- C Data Types
- C Operators
- C Input and Output
- C Control Flow
- C Functions
- C Preprocessors
- C File Handling
- C Cheatsheet
- C Interview Questions

Assignment Operators in C
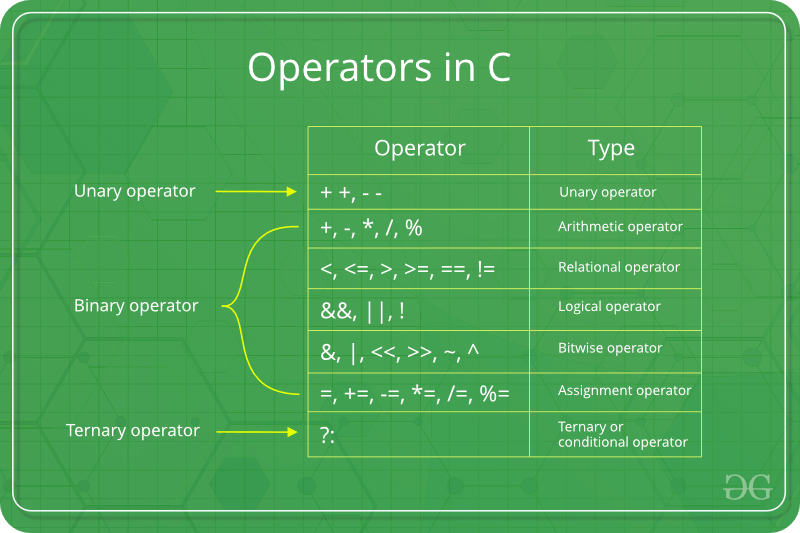
Assignment operators are used for assigning value to a variable. The left side operand of the assignment operator is a variable and right side operand of the assignment operator is a value. The value on the right side must be of the same data-type of the variable on the left side otherwise the compiler will raise an error.
Different types of assignment operators are shown below:
1. “=”: This is the simplest assignment operator. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. Example:
2. “+=” : This operator is combination of ‘+’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first adds the current value of the variable on left to the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
If initially value stored in a is 5. Then (a += 6) = 11.
3. “-=” This operator is combination of ‘-‘ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first subtracts the value on the right from the current value of the variable on left and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
If initially value stored in a is 8. Then (a -= 6) = 2.
4. “*=” This operator is combination of ‘*’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first multiplies the current value of the variable on left to the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
If initially value stored in a is 5. Then (a *= 6) = 30.
5. “/=” This operator is combination of ‘/’ and ‘=’ operators. This operator first divides the current value of the variable on left by the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left. Example:
If initially value stored in a is 6. Then (a /= 2) = 3.
Below example illustrates the various Assignment Operators:
Similar Reads
- C-Operators
- cpp-operator
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

- C Programming Tutorial
- Basics of C
- C - Overview
- C - Features
- C - History
- C - Environment Setup
- C - Program Structure
- C - Hello World
- C - Compilation Process
- C - Comments
- C - Keywords
- C - Identifiers
- C - User Input
- C - Basic Syntax
- C - Data Types
- C - Variables
- C - Integer Promotions
- C - Type Conversion
- C - Type Casting
- C - Booleans
- Constants and Literals in C
- C - Constants
- C - Literals
- C - Escape sequences
- C - Format Specifiers
- Operators in C
- C - Operators
- C - Arithmetic Operators
- C - Relational Operators
- C - Logical Operators
- C - Bitwise Operators
- C - Assignment Operators
- C - Unary Operators
- C - Increment and Decrement Operators
- C - Ternary Operator
- C - sizeof Operator
- C - Operator Precedence
- C - Misc Operators
- Decision Making in C
- C - Decision Making
- C - if statement
- C - if...else statement
- C - nested if statements
- C - switch statement
- C - nested switch statements
- C - While loop
- C - For loop
- C - Do...while loop
- C - Nested loop
- C - Infinite loop
- C - Break Statement
- C - Continue Statement
- C - goto Statement
- Functions in C
- C - Functions
- C - Main Function
- C - Function call by Value
- C - Function call by reference
- C - Nested Functions
- C - Variadic Functions
- C - User-Defined Functions
- C - Callback Function
- C - Return Statement
- C - Recursion
- Scope Rules in C
- C - Scope Rules
- C - Static Variables
- C - Global Variables
- Arrays in C
- C - Properties of Array
- C - Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- C - Passing Arrays to Function
- C - Return Array from Function
- C - Variable Length Arrays
- Pointers in C
- C - Pointers
- C - Pointers and Arrays
- C - Applications of Pointers
- C - Pointer Arithmetics
- C - Array of Pointers
- C - Pointer to Pointer
- C - Passing Pointers to Functions
- C - Return Pointer from Functions
- C - Function Pointers
- C - Pointer to an Array
- C - Pointers to Structures
- C - Chain of Pointers
- C - Pointer vs Array
- C - Character Pointers and Functions
- C - NULL Pointer
- C - void Pointer
- C - Dangling Pointers
- C - Dereference Pointer
- C - Near, Far and Huge Pointers
- C - Initialization of Pointer Arrays
- C - Pointers vs. Multi-dimensional Arrays
- Strings in C
- C - Strings
- C - Array of Strings
- C - Special Characters
- C Structures and Unions
- C - Structures
- C - Structures and Functions
- C - Arrays of Structures
- C - Self-Referential Structures
- C - Lookup Tables
- C - Dot (.) Operator
- C - Enumeration (or enum)
- C - Structure Padding and Packing
- C - Nested Structures
- C - Anonymous Structure and Union
- C - Bit Fields
- C - Typedef
- File Handling in C
- C - Input & Output
- C - File I/O (File Handling)
- C Preprocessors
- C - Preprocessors
- C - Pragmas
- C - Preprocessor Operators
- C - Header Files
- Memory Management in C
- C - Memory Management
- C - Memory Address
- C - Storage Classes
- Miscellaneous Topics
- C - Error Handling
- C - Variable Arguments
- C - Command Execution
- C - Math Functions
- C - Static Keyword
- C - Random Number Generation
- C - Command Line Arguments
- C Programming Resources
- C - Questions & Answers
- C - Quick Guide
- C - Cheat Sheet
- C - Useful Resources
- C - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Assignment Operators in C
In C language, the assignment operator stores a certain value in an already declared variable. A variable in C can be assigned the value in the form of a literal, another variable, or an expression.
The value to be assigned forms the right-hand operand, whereas the variable to be assigned should be the operand to the left of the " = " symbol, which is defined as a simple assignment operator in C.
In addition, C has several augmented assignment operators.
The following table lists the assignment operators supported by the C language −
Simple Assignment Operator (=)
The = operator is one of the most frequently used operators in C. As per the ANSI C standard, all the variables must be declared in the beginning. Variable declaration after the first processing statement is not allowed.
You can declare a variable to be assigned a value later in the code, or you can initialize it at the time of declaration.
You can use a literal, another variable, or an expression in the assignment statement.
Once a variable of a certain type is declared, it cannot be assigned a value of any other type. In such a case the C compiler reports a type mismatch error.
In C, the expressions that refer to a memory location are called "lvalue" expressions. A lvalue may appear as either the left-hand or right-hand side of an assignment.
On the other hand, the term rvalue refers to a data value that is stored at some address in memory. A rvalue is an expression that cannot have a value assigned to it which means an rvalue may appear on the right-hand side but not on the left-hand side of an assignment.
Variables are lvalues and so they may appear on the left-hand side of an assignment. Numeric literals are rvalues and so they may not be assigned and cannot appear on the left-hand side. Take a look at the following valid and invalid statements −
Augmented Assignment Operators
In addition to the = operator, C allows you to combine arithmetic and bitwise operators with the = symbol to form augmented or compound assignment operator. The augmented operators offer a convenient shortcut for combining arithmetic or bitwise operation with assignment.
For example, the expression "a += b" has the same effect of performing "a + b" first and then assigning the result back to the variable "a".
Run the code and check its output −
Similarly, the expression "a <<= b" has the same effect of performing "a << b" first and then assigning the result back to the variable "a".
Here is a C program that demonstrates the use of assignment operators in C −
When you compile and execute the above program, it will produce the following result −
- Assignment Statement
An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program .
Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted by a variable name.

The symbol used in an assignment statement is called as an operator . The symbol is ‘=’ .
Note: The Assignment Operator should never be used for Equality purpose which is double equal sign ‘==’.
The Basic Syntax of Assignment Statement in a programming language is :
variable = expression ;
variable = variable name
expression = it could be either a direct value or a math expression/formula or a function call
Few programming languages such as Java, C, C++ require data type to be specified for the variable, so that it is easy to allocate memory space and store those values during program execution.
data_type variable_name = value ;
In the above-given examples, Variable ‘a’ is assigned a value in the same statement as per its defined data type. A data type is only declared for Variable ‘b’. In the 3 rd line of code, Variable ‘a’ is reassigned the value 25. The 4 th line of code assigns the value for Variable ‘b’.
Assignment Statement Forms
This is one of the most common forms of Assignment Statements. Here the Variable name is defined, initialized, and assigned a value in the same statement. This form is generally used when we want to use the Variable quite a few times and we do not want to change its value very frequently.
Tuple Assignment
Generally, we use this form when we want to define and assign values for more than 1 variable at the same time. This saves time and is an easy method. Note that here every individual variable has a different value assigned to it.
(Code In Python)
Sequence Assignment
(Code in Python)
Multiple-target Assignment or Chain Assignment
In this format, a single value is assigned to two or more variables.
Augmented Assignment
In this format, we use the combination of mathematical expressions and values for the Variable. Other augmented Assignment forms are: &=, -=, **=, etc.
Browse more Topics Under Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Concept of Data types
- Built-in Data Types
- Constants in Programing Language
- Access Modifier
- Variables of Built-in-Datatypes
- Declaration/Initialization of Variables
- Type Modifier
Few Rules for Assignment Statement
Few Rules to be followed while writing the Assignment Statements are:
- Variable names must begin with a letter, underscore, non-number character. Each language has its own conventions.
- The Data type defined and the variable value must match.
- A variable name once defined can only be used once in the program. You cannot define it again to store other types of value.
- If you assign a new value to an existing variable, it will overwrite the previous value and assign the new value.
FAQs on Assignment Statement
Q1. Which of the following shows the syntax of an assignment statement ?
- variablename = expression ;
- expression = variable ;
- datatype = variablename ;
- expression = datatype variable ;
Answer – Option A.
Q2. What is an expression ?
- Same as statement
- List of statements that make up a program
- Combination of literals, operators, variables, math formulas used to calculate a value
- Numbers expressed in digits
Answer – Option C.
Q3. What are the two steps that take place when an assignment statement is executed?
- Evaluate the expression, store the value in the variable
- Reserve memory, fill it with value
- Evaluate variable, store the result
- Store the value in the variable, evaluate the expression.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Variables in Programming Language
- Concept of Data Types
- Declaration of Variables
- Type Modifiers
- Access Modifiers
- Constants in Programming Language
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

01 Career Opportunities
02 beginner, 03 intermediate, 04 advanced, 05 training programs, c programming assignment operators, free c programming online course with certificate, what is an assignment operator in c, types of assignment operators in c, 1. simple assignment operator (=), example of simple assignment operator, 2. compound assignment operators, example of augmented arithmetic and assignment operators, example of augmented bitwise and assignment operators, practice problems on assignment operators in c, 1. what will the value of "x" be after the execution of the following code, 2. after executing the following code, what is the value of the number variable, benefits of using assignment operators, best practices and tips for using the assignment operator, about author, live batches schedule view all.
Home » Learn C Programming from Scratch » C Assignment Operators
C Assignment Operators
Summary : in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the C assignment operators and how to use them effectively.
Introduction to the C assignment operators
An assignment operator assigns the vale of the right-hand operand to the left-hand operand. The following example uses the assignment operator (=) to assign 1 to the counter variable:
After the assignmment, the counter variable holds the number 1.
The following example adds 1 to the counter and assign the result to the counter:
The = assignment operator is called a simple assignment operator. It assigns the value of the left operand to the right operand.
Besides the simple assignment operator, C supports compound assignment operators. A compound assignment operator performs the operation specified by the additional operator and then assigns the result to the left operand.
The following example uses a compound-assignment operator (+=):
The expression:
is equivalent to the following expression:
The following table illustrates the compound-assignment operators in C:
- A simple assignment operator assigns the value of the left operand to the right operand.
- A compound assignment operator performs the operation specified by the additional operator and then assigns the result to the left operand.
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
C Assignment Operators
- 6 contributors
An assignment operation assigns the value of the right-hand operand to the storage location named by the left-hand operand. Therefore, the left-hand operand of an assignment operation must be a modifiable l-value. After the assignment, an assignment expression has the value of the left operand but isn't an l-value.
assignment-expression : conditional-expression unary-expression assignment-operator assignment-expression
assignment-operator : one of = *= /= %= += -= <<= >>= &= ^= |=
The assignment operators in C can both transform and assign values in a single operation. C provides the following assignment operators:
In assignment, the type of the right-hand value is converted to the type of the left-hand value, and the value is stored in the left operand after the assignment has taken place. The left operand must not be an array, a function, or a constant. The specific conversion path, which depends on the two types, is outlined in detail in Type Conversions .
- Assignment Operators
Was this page helpful?

Additional resources
Assignment Statement (=) in C Language
Assignment Statement in C language is a statement that assigns or set a value to a variable during program execution. Assignement statements in programming allows the programmer to change or set the value stored in variable using Assignment(=) Operator. The process of assigning the value to a variable using the assignment(=) operator is known as an assignment statement in C. Assignment(=) Operator Assigns The value or value in a variable on right hand side to the variable on the left hand side. The data type of the variable on right hand side should match to the data type of variable or constant or expression on right hand side. C Language has different (types) ways to assigns values to variable, we will learn from the diagram given below.
Syntax :1.Basic Assignment statement
Data Type Variable_name = variable/ constant /expression; The Variable_name is assigned the values in variable or constants or expression. The data type of the variable/ constant/expression on right hand side should match to the left hand side variable Variable_name with a few exceptions where automatic type conversions are possible.
Naming Rules or conventions for Assignment Statement
Programmer need to follow some Rules while writing the Assignment Statements in C program: 1. Variable names should not begin or start with number. Variable name can a letter, underscore, non-number any character like alphabet,underscore. 2. A new value assigned to an existing variable will overwrite the previous value and assign the new value to the variable. 3. The Data type defined and the variable value must match. 4.All the statements declaration must end with a semi-colon. (;) 5. The name of variable must be meaningful and clearly describe the purpose of variable name. 6.Duplicate name of variable is not allowed i.e the name once defined can only be used once in the program. programmer cannot redefine it to store other types of value.

Example 1: C program to illustrates the use of Simple Assignment statement .
/* e.g. C program to illustrate the use of simple Assignment statement or basic of assignment statements */ #include<stdio.h> int main() { int a,b,c; float avg; a = 9 ; c = 10 ; b = c ; printf("\n a=%d",a); printf("\n b=%d",b); printf("\n c=%d",c); b = c+3; printf("\n Value of b after b=c+3-->%d",b); avg = (b+c) / 2.0; printf("\n Value of avg=%.2f",avg); a = b && c; printf("\n a=b&&c--->%d",a); a = (b+c) && (b <c); printf("\n a=(b+c) && (b <c)--->%d",a); return(0); } Output: a=9 b=10 c=10 Value of b after b=c+3-->13 Value of avg=11.50 a=b&&c--->1 a=(b+c) && (b <c)--->0
Program Explanation: 1. In the above program a,b,c is declared as integer variable to store the numbers where as avg is declared as float. int a,b,c; float avg; 2. a = 9 ; c = 10 ; b = c ; variable a is assigned value 9. variable c is assigned value 10. and b is assigned the value of c. Here value of b is 10 .i.e. b=10 3. printf("\n a=%d",a); printf("\n b=%d",b); printf("\n c=%d",c); The above statements displays the integer values of variable a,b,c a=9 b=10 c=10 4. b = c+3; printf("\n Value of b after b=c+3-->%d",b); here 3 is added in c(value of vaiable c is 10) it becomes 13 and value 13 is assigned to left hand side variable b , here b is 13 i.e. b=13. the printf() displays output " Value of b after b=c+3--->13". 5. avg = (b+c) / 2.0; printf("\n Value of avg=%.2f",avg); After execution of a=(b+c)/2.0 the value of a is 11.50 so the output shown by printf() is "Value of avg=11.50". 6. a = b && c; printf("\n a=b&&c--->%d",a); Logical anding operation is performed on the values in the variables a and b. The value of c=10 and the value of b=13. After succesful execution of this statement value of variable a is 1 or 'true'. Any value in a variable except 'zero' (0 i.e false) is considered 'true' or 1. The variable a is assigned to the integer value 1 which is true. so a=1 && 1 is a=1 or a=true && true is a=true or a=1. printf("\n a=b&&c--->%d",a); displays output a=b&&c---->1 7. a = (b+c) && (b <c); printf("\n a=(b+c) && (b <c)--->%d",a); here expression (b+c) is true(1) and (b <c) is false(0). so the entire expression evaluates to false(0) and the value is assigned to the variable a i.e a=0. the printf() display the message " a=(b+c) && (b <c)--->0 "
2.Compound Assignment: As we learn in above section the simple assignment statement is used to assign values in right hand side variable to left hand side variable using = operator. A compound assignment operator has a shorter syntax to assign the result. A compound assignment operator or statements are used to do mathematical operation in shortcut. Two operands needs to perform the compound assignment operations. The operation is performed on the two operands before the result is assigned to the first operand. compound assignment operator are binary operators that modify the variable to their left hand side using the value or variable to their right.
Syntax: expression1+= expression2; These type of expression can also be written in expanded form, that is expression1=expression1+expression2;
+= Operator is called compound assignment operator. C Language provides the following list of compound Assignment Operators. 1. += plus equal to += is Addition and Assignment operators. It add the value of the variable1 and variable2 and assigns the result to variable1. e.g. X+=Y In the above expression the addition of values in X and Y is performd and assigns result to X. The expression X+=Y is same as X=X+Y 2. -= minus equal to -= is Subtraction and Assignment operators. It Subtract the value of the variable2 from variable1 and assigns the result to variable1. e.g. X-=Y In the above expression the subtraction is performd,the value of X is subtracted from the value in X and assigns result to X. The expression X-=Y is same as X=X-Y 3. *= Multiplication equal to *= is Multiplication and Assignment operators. It Multiply the value of the variable1 and variable2 and assigns the result to variable1. e.g. X*=Y In the above expression the Multiplication is performd,the value of X is Multiplyed to the value in Y and assigns result to X. The expression X*=Y is same as X=X*Y 4. /= Division equal to *= is Division and Assignment operators. It Divides the value of the variable1 byvariable2 and assigns the result to variable1. e.g. X/=Y In the above expression the Division is performd,the value of X is Divided by the value in Y and assigns result to X. The expression X/=Y is same as X=X/Y 5. %= Modulus equal to %= is Modulus and Assignment operators. It Divides the value of the variable1 byvariable2 and assigns the remainder to variable1. e.g. X%=Y In the above expression the Division is performd,the value of X is Divided by the value in Y and assigns remainder to X. The expression X%=Y is same as X=X%Y 6. &= Bitwise and equal to &= is Bitwise AND and Assignment operators. It performs the bitwise AND with variable1 and variable2 and assigns the result to variable1. e.g. X&=Y In the above expression the bitwise anding operation is performd, after executing the X&=Y expression the result is assigned to X. The expression X&=Y is same as X=X&Y 7. |= Bitwise OR equal to != is Bitwise OR Assignment operators. It performs the bitwise OR with variable1 and variable2 and assigns the result to variable1. e.g. X|=Y In the above expression the bitwise OR operation is performd, after executing the X|=Y expression the result is assigned to X. The expression X|=Y is same as X=X|Y 8. ^= Bitwise XOR equal to ^= is Bitwise XOR Assignment operators. It performs the bitwise XOR with variable1 and variable2 and assigns the result to variable1. e.g. X^=Y In the above expression the bitwise XOR operation is performd, after executing the X^=Y expression the result is assigned to X. The expression X^=Y is same as X=X^Y. 9. Bitwise left shift and equal to e.g. X In the above expression the bitwise left shift operation is performd, after executing the X The expression X 10. >>= Bitwise right shift and equal to >>= is Bitwise Right Shift and Assignment operators. It performs the bitwise Right shift with variable1 and assigns the result to variable1. e.g. X>>=Y In the above expression the bitwise right shift operation is performd, after executing the X>>=Y expression the result is assigned to X. The expression X>>=Y is same as X=X>>Y Lets Learn and practice The Assigment operator in detail using the following C program.
2. Assignment Operator complete C Program.
#include <stdio.h> int main() { /* Simple Assignment*/ int x,i; int y,j; float c=30.0; float d=5.0; /*Nested or Multiple Assignment */ x = i = 5; y = j = 3; /*Compound Assignment*/ x += y; printf("After Add and Assign :%d \n",x); i -= j; printf("After Subtract and Assign :%d \n",i); x *= y; printf("After Multiple and Assign :%d \n",x); c /= d; printf("After Divide and Assign :%f \n",c); j %= i; printf("After Modulo and Assign :%d \n",j); j &= i; printf("After Bitwise And and Assign :%d \n",j); j |= i; printf("After Bitwise OR and Assign :%d \n",j); x ^= y; printf("After Bitwise XOR and Assign :%d \n",a); x printf ("After Bitwise Left Shift and Assign :%d \n",a); x >>= 3; printf ("After Bitwise Right Shift and Assign :%d \n",a); return(0); }
Output: After Add and Assign :8 After Subtract and Assign :2 After Multiple and Assign :24 After Divide and Assign :6.000000 After Modulo and Assign :1 After Bitwise And and Assign :0 After Bitwise OR and Assign :2 After Bitwise XOR and Assign :27 After Bitwise Left Shift and Assign :108 After Bitwise Right Shift and Assign :13
/** * C program to check leap year using conditional operator ? */ #include <stdio.h> int main() { int year; /* * Input the year from user */ printf("Enter any year: "); scanf("%d", &year); /* * If year%4==0 and year%100==0 then * print leap year * else if year%400==0 then * print leap year * else * print common year */ (year%4==0 && year%100!=0) ? printf("LEAP YEAR") : (year%400 ==0 ) ? printf("LEAP YEAR") : printf("COMMON YEAR"); return 0; } Output: Enter any year 2004 LEAP YEAR
/** * C program to check leap year using conditional operator ? */ #include <stdio.h> int main() { int year; /* * Input the year from user */ printf("Enter any year: "); scanf("%d", &year); /* If year%4==0 and year%100==0 then print leap year else if year%400==0 then print leap year else print common year */ (year%4==0 && year%100!=0) ? printf("LEAP YEAR") : (year%400 ==0 ) ? printf("LEAP YEAR") : printf("COMMON YEAR"); return 0; } Output: Enter any year 2004 LEAP YEAR
Previous Topic:-->> Constant and Literals in C || Next topic:-->> Input/Output in C.
Get in touch
C Programming Tutorial
- Assignment Operator in C
Last updated on July 27, 2020
We have already used the assignment operator ( = ) several times before. Let's discuss it here in detail. The assignment operator ( = ) is used to assign a value to the variable. Its general format is as follows:
The operand on the left side of the assignment operator must be a variable and operand on the right-hand side must be a constant, variable or expression. Here are some examples:
The precedence of the assignment operator is lower than all the operators we have discussed so far and it associates from right to left.
We can also assign the same value to multiple variables at once.
here x , y and z are initialized to 100 .
Since the associativity of the assignment operator ( = ) is from right to left. The above expression is equivalent to the following:
Note that expressions like:
are called assignment expression. If we put a semicolon( ; ) at the end of the expression like this:
then the assignment expression becomes assignment statement.
Compound Assignment Operator #
Assignment operations that use the old value of a variable to compute its new value are called Compound Assignment.
Consider the following two statements:
Here the second statement adds 5 to the existing value of x . This value is then assigned back to x . Now, the new value of x is 105 .
To handle such operations more succinctly, C provides a special operator called Compound Assignment operator.
The general format of compound assignment operator is as follows:
where op can be any of the arithmetic operators ( + , - , * , / , % ). The above statement is functionally equivalent to the following:
Note : In addition to arithmetic operators, op can also be >> (right shift), << (left shift), | (Bitwise OR), & (Bitwise AND), ^ (Bitwise XOR). We haven't discussed these operators yet.
After evaluating the expression, the op operator is then applied to the result of the expression and the current value of the variable (on the RHS). The result of this operation is then assigned back to the variable (on the LHS). Let's take some examples: The statement:
is equivalent to x = x + 5; or x = x + (5); .
Similarly, the statement:
is equivalent to x = x * 2; or x = x * (2); .
Since, expression on the right side of op operator is evaluated first, the statement:
is equivalent to x = x * (y + 1) .
The precedence of compound assignment operators are same and they associate from right to left (see the precedence table ).
The following table lists some Compound assignment operators:
The following program demonstrates Compound assignment operators in action:
Expected Output:
Load Comments
- Intro to C Programming
- Installing Code Blocks
- Creating and Running The First C Program
- Basic Elements of a C Program
- Keywords and Identifiers
- Data Types in C
- Constants in C
- Variables in C
- Input and Output in C
- Formatted Input and Output in C
- Arithmetic Operators in C
- Operator Precedence and Associativity in C
- Increment and Decrement Operators in C
- Relational Operators in C
- Logical Operators in C
- Conditional Operator, Comma operator and sizeof() operator in C
- Implicit Type Conversion in C
- Explicit Type Conversion in C
- if-else statements in C
- The while loop in C
- The do while loop in C
- The for loop in C
- The Infinite Loop in C
- The break and continue statement in C
- The Switch statement in C
- Function basics in C
- The return statement in C
- Actual and Formal arguments in C
- Local, Global and Static variables in C
- Recursive Function in C
- One dimensional Array in C
- One Dimensional Array and Function in C
- Two Dimensional Array in C
- Pointer Basics in C
- Pointer Arithmetic in C
- Pointers and 1-D arrays
- Pointers and 2-D arrays
- Call by Value and Call by Reference in C
- Returning more than one value from function in C
- Returning a Pointer from a Function in C
- Passing 1-D Array to a Function in C
- Passing 2-D Array to a Function in C
- Array of Pointers in C
- Void Pointers in C
- The malloc() Function in C
- The calloc() Function in C
- The realloc() Function in C
- String Basics in C
- The strlen() Function in C
- The strcmp() Function in C
- The strcpy() Function in C
- The strcat() Function in C
- Character Array and Character Pointer in C
- Array of Strings in C
- Array of Pointers to Strings in C
- The sprintf() Function in C
- The sscanf() Function in C
- Structure Basics in C
- Array of Structures in C
- Array as Member of Structure in C
- Nested Structures in C
- Pointer to a Structure in C
- Pointers as Structure Member in C
- Structures and Functions in C
- Union Basics in C
- typedef statement in C
- Basics of File Handling in C
- fputc() Function in C
- fgetc() Function in C
- fputs() Function in C
- fgets() Function in C
- fprintf() Function in C
- fscanf() Function in C
- fwrite() Function in C
- fread() Function in C
Recent Posts
- Machine Learning Experts You Should Be Following Online
- 4 Ways to Prepare for the AP Computer Science A Exam
- Finance Assignment Online Help for the Busy and Tired Students: Get Help from Experts
- Top 9 Machine Learning Algorithms for Data Scientists
- Data Science Learning Path or Steps to become a data scientist Final
- Enable Edit Button in Shutter In Linux Mint 19 and Ubuntu 18.04
- Python 3 time module
- Pygments Tutorial
- How to use Virtualenv?
- Installing MySQL (Windows, Linux and Mac)
- What is if __name__ == '__main__' in Python ?
- Installing GoAccess (A Real-time web log analyzer)
- Installing Isso

Assignment Operators In C [ Full Information With Examples ]
![Assignment Operators In C [ Full Information With Examples ] Assignment Operators In C](https://cstutorialpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Assignment-Operators-in-C-.png)
Assignment Operators In C
Assignment operators is a binary operator which is used to assign values in a variable , with its right and left sides being a one-one operand. The operand on the left side is variable in which the value is assigned and the right side operands can contain any of the constant, variable, and expression.
The Assignment operator is a lower priority operator. its priority has much lower than the rest of the other operators. Its priority is more than just the comma operator. The priority of all other operators is more than the assignment operator.
We can assign the same value to multiple variables simultaneously by the assignment operator.
x = y = z = 100
Here x, y, and z are initialized to 100.
In C language, the assignment operator can be divided into two categories.
- Simple assignment operator
- Compound assignment operators
1. Simple Assignment Operator In C
This operator is used to assign left-side values to the right-side operands, simple assignment operators are represented by (=).
2. Compound Assignment Operators In C
Compound Assignment Operators use the old value of a variable to calculate its new value and reassign the value obtained from the calculation to the same variable.
Examples of compound assignment operators are: (Example: + =, – =, * =, / =,% =, & =, ^ =)
Look at these two statements:
Here in this example, adding 5 to the x variable in the second statement is again being assigned to the x variable.
Compound Assignment Operators provide us with the C language to perform such operation even more effecient and in less time.
Syntax of Compound Assignment Operators
Here op can be any arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /,%).
The above statement is equivalent to the following depending on the function:
Let us now know about some important compound assignment operators one by one.
“+ =” -: This operator adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the output to the left operand.
“- =” -: This operator subtracts the right operand from the left operand and returns the result to the left operand.
“* =” -: This operator multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
“/ =” -: This operator splits the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
“% =” -: This operator takes the modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand.
There are many other assignment operators such as left shift and (<< =) operator, right shift and operator (>> =), bitwise and assignment operator (& =), bitwise OR assignment operator (^ =)
List of Assignment Operators In C
Read More -:
- What is Operators In C
- Relational Operators In C
- Logical Operators In C
- Bitwise Operators In C
- Arithmetic Operators In C
- Conditional Operator in C
- Download C Language Notes Pdf
- C Language Tutorial For Beginners
- C Programming Examples With Output
- 250+ C Programs for Practice PDF Free Download
Friends, I hope you have found the answer of your question and you will not have to search about the Assignment operators in C Language
However, if you want any information related to this post or related to programming language, computer science, then comment below I will clear your all doubts.
If you want a complete tutorial of C language, then see here C Language Tutorial . Here you will get all the topics of C Programming Tutorial step by step.
Friends, if you liked this post, then definitely share this post with your friends so that they can get information about the Assignment operators in C Language
To get the information related to Programming Language, Coding, C, C ++, subscribe to our website newsletter. So that you will get information about our upcoming new posts soon.
Jeetu Sahu is A Web Developer | Computer Engineer | Passionate about Coding, Competitive Programming, and Blogging
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
cppreference.com
Assignment operators.
Assignment and compound assignment operators are binary operators that modify the variable to their left using the value to their right.
[ edit ] Simple assignment
The simple assignment operator expressions have the form
Assignment performs implicit conversion from the value of rhs to the type of lhs and then replaces the value in the object designated by lhs with the converted value of rhs .
Assignment also returns the same value as what was stored in lhs (so that expressions such as a = b = c are possible). The value category of the assignment operator is non-lvalue (so that expressions such as ( a = b ) = c are invalid).
rhs and lhs must satisfy one of the following:
- both lhs and rhs have compatible struct or union type, or..
- rhs must be implicitly convertible to lhs , which implies
- both lhs and rhs have arithmetic types , in which case lhs may be volatile -qualified or atomic (since C11)
- both lhs and rhs have pointer to compatible (ignoring qualifiers) types, or one of the pointers is a pointer to void, and the conversion would not add qualifiers to the pointed-to type. lhs may be volatile or restrict (since C99) -qualified or atomic (since C11) .
- lhs is a (possibly qualified or atomic (since C11) ) pointer and rhs is a null pointer constant such as NULL or a nullptr_t value (since C23)
[ edit ] Notes
If rhs and lhs overlap in memory (e.g. they are members of the same union), the behavior is undefined unless the overlap is exact and the types are compatible .
Although arrays are not assignable, an array wrapped in a struct is assignable to another object of the same (or compatible) struct type.
The side effect of updating lhs is sequenced after the value computations, but not the side effects of lhs and rhs themselves and the evaluations of the operands are, as usual, unsequenced relative to each other (so the expressions such as i = ++ i ; are undefined)
Assignment strips extra range and precision from floating-point expressions (see FLT_EVAL_METHOD ).
In C++, assignment operators are lvalue expressions, not so in C.
[ edit ] Compound assignment
The compound assignment operator expressions have the form
The expression lhs @= rhs is exactly the same as lhs = lhs @ ( rhs ) , except that lhs is evaluated only once.
[ edit ] References
- C17 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2018):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 72-73)
- C11 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2011):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 101-104)
- C99 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:1999):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 91-93)
- C89/C90 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:1990):
- 3.3.16 Assignment operators
[ edit ] See Also
Operator precedence
[ edit ] See also
- Recent changes
- Offline version
- What links here
- Related changes
- Upload file
- Special pages
- Printable version
- Permanent link
- Page information
- In other languages
- This page was last modified on 19 August 2022, at 09:36.
- Privacy policy
- About cppreference.com
- Disclaimers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
7.1 Simple Assignment. A simple assignment expression computes the value of the right operand and stores it into the lvalue on the left. Here is a simple assignment expression that stores 5 in i: We say that this is an assignment to the variable i and that it assignsi the value 5. It has no semicolon because it is an expression (so it has a value).
1. "=": This is the simplest assignment operator. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. Example: a = 10; b = 20; ch = 'y'; 2. "+=": This operator is combination of '+' and '=' operators.This operator first adds the current value of the variable on left to the value on the right and then assigns the result to the variable on the left.
Simple assignment operator. Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand. C = A + B will assign the value of A + B to C. +=. Add AND assignment operator. It adds the right operand to the left operand and assign the result to the left operand. C += A is equivalent to C = C + A. -=.
An assignment in C is an expression because it has a value; we call it an assignment expression. A simple assignment looks like. lvalue = value-to-store. We say it assigns the value of the expression value-to-store to the location lvalue, or that it stores value-to-store there. You can think of the "l" in "lvalue" as standing for ...
In C programming, assignment operators are used to assign values to variables. The simple assignment operator is =. C also supports shorthand assignment operators that combine an operation with assignment, making the code more concise. Key Topics: Simple Assignment Operator; Shorthand Addition Assignment (+=) Shorthand Subtraction Assignment (-=)
Assignment Statement. An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program. Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted.
Simple Assignment (C) The simple-assignment operator assigns its right operand to its left operand. The value of the right operand is converted to the type of the assignment expression and replaces the value stored in the object designated by the left operand. The conversion rules for assignment apply (see Assignment Conversions).
There are two types of assignment operators in C: 1. Simple Assignment Operator (=) This assigns the value on the right-hand side (RHS) to the variable on the left-hand side (LHS). You can use a literal, another variable, or an expression in the assignment statement.
C supports following Assignment operators: 1. Simple Assignment = Operator Example. This is one of the simplest assignment operator, it simply assigns the right side value to the left side operand. #include <stdio.h> int main () { int n; //integer variable char ch; //character variable float f; //float variable // Simple assignment operator to ...
Code language:C++(cpp) The = assignment operator is called a simple assignment operator. It assigns the value of the left operand to the right operand. Besides the simple assignment operator, C supports compound assignment operators. A compound assignment operator performs the operation specified by the additional operator and then assigns the ...
Syntax. The assignment operators in C can both transform and assign values in a single operation. C provides the following assignment operators: | =. In assignment, the type of the right-hand value is converted to the type of the left-hand value, and the value is stored in the left operand after the assignment has taken place.
1.Simple Assignment or Basic Form: Simple Assignment or Basic form is one of the common forms of Assignment Statements in C program. Simple Assignment allow the programmer to declare,define and initialize and assign a value in the same statement to a variable. This form is generally used when the programmer want to use the Variable a few times.
Assignment Statements CS216 4 Simple Assignment Statements • Simple Assignments - <target_variable> <assignment_operator> <exp> • The assignment operator symbol::= ALGOLs, Pascal, Modula-2, Ada = FORTRAN, BASIC, PL/I, C, C++, Java • = can be bad if it is overloaded for the relational operator for equality. CS216 5 Assignment Statements ...
Here the second statement adds 5 to the existing value of x. This value is then assigned back to x. Now, the new value of x is 105. To handle such operations more succinctly, C provides a special operator called Compound Assignment operator. The general format of compound assignment operator is as follows:
Examples of compound assignment operators are: (Example: + =, - =, * =, / =,% =, & =, ^ =) Look at these two statements: x = 100; x = x + 5; Here in this example, adding 5 to the x variable in the second statement is again being assigned to the x variable. Compound Assignment Operators provide us with the C language to perform such operation ...
4. Yes, you can assign one instance of a struct to another using a simple assignment statement. In the case of non-pointer or non pointer containing struct members, assignment means copy. In the case of pointer struct members, assignment means pointer will point to the same address of the other pointer.
Assignment performs implicit conversion from the value of rhs to the type of lhs and then replaces the value in the object designated by lhs with the converted value of rhs. Assignment also returns the same value as what was stored in lhs (so that expressions such as a = b = c are possible). The value category of the assignment operator is non ...
The Assignment operators in C are some of the Programming operators that are useful for assigning the values to the declared variables. Equals (=) operator is the most commonly used assignment operator. For example: int i = 10; The below table displays all the assignment operators present in C Programming with an example. C Assignment Operators.