
- Sales and marketing strategies
- Operations plan
- Management team
- Financial plan
Can a good charity business plan help me secure funding?
Indeed. A well-crafted charity business will help your investors better understand your business domain, market trends, strategies, business financials, and growth potential—helping them make better financial decisions.
So, if you have a profitable and investable business, a comprehensive business plan can certainly help you secure your business funding.
What's the importance of a marketing strategy in a charity business plan?
Marketing strategy is a key component of your charity business plan. Whether it is about achieving certain business goals or helping your investors understand your plan to maximize their return on investment—an impactful marketing strategy is the way to do it!
Here are a few pointers to help you understand the importance of having an impactful marketing strategy:
- It provides your business an edge over your competitors.
- It helps investors better understand your business and growth potential.
- It helps you develop products with the best profit potential.
- It helps you set accurate pricing for your products or services.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more

Turn your business idea into a solid business plan
Explore Plan Builder
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan can be an invaluable tool for your nonprofit. Even a short business plan pushes you to do research, crystalize your purpose, and polish your messaging. This blog shares what it is and why you need it, ten steps to help you write one, and the dos and don’ts of creating a nonprofit business plan.
A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine running – how much will be earned, how much from government grants or contracts, how much will be contributed?
A nonprofit business plan outlines your business’ current situation and provides a roadmap for reaching your desired position. It explains your strengths, weaknesses, target market, opportunities, and fundraising strategy at a glance.
Everything you need to know about a nonprofit business plan, including what it is (with examples) and how to write one effectively.
This section should be detailed and get into the operational weeds of how your business delivers on its mission statement. Explain the strategies your team will take to service clients, including outreach and marketing, inventory and equipment needs, a hiring plan, and other key elements.
Discover the key elements to include in your charity business plan. Our guide offers practical advice, templates, and examples to help you write your own.